| Gastroenterology Research, ISSN 1918-2805 print, 1918-2813 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, Gastroenterol Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.gastrores.org |
Case Report
Volume 12, Number 5, October 2019, pages 267-270
Experience of Endoscopic Jejunojejunostomy for Anastomotic Obstruction After Subtotal Gastrectomy Using Magnetic Compression Anastomosis
Hideaki Kawabataa, c, Naonori Inouea, Yuji Okazakia, Daiki Sonea, Katsutoshi Yamaguchia, Yuki Uedaa, Misuzu Hitomia, Masatoshi Miyataa, Shigehiro Motoia, Takashi Fuseb, Kenichirou Fukudab, Yoshihiro Shimizub
aDepartment of Gastroenterology, Kyoto Okamoto Memorial Hospital, Kyoto 613-0034, Japan
bDepartment of Surgery, Kyoto Okamoto Memorial Hospital, Kyoto 613-0034, Japan
cCorresponding Author: Hideaki Kawabata, Department of Gastroenterology, Kyoto Okamoto Memorial Hospital, 100 Nishinokuchi, Sayama, Kumiyama-cho, Kuze-gun, Kyoto 613-0034, Japan
Manuscript submitted August 22, 2019, accepted September 7, 2019
Short title: Jejunojejunostomy Using MCA
doi: https://doi.org/10.14740/gr1214
| Abstract | ▴Top |
Magnetic compression anastomosis (MCA) was developed as a low-invasive treatment for gastro-enteric or entero-enteric obstruction. A 72-year-old man underwent subtotal gastrectomy with Billroth II reconstruction for early gastric cancer. After the operation, he suffered from repeated aspiration pneumonia due to anastomotic obstruction caused by jejunal kinking at the efferent loop of anastomosis. We therefore performed jejunojejunostomy via the MCA technique, as his situation was not improved despite conservative therapy and he had a high reoperative risk. We prepared two flat plate-shaped neodymium magnets (15 × 3 mm) each with a small hole, and a nylon thread was passed through each hole. Each magnet was then delivered endoscopically to the anal side of the jejunal kinking, subsequently to the anastomosis, using biopsy forceps. The two magnets immediately became attracted towards each other transmurally. Oozing hemorrhage with clot at the mated magnets was observed 10 days after starting the compression. After retrieving the magnets, we confirmed the completion of jejunojejunostomy and then successfully achieved hemostasis of the anastomotic hemorrhage using argon plasma coagulation. The widely patent anastomosis was confirmed endoscopically 1 month after canalization; and he has been asymptomatic and able to eat a normal diet ever since. Endoscopic MCA is an effective, low-invasive treatment for anastomotic obstruction after subtotal gastrectomy. A standardized, safer procedure should be established for general use in the clinical setting.
Keywords: Magnetic compression anastomosis; Jejunojejunostomy; Anastomotic obstruction; Endoscopy
| Introduction | ▴Top |
Anastomotic site obstruction after gastrectomy (afferent or efferent loop syndrome) is a rare complication (approximately 0.3-1.0%) [1] mainly induced by an intestinal hernia, an adhesive band and kinking because of scarring or poor reconstruction during operation [2, 3]. Surgical interventions is required for the treatment of efferent loop syndrome in cases of complete loop obstruction with a mechanical cause or refractory to conservative treatments, including nasogastric drainage, fasting and total parenteral nutrition. Recently, the low-invasive treatment of endoscopic stent insertion has been attempted; however, it may induce complications such as dislocation and clogging with subsequent infection [4, 5].
Magnetic compression anastomosis (MCA) was developed as a low-invasive treatment for gastro-enteric or entero-enteric obstruction [6-9]. MCA can consistently create histologically well-formed anastomosis with a burst strength comparable to or better than that of handsewn or stapled anastomosis in animal studies [10-12]. Indeed, favorable results in surgically assisted gastro-enteric or entero-enteric MCA have been reported [9-12]. However, the clinical availability of endoscopic gastro-enteric or entero-enteric MCA is controversial because a standard, safe procedure has not been established yet [6-8, 13].
