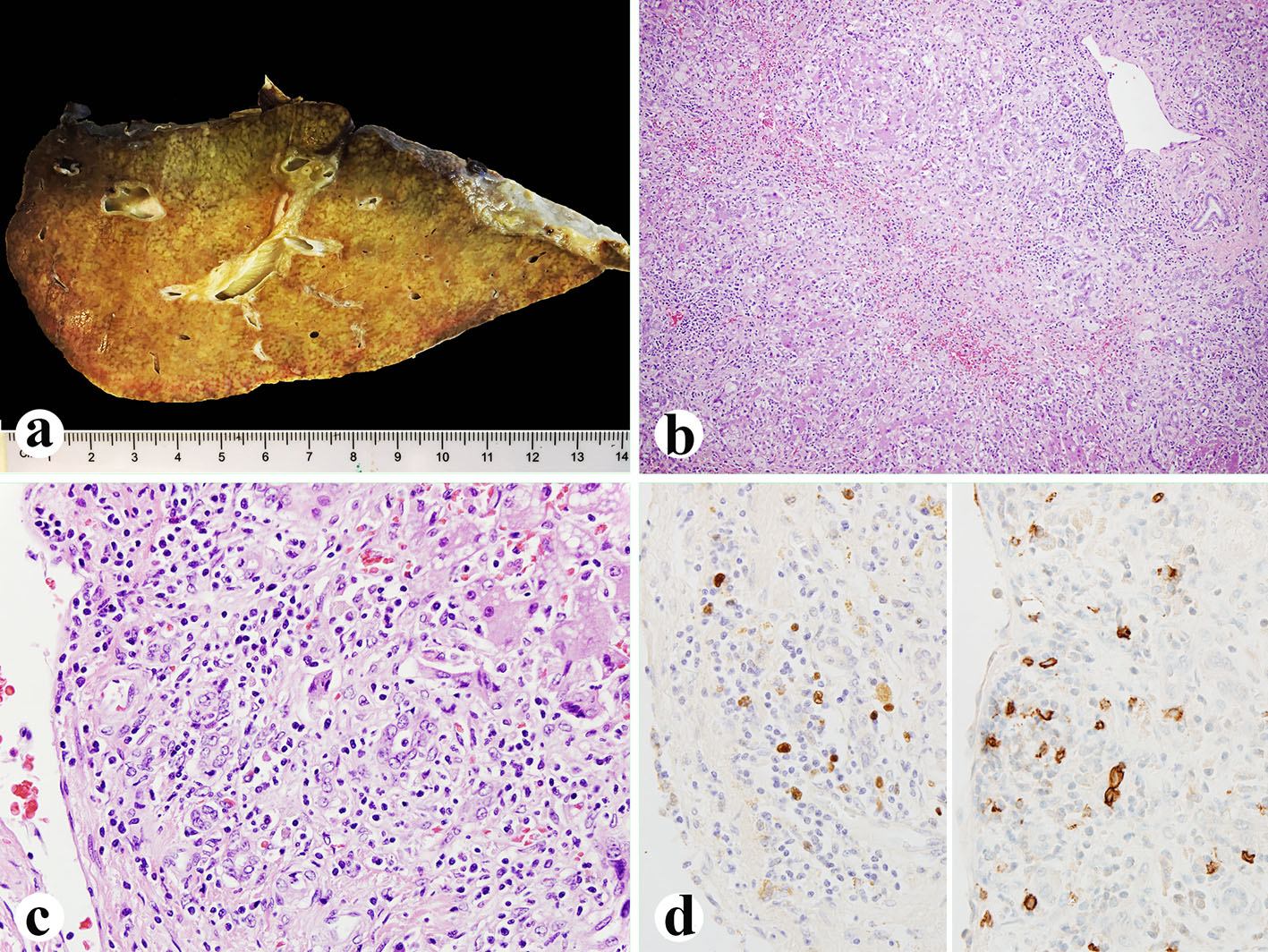
Figure 1. Explanted liver. (a) Small explanted liver weighing 720 g. (b, c) Histologically, the liver showing 75% of parenchyma extinction and massive necrosis with sinusoidal lymphocytosis and atypical lymphocytes (H&E, b: × 100; c: × 400). (d) EBV in situ hybridization (left, × 600) and CD20 immunostain (right, × 600) showing numerous EBV-positive atypical B lymphocytes.
