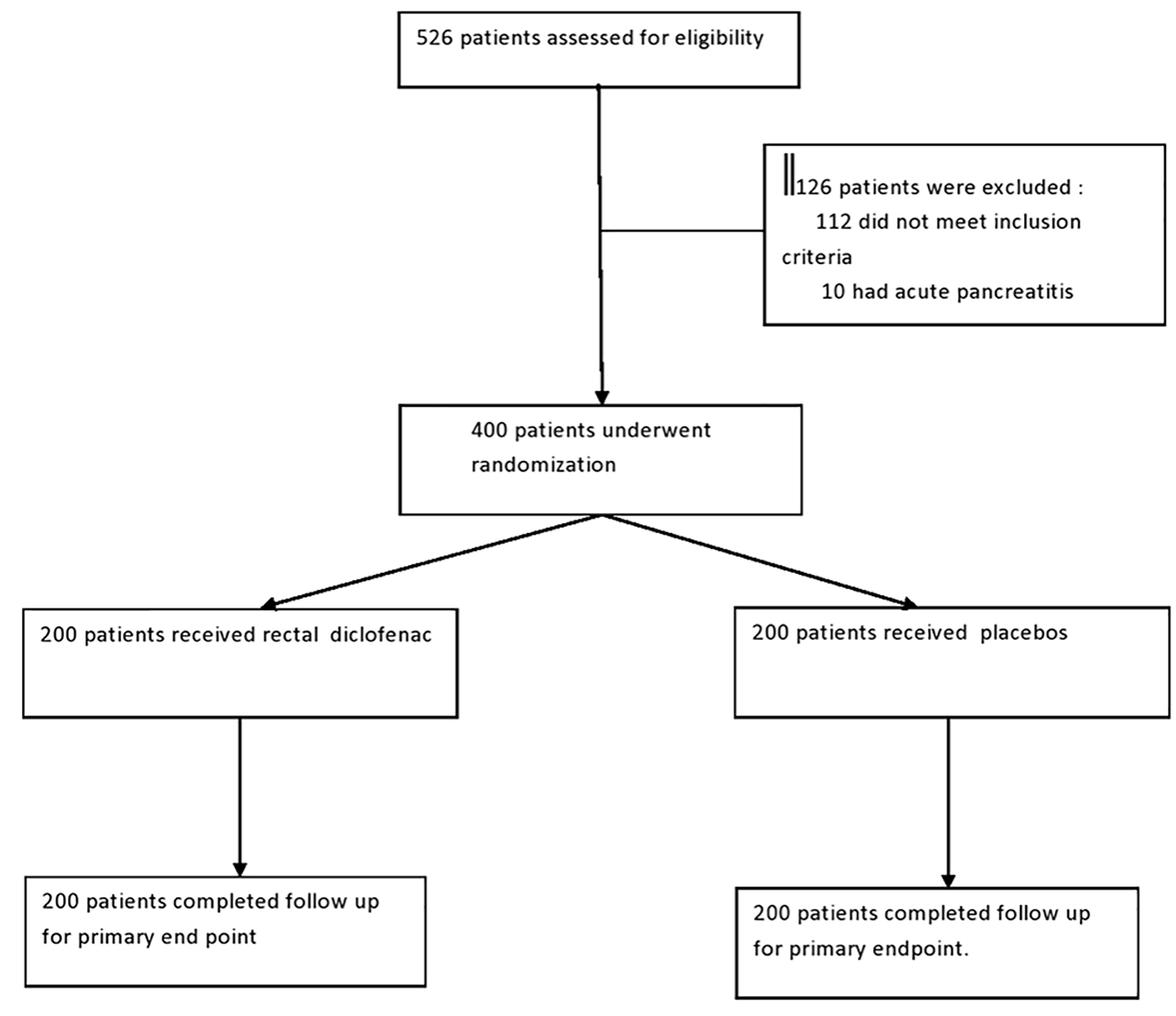
Figure 1. Patients flow chart.