We herein report a case of endoscopic jejunojejunostomy for anastomotic obstruction after subtotal gastrectomy using MCA.
| Case Report | ▴Top |
A 72-year-old man who was bedridden due to sequelae of traffic accident underwent subtotal gastrectomy with Billroth II reconstruction for early gastric cancer in March 2019. After the operation, the patient suffered from repeated aspiration pneumonia, requiring management with a transient artificial respirator followed by tracheotomy, and continuous nasogastric aspiration with a bile-like drainage volume of 1,300 - 2,100 mL/day.
Enteroscopy revealed jejunal kinking at the efferent loop of the anastomosis without stricture or tumor recurrence (Fig. 1a); and the endoscope easily passed through to its anal side. However, fluoroscopy via a nasogastric tube showed gastric stasis of the contrast medium at the anastomosis and gastroesophageal reflux (Fig. 1b).
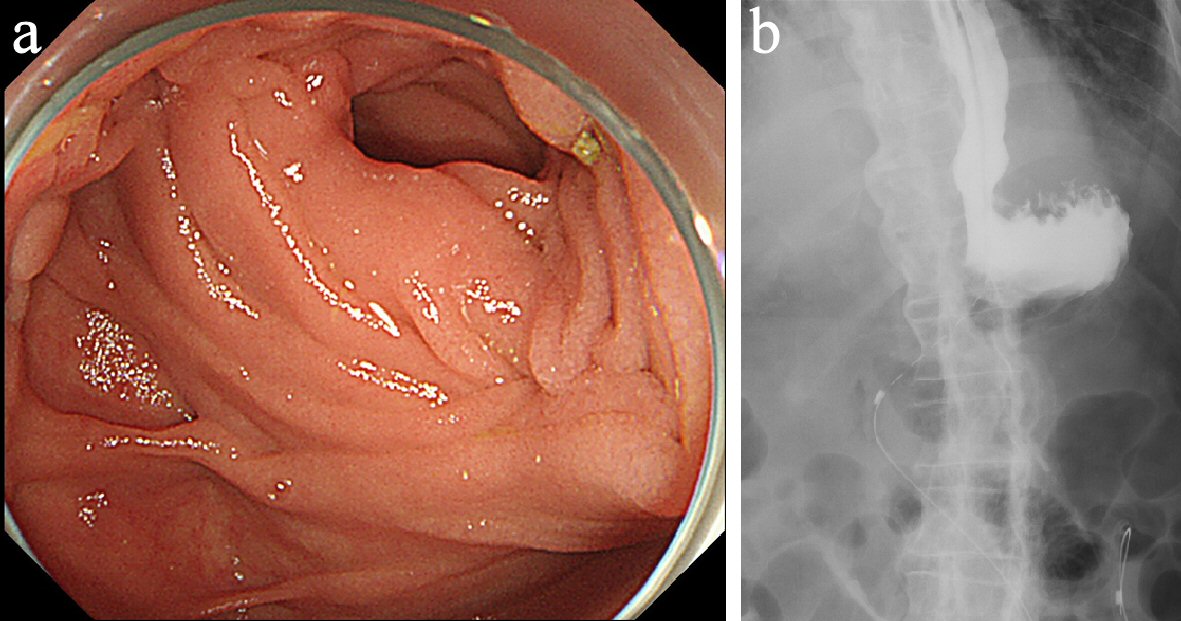 Click for large image | Figure 1. (a) Enteroscopy revealed jejunal kinking at the efferent loop of the anastomosis without stricture or tumor recurrence. (b) Fluoroscopy via a nasogastric tube showed gastric stasis of the contrast medium at the anastomosis and gastroesophageal reflux. |
We therefore performed jejunojejunostomy via the MCA technique, as his situation was not improved despite conservative therapy for 2 months, and he had a high reoperative risk. Written informed consent was obtained from the patient. We prepared two flat plate-shaped neodymium magnets (15 × 3 mm; Magfine, Sendai, Japan) each with a small hole (3 mm in diameter), and a nylon thread was passed through each hole. We then confirmed by fluoroscopy and computed tomography (CT) that no unintended tissue, such as small intestine or colon, was near the anastomosis where the magnets were to be placed. Each magnet was delivered endoscopically to the anal side of the jejunal kinking, subsequently to the anal side of the anastomosis, using biopsy forceps. The two magnets were immediately attracted towards each other transmurally (Fig. 2a-c).