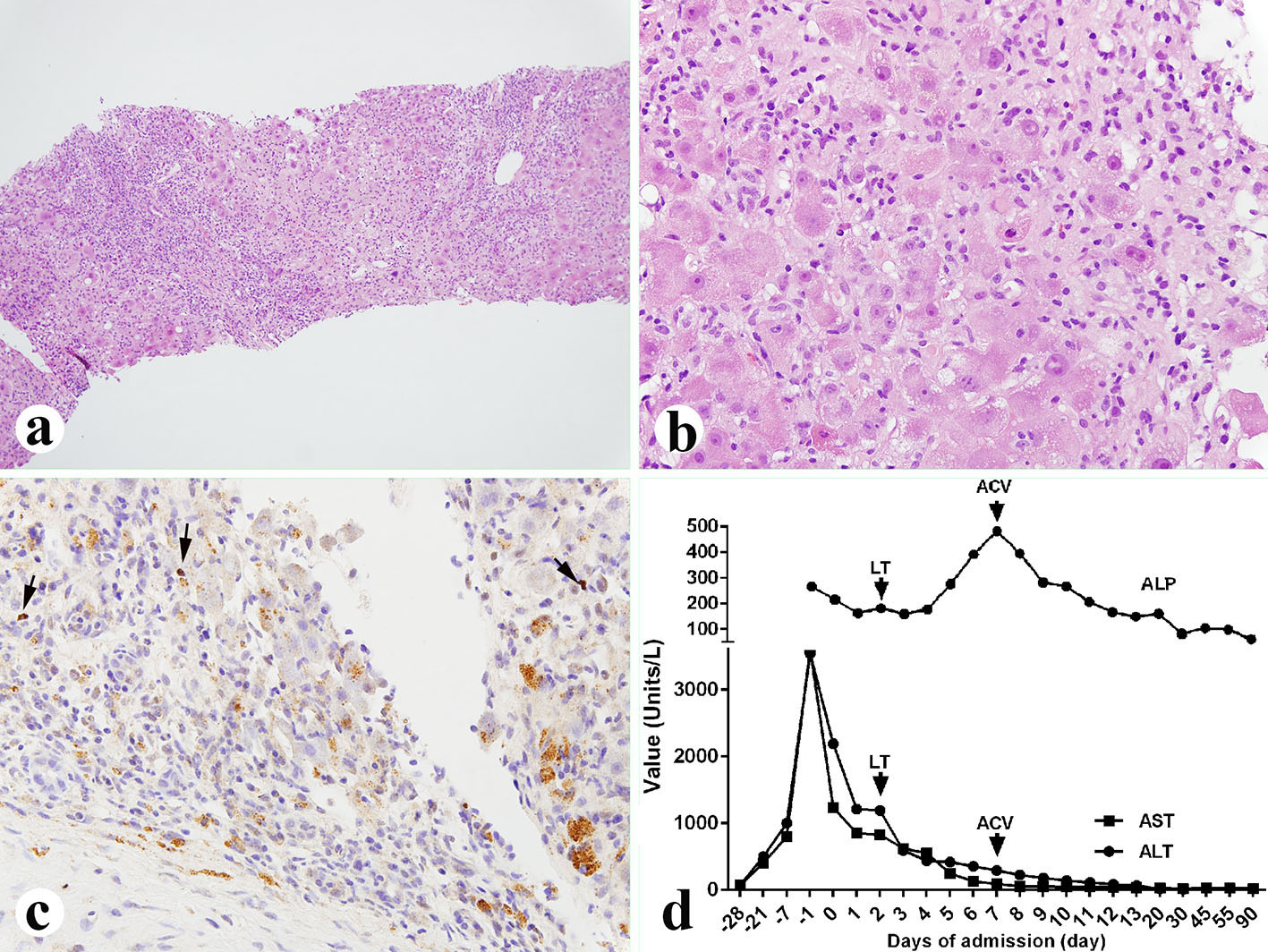
Figure 2. Liver biopsy performed 5 days before the liver transplant. (a, b) Liver showing 25% parenchyma necrosis with bridging necrosis, acidophilic bodies, mixed inflammatory infiltrate and sinusoidal lymphocytosis (a: × 100; b: × 400). (c) EBV in situ hybridization showing occasional EBV-positive B lymphocytes (× 400, arrows). (d) Liver function tests before and after diagnosis of the EBV. LT: liver transplant; ACV: acyclovir; ALP: alkaline phosphatase; AST: aspartate aminotransferase; ALT: alanine aminotransferase.