| Gastroenterology Research, ISSN 1918-2805 print, 1918-2813 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, Gastroenterol Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.gastrores.org |
Original Article
Volume 9, Number 2-3, June 2016, pages 47-52
Role of Rectal Diclofenac Suppository for Prevention and Its Impact on Severity of Post-Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography Pancreatitis in High-Risk Patients
Figures

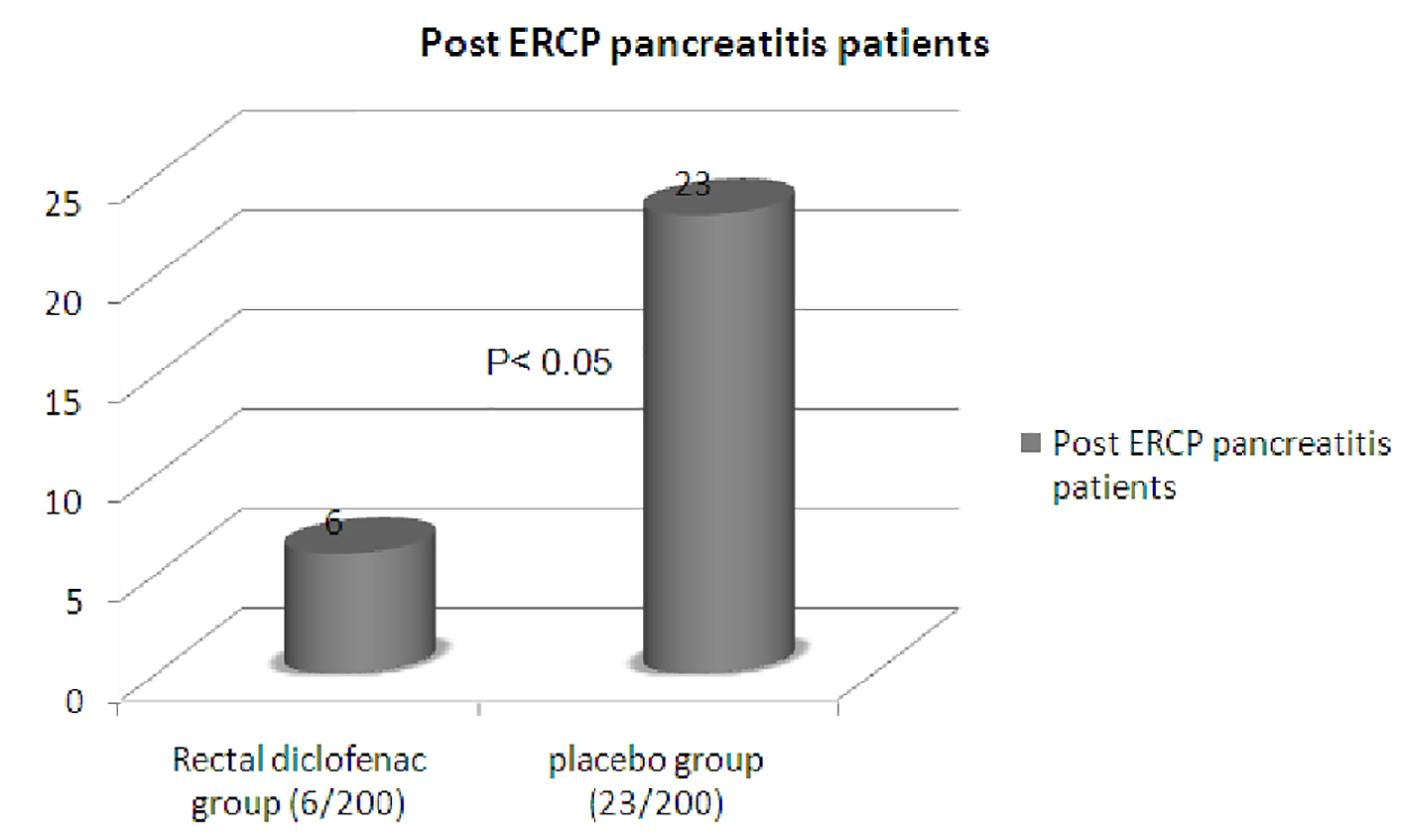
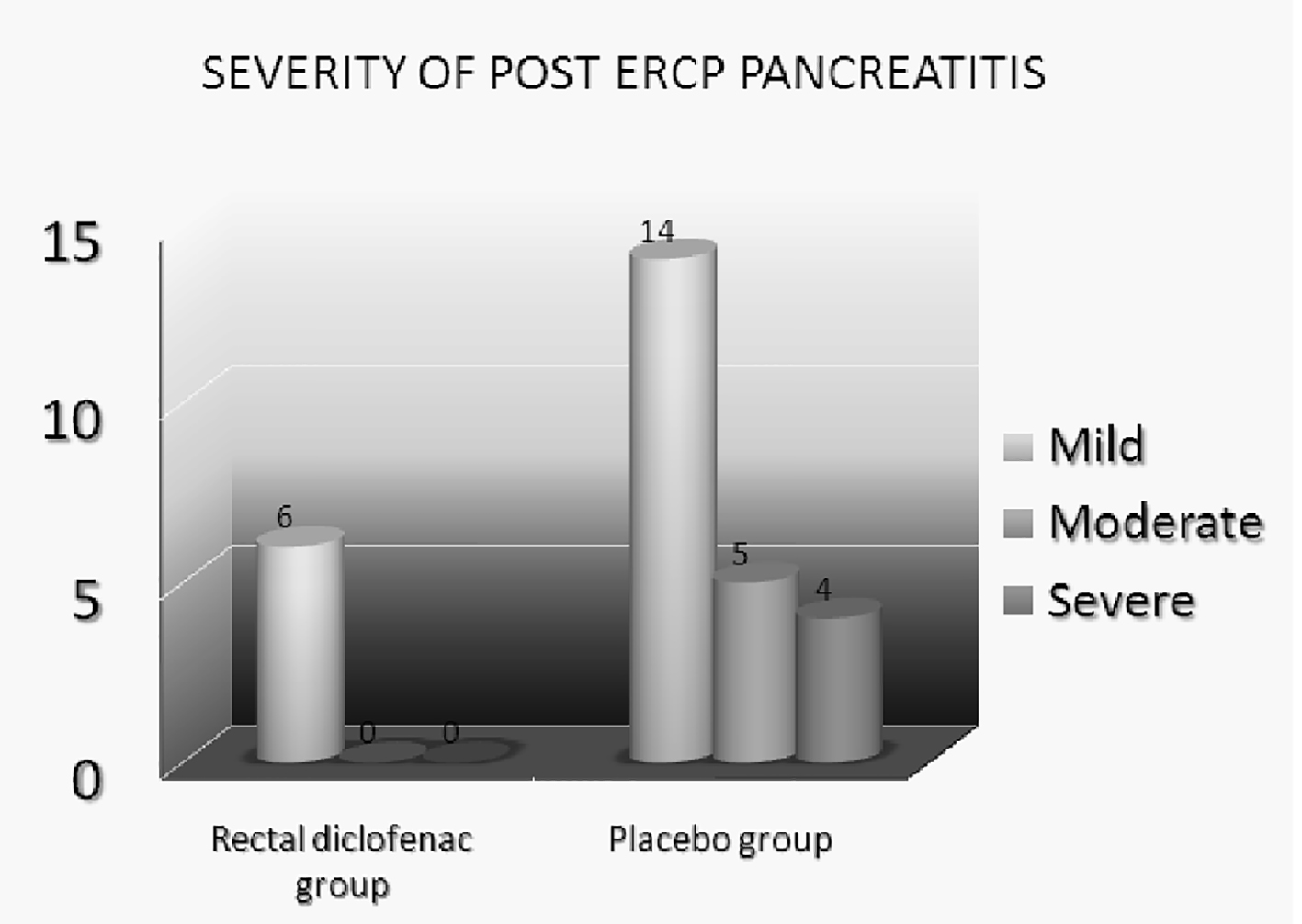
Tables
| Indication of ERCP | Rectal diclofenac group (n = 200) | Placebo group (n = 200) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gallbladder stones (with dilated CBD) | 25 | 27 | > 0.05 |
| Common bile duct stones | 52 | 57 | > 0.05 |
| Post cholecystectomy | 20 | 18 | > 0.05 |
| Malignancy (gallbladder, periampullary, cholangiocarcinoma) | 21 | 16 | > 0.05 |
| ERCP + suspected sphincter of Oddi dysfunction | 66 | 69 | > 0.05 |