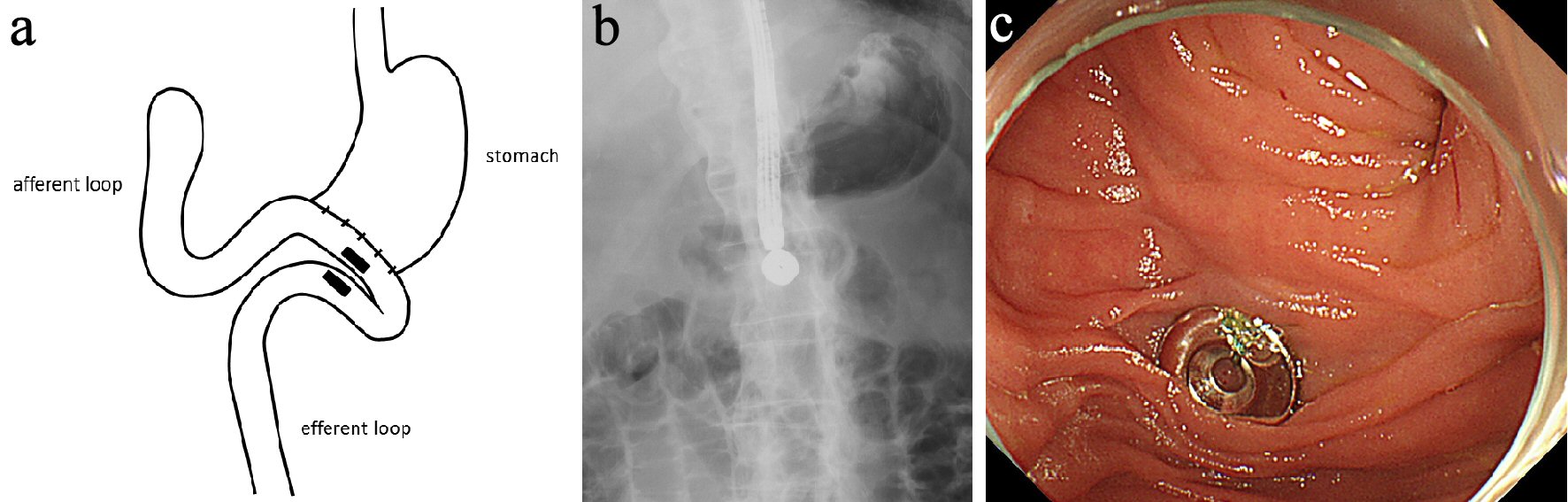 Click for large image | Figure 2. Each magnet was delivered endoscopically to the anal side of jejunal kinking, subsequently to the anastomosis, using biopsy forceps (a). The two magnets were immediately attracted towards each other transmurally (b, c). |
When we evaluated the anastomosis endoscopically 10 days after starting the compression, oozing hemorrhage with clot at the mated magnets was observed without anemia progression or any bleeding symptoms such as hematemesis and melena. After retrieving the magnets using biopsy forceps, we confirmed the completion of jejunojejunostomy and then successfully achieved hemostasis for the anastomotic hemorrhage using argon plasma coagulation (APC) (Fig. 3). The widely patent anastomosis was confirmed endoscopically 1 month after canalization (Fig. 4). The patient has been asymptomatic and able to eat a normal diet in the 2 months since the anastomosis.
