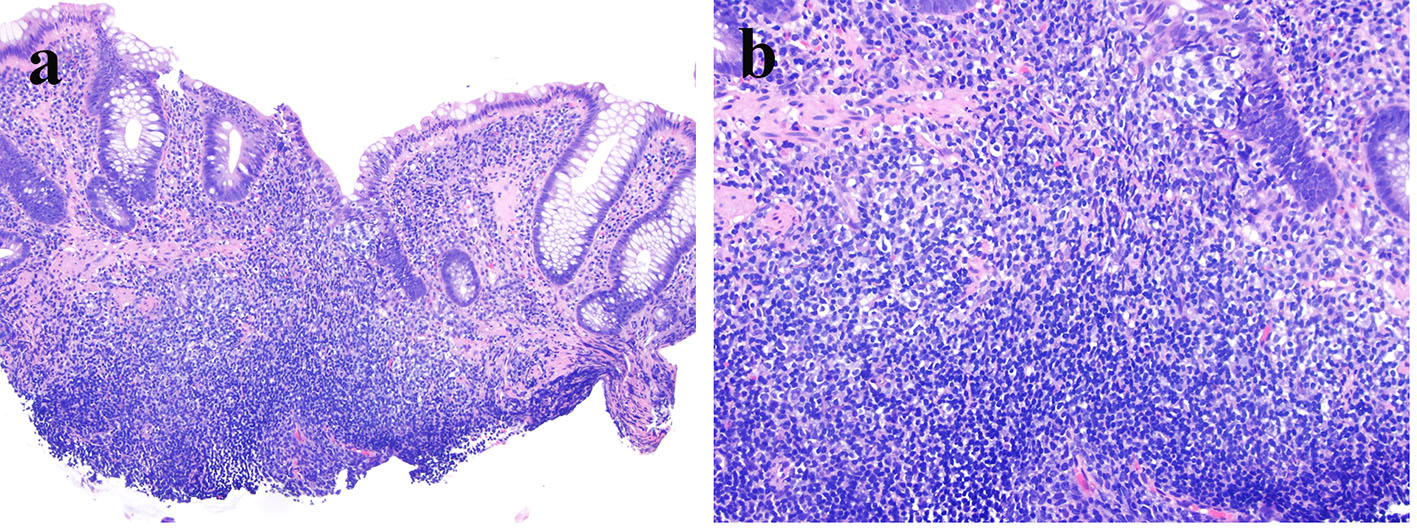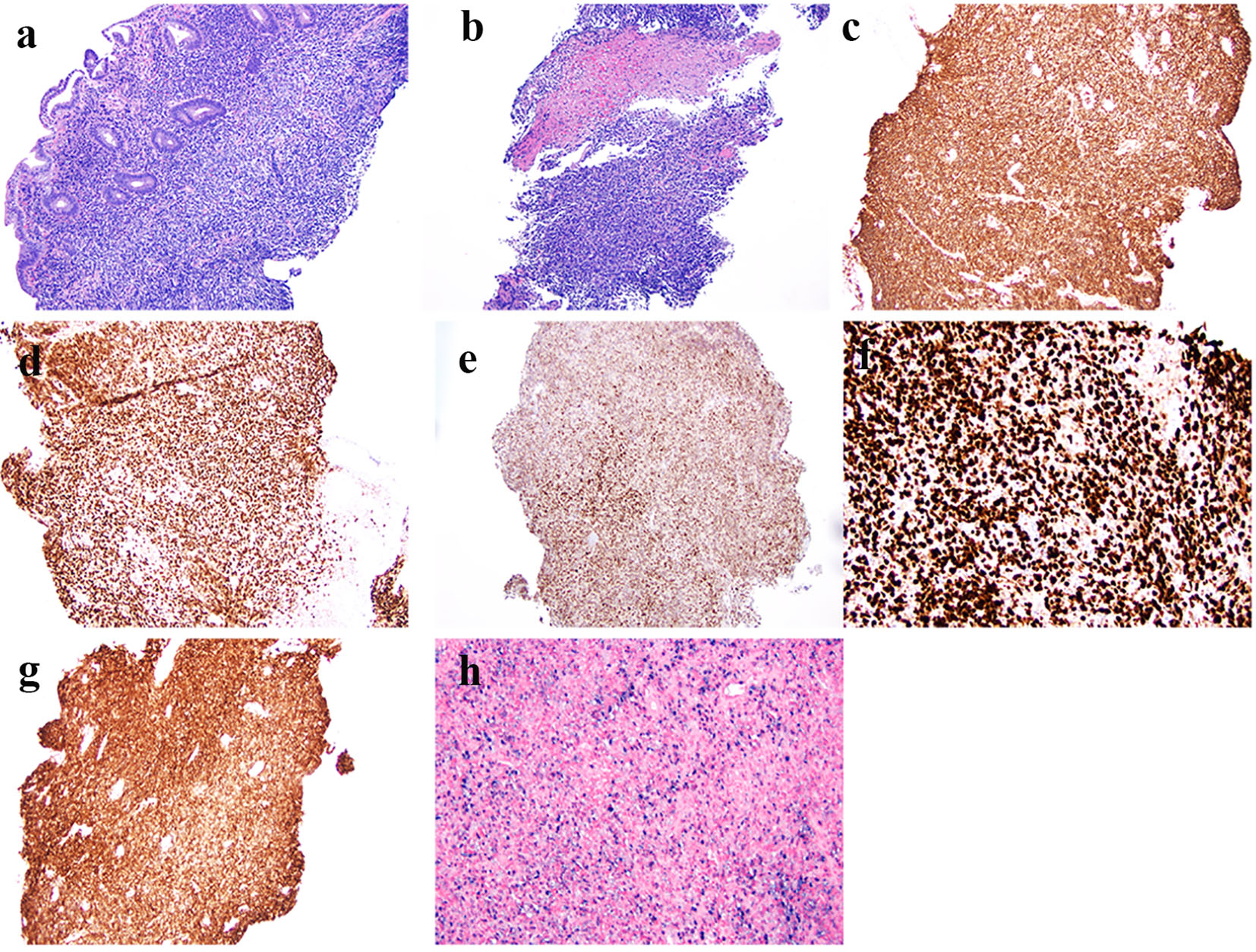
Figure 1. Histologic features and immunophenotype of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in biopsy from the sigmoid colon polyp. (a) Atypical mononuclear infiltration in the lamina propria of the colonic biopsy (hematoxylin & eosin stain, original magnification × 100). (b) Focal tumor necrosis (hematoxylin & eosin stain, original magnification × 100). (c) Immunoreactivity of CD20 in tumor cells (immunoperoxidase stain, original magnification × 100). (d) Immunoreactivity of PAX5 in tumor cells (immunoperoxidase stain, original magnification × 100). (e) Immunoreactivity of BCL6 in tumor cells (immunoperoxidase stain, original magnification × 100). (f) High Ki67 labeling index (up to 80-90%) (immunoperoxidase stain, original magnification × 200). (g) Immunoreactivity of CD30 in tumor cells (immunoperoxidase stain, original magnification × 100). (h) Many Epstein-Barr virus-infected tumor cells by in situ hybridization (chromogenic in situ hybridization, original magnification × 200).