| Common bile duct stricture (including those with chronic pancreatitis) | 16 | 13 | > 0.05 |
| Characteristic | Rectal diclofenac group (n = 200) | Placebo group (n = 200) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean age, years | 45.44 | 47.86 | > 0.05 |
| Female sex, no. (%) | 128 (64%) | 123 (61.5%) | > 0.05 |
| Suspected sphincter of Oddi dysfunction (%) | 66 (33%) | 69 (34.5%) | > 0.05 |
| Precut sphincterotomy (%) | 21 (10.5%) | 24 (12%) | > 0.05 |
| Pancreatic duct cannulation (%) | 26 (13%) | 24 (12%) | > 0.05 |
| Pancreatic acinarization (%) | 9 (4.5%) | 8 (4%) | > 0.05 |
| History of recurrent pancreatitis (%) | 40 (20%) | 35 (17.5%) | > 0.05 |
| History of post ERCP pancreatitis (%) | 6 (3%) | 5 (2.5%) | > 0.05 |
| Pancreatic sphincterotomy (%) | 11 (5.5%) | 12 (6%) | > 0.05 |
| Ampullectomy | None | None | > 0.05 |
| Difficult cannulation (%) | 61 (30.5%) | 66 (33%) | > 0.05 |
| Pancreatic duct stenting (%) | 11 (5.5%) | 12 (6%) | > 0.05 |