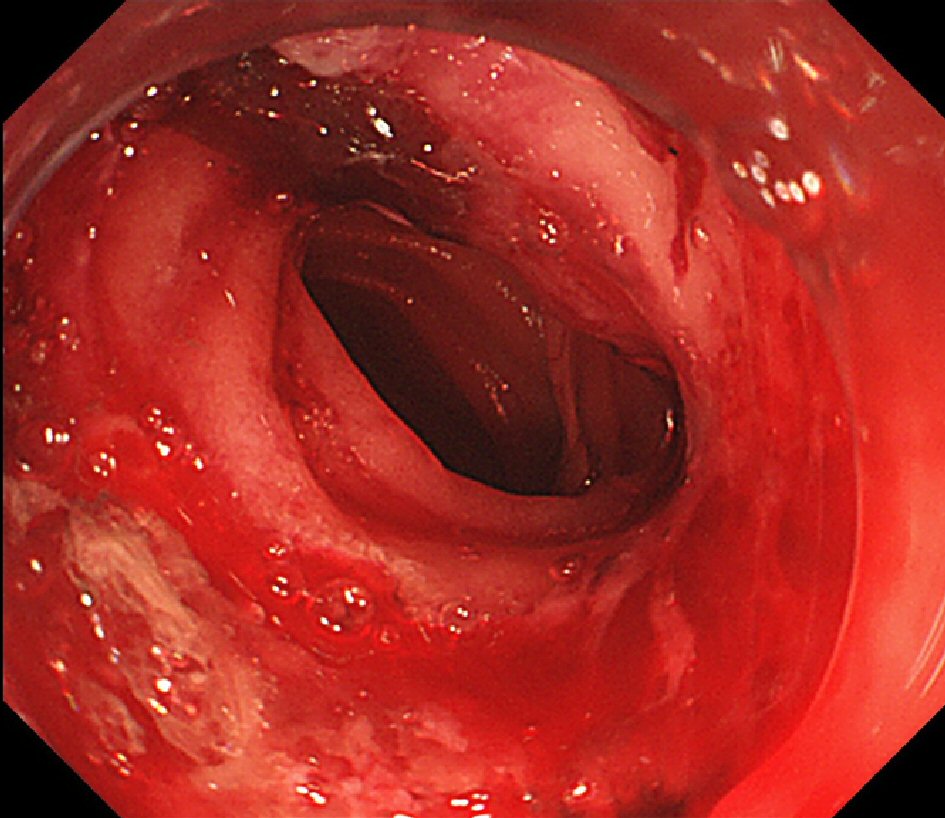 Click for large image | Figure 3. The completion of jejunojejunostomy and oozing hemorrhage from the anastomotic ulcer was confirmed after retrieving the magnets. |
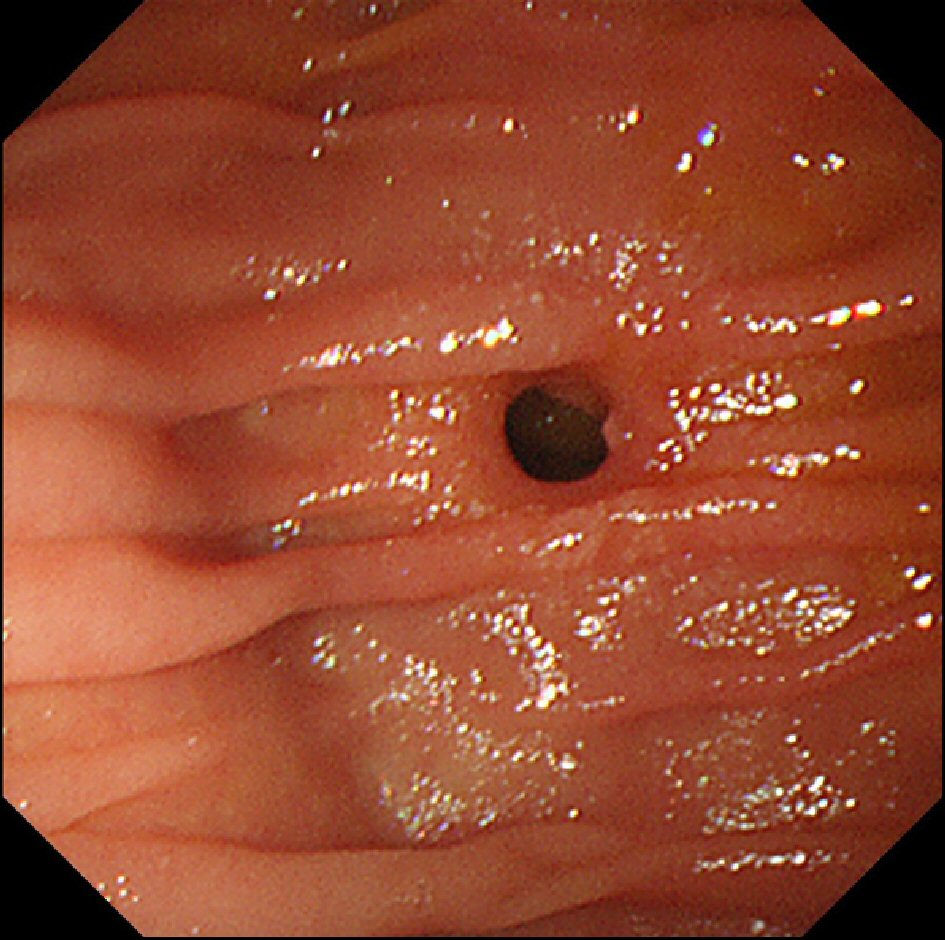 Click for large image | Figure 4. The widely patent anastomosis was confirmed endoscopically 1 month after canalization. |
| Discussion | ▴Top |
Two important clinical issues were noted in the present case: 1) Jejunojejunostomy using MCA was found to be an effective, low-invasive treatment for resolving anastomotic obstruction after subtotal gastrectomy; 2) Anastomotic hemorrhage can occur as a post-MCA complication.
First, jejunojejunostomy using MCA was an effective, low-invasive treatment for resolving anastomotic obstruction after subtotal gastrectomy. Stent placement was also low-invasive; however, this treatment was not indicated for cases with benign gastric stasis induced by enteral kinking because stent can easily become dislocated in such cases. Reported success rates of endoscopic gastro-enteric or entero-enteric anastomosis using MCA procedure have been 66-88% [6, 7, 13]. Yamanouchi et al [6] reported that all 51 patients achieved endoscopic gastro-enteric or entero-enteric anastomosis using MCA; however, four patients suffered from postoperative complications (anastomotic leakage in one case; damage to unintended tissue between the mated magnets in three cases), with three cases requiring surgical treatment. Furthermore, 20-25% of the patients had postoperative stricture due to anastomotic scar contraction. Another two studies using prophylactic transanastomotic deployment of a self-expandable stent following anastomosis formation reported a few severe stent-related complications, such as perforation and