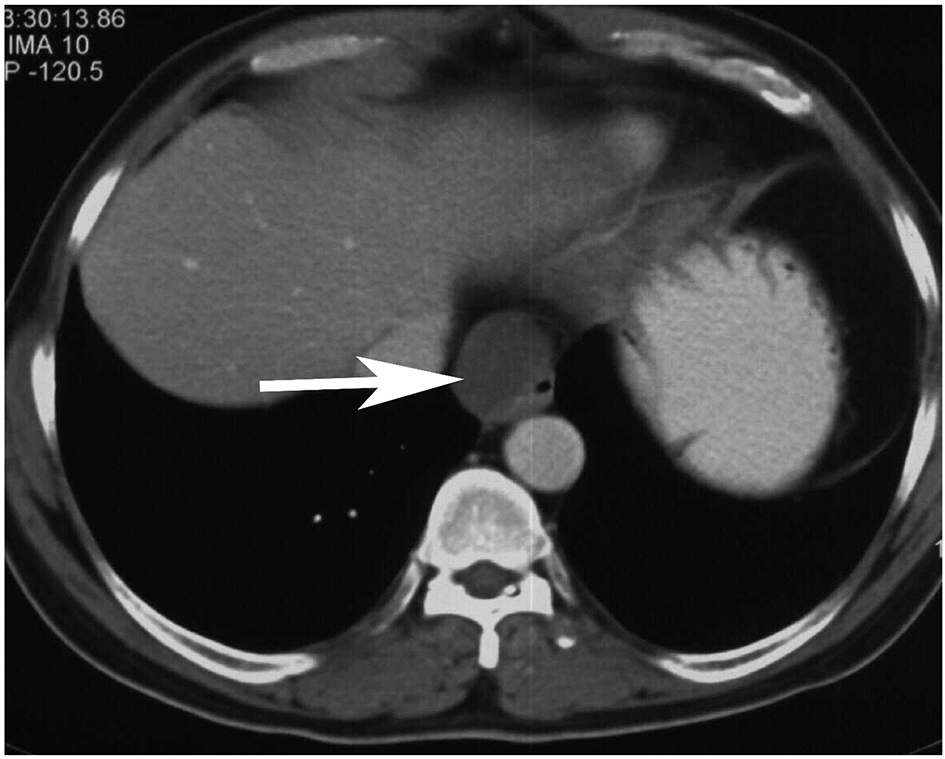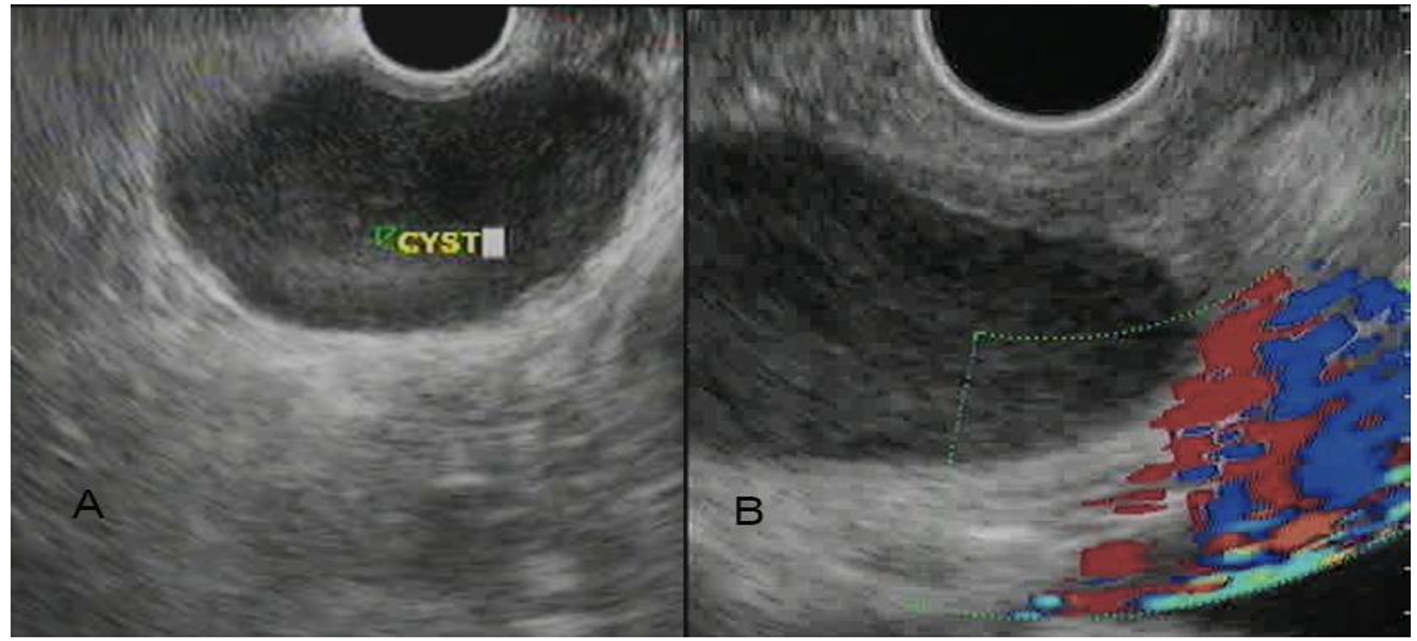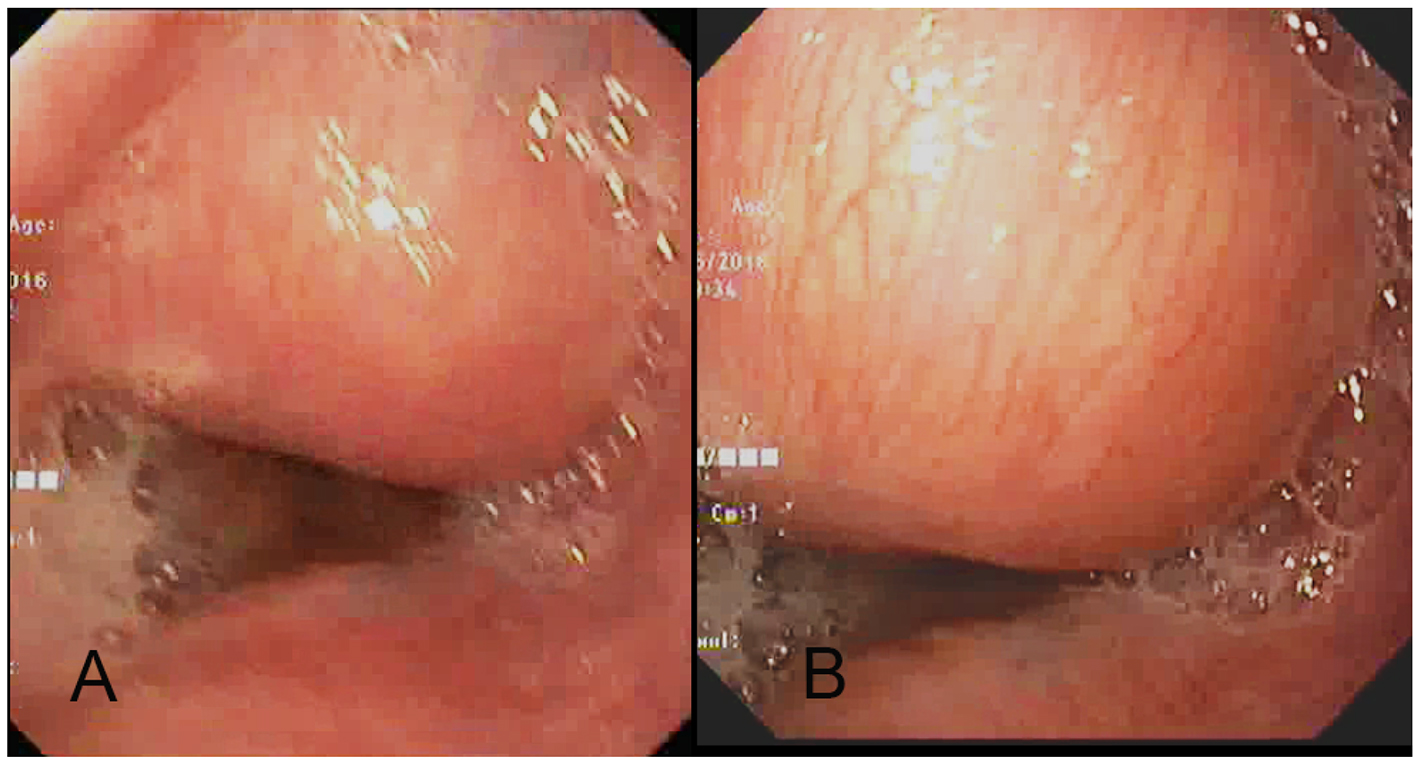
Figure 1. (A, B) Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy image shows a submucosal lesion in the right antero-lateral wall of the distal thoracic esophagus which is bulging into the esophageal lumen with normal overlying mucosa and mild luminal narrowing.
| Gastroenterology Research, ISSN 1918-2805 print, 1918-2813 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, Gastroenterol Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.gastrores.org |
Case Report
Volume 9, Number 4-5, October 2016, pages 79-82
Congenital Esophageal Duplication Cyst: A Rare Cause of Dysphagia in an Adult
Figures