stent migration [7, 13]. Thus, endoscopic gastro-enteric or entero-enteric anastomosis should be indicated only for patients with contraindications to surgery or those with malignant bowel obstruction, as in our present case, until a standardized, safer MCA procedure is established [8].
Second, anastomotic hemorrhage can occur as a post-MCA complication. We detected anastomotic hemorrhage while performing follow-up endoscopy 10 days after starting compression without any bleeding symptoms. Persistent stimulation by magnets may induce slight bleeding from anastomotic ulcers although no MCA-related bleeding has been reported, not only in gastro-enteric or entero-enteric anastomosis but also in bilio-enteric or bilio-biliary anastomosis [6, 7, 13-16]. This case of anastomotic hemorrhage was easily arrested using APC after removing the magnets, and no rebleeding has been experienced since then.
In conclusion, endoscopic MCA is an effective, low-invasive treatment for anastomotic obstruction after subtotal gastrectomy. A standardized, safer procedure should be established for general use in the clinical setting.
Acknowledgments
None to declare.
Financial Disclosure
None to declare.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed Consent
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient.
Author Contributions
H. Kawabata, N. Inoue, Y. Okazaki, D. Sone, K. Yamaguchi, Y. Ueda, M. Hitomi, and M. Miyata contributed to endoscopic diagnosis and treatment. T. Fuse, K. Fukuda, and Y. Shimizu contributed to surgical treatment and postoperative management. M. Miyata and S. Motoi supervised the findings of this work. H. Kawabata wrote the manuscript with support from M. Hitomi and S. Motoi. All authors discussed the results and contributed to the final manuscript.
| References | ▴Top |
- Aoki M, Saka M, Morita S, Fukagawa T, Katai H. Afferent loop obstruction after distal gastrectomy with Roux-en-Y reconstruction. World J Surg. 2010;34(10):2389-2392.
doi pubmed - Cleator IG, Falconer CW, Small WP, Smith AN. Cause of stomal obstruction after gastroenterostomy. Br Med J. 1968;2(5604):530-532.
doi pubmed - Pickleman J, Lee RM. The management of patients with suspected early postoperative small bowel obstruction. Ann Surg. 1989;210(2):216-219.
doi pubmed - Lee WY, Moon JS. Endoscopic treatment of efferent loop syndrome with insertion of double pigtail stent. World J Gastroenterol. 2013;19(41):7209-7212.
doi pubmed - Cha RR, Lee SS, Kim H, Kim HJ, Kim TH, Jung WT, Lee OJ, et al. Management of post-gastrectomy anastomosis site obstruction with a self-expandable metallic stent. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21(16):5110-5114.
doi pubmed - Yamanouchi E, Kumano R, Kobayashi K, Hattori T, Matsumoto J, Oonishi T, Hayakawa M, et al. [Treatment for bowel or biliary obstruction by magnetic compression anastomosis development of Yamanouchi's method and its clinical evaluation]. J Nippon Med Sch. 2002;69(5):471-475.
doi pubmed - Chopita N, Vaillaverde A, Cope C, Bernedo A, Martinez H, Landoni N, Jmelnitzky A, et al. Endoscopic gastroenteric anastomosis using magnets. Endoscopy. 2005;37(4):313-317.
doi pubmed - Lebares CC, Graves CE, Lin MY, Fidelman N, Cello J, Harrison MR, Rogers S. Endoscopic magnetic compression anastomosis for small bowel bypass in a high operative risk setting. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2019.
doi pubmed - Graves CE, Co C, Hsi RS, Kwiat D, Imamura-Ching J, Harrison MR, Stoller ML. Magnetic Compression Anastomosis (Magnamosis): first-in-human trial. J Am Coll Surg. 2017;225(5):676-681 e671.
doi pubmed - Gonzales KD, Douglas G, Pichakron KO, Kwiat DA, Gallardo SG, Encinas JL, Hirose S, et al. Magnamosis III: delivery of a magnetic compression anastomosis device using minimally invasive endoscopic techniques. J Pediatr Surg. 2012;47(6):1291-1295.
doi pubmed - Pichakron KO, Jelin EB, Hirose S, Curran PF, Jamshidi R, Stephenson JT, Fechter R, et al. Magnamosis II: Magnetic compression anastomosis for minimally invasive gastrojejunostomy and jejunojejunostomy. J Am Coll Surg. 2011;212(1):42-49.
doi pubmed - Jamshidi R, Stephenson JT, Clay JG, Pichakron KO, Harrison MR. Magnamosis: magnetic compression anastomosis with comparison to suture and staple techniques. J Pediatr Surg. 2009;44(1):222-228.
doi pubmed - van Hooft JE, Vleggaar FP, Le Moine O, Bizzotto A, Voermans RP, Costamagna G, Deviere J, et al. Endoscopic magnetic gastroenteric anastomosis for palliation of malignant gastric outlet obstruction: a prospective multicenter study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010;72(3):530-535.
doi pubmed - Jang SI, Choi J, Lee DK. Magnetic compression anastomosis for treatment of benign biliary stricture. Dig Endosc. 2015;27(2):239-249.
doi pubmed - Itoi T, Kasuya K, Sofuni A, Itokawa F, Tsuchiya T, Kurihara T, Ikeuchi N, et al. Magnetic compression anastomosis for biliary obstruction: review and experience at Tokyo Medical University Hospital. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2011;18(3):357-365.
doi pubmed - Kawabata H, Hitomi M, Inoue N, Kawakatsu Y, Okazaki Y, Miyata M. Intraductal ultrasonography as a local assessment before magnetic compression anastomosis for obstructed choledochojejunostomy. Gastroenterology Res. 2017;10(4):255-258.
doi pubmed
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial 4.0 International License, which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Gastroenterology Research is published by Elmer Press Inc.


