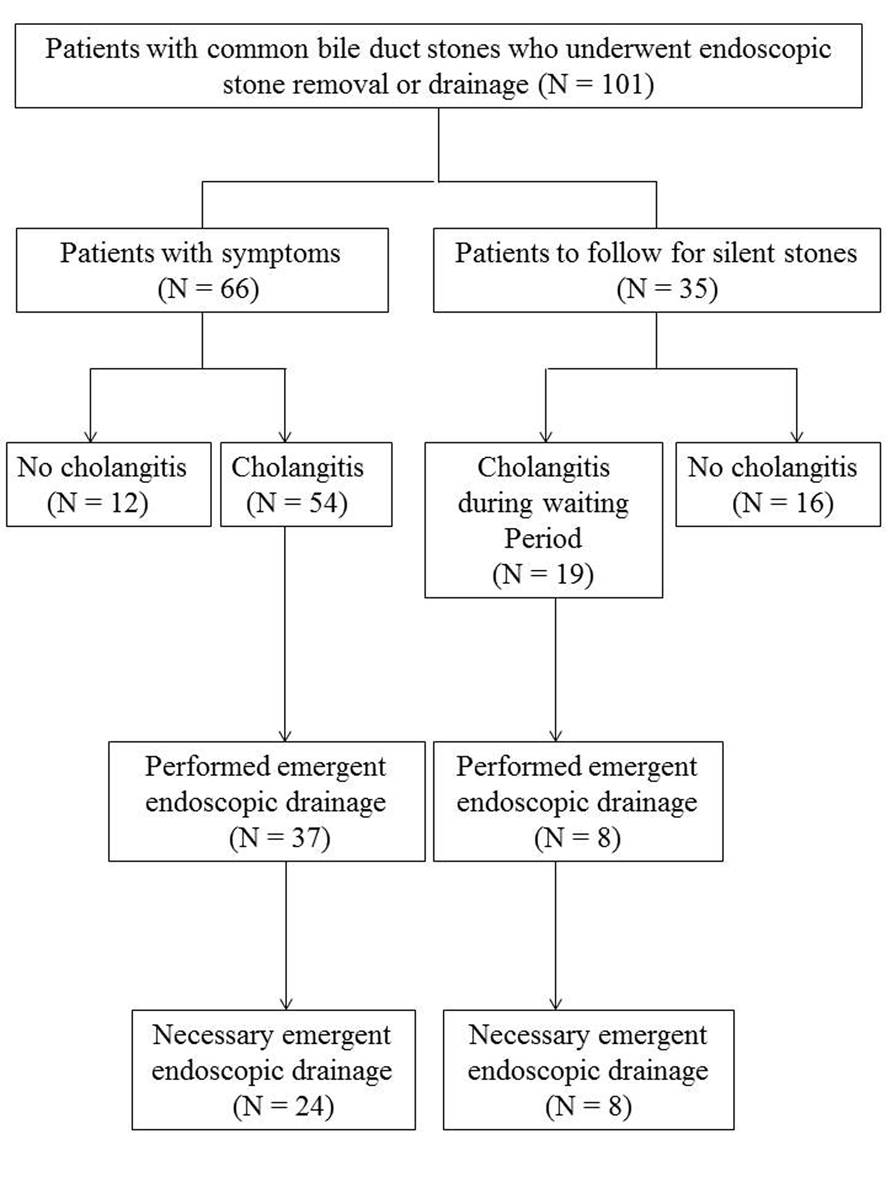
Figure 1. Study flow chart for treatment of patients with common bile duct stones.
| Gastroenterology Research, ISSN 1918-2805 print, 1918-2813 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, Gastroenterol Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.gastrores.org |
Original Article
Volume 6, Number 6, December 2013, pages 219-226
Common Bile Duct Dilatation With Stones Indicates Requirement for Early Drainage in Patients With or Without Cholangitis
Figure

Tables
| Definite diagnosis: one item in A, one item in B and one item in C. | |
| A | Systemic inflammation |
| A-1 | Fever and/or shaking chills |
| A-2 | Laboratory data: evidence of inflammatory response |
| B | Cholestasis |
| B-1 | Jaundice |
| B-2 | Laboratory data: evidence of abnormal liver function tests |
| C | Imaging |
| C-1 | Biliary dilation |
| C-2 | Evidence of the etiology on imaging |
| STD, lower limit of normal value. |
| Grade III (severe) acute cholangitis |
| Grade III acute cholangitis is defined as acute cholangitis that is associated with the onset of dysfunction in at least one of any of the following organs/systems: |
| 1. Cardiovascular dysfunction: hypotension requiring dopamine ≥ 5 µg/kg/min, or any dose of norepinephrine |
| 2. Neurologic dysfunction: disturbance of consciousness |
| 3. Respiratory dysfunction: PaO2/FiO2 ratio < 300 |
| 4. Renal dysfunction: oliguria, serum creatine > 2.0 mg/dL |
| 5. Hepatic dysfunction: PT-INR > 1.5 |
| 6. Hematologic dysfunction: platelet count < 100,000/mm3 |
| Grade II (moderate) acute cholangitis |
| Grade II acute cholangitis is associated with any two of following conditions: |
| 1. Abnormal WBC count (> 12,000/mm3, < 4,000/mm3) |
| 2. High fever (≥ 39 °C) |
| 3. Age (≥ 75 years old) |
| 4. Hyperbilirubinemia (total bilirubin ≥ 5 mg/dL) |
| 5. Hypoalubuminemia (< STD x 0.7) |
| Grade I (mild) acute cholangitis |
| Grade I acute cholangitis does not meet the criteria of Grade III or Grade II acute cholangitis at initial diagnosis. |
| N = 101 | Emergent drainage required (N = 32) | No emergent drainage required (N = 69) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| CBD, common bile duct; EST, endoscopic sphincterotomy. | |||
| Patient (M/F) | 32 (18/14) | 69 (37/32) | 0.81 |
| Smoking | 16 | 28 | 0.37 |
| Alcohol | 13 | 29 | 0.89 |
| Diabetes | 9 | 13 | 0.29 |
| Gallstone | 14 | 46 | 0.029 |
| CBD dilation | 25 | 33 | 0.004 |
| No. of CBD stones > 2 | 17 | 35 | 0.82 |
| Size of CBD stones > 10 mm | 17 | 20 | 0.019 |
| History of EST | 6 | 7 | 0.23 |
| Periampullary diverticlum | 16 | 22 | 0.58 |
| OR (95% CI) | P value | |
|---|---|---|
| CBD, common bile duct; OR, odds ration; CI, confidence interval. | ||
| CBD dilation | 3.75 (1.41-9.96) | 0.008 |
| Gallstone | 2.44 (0.997-5.952) | 0.051 |
| Size of CBD stones > 10 mm | 1.58 (0.59-4.23) | 0.36 |
| N = 35 | Emergent treatment (N = 8) | Scheduled treatment (N = 27) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| CBD, common bile duct. | |||
| Patient (M/F) | 8 (5/3) | 27 (17/10) | 0.65 |
| Smoking | 6 | 15 | 0.29 |
| Alcohol | 5 | 13 | 0.38 |
| Diabetes | 3 | 6 | 0.33 |
| Gallstone | 3 | 16 | 0.25 |
| CBD dilation | 7 | 11 | 0.025 |
| No. of CBD stones > 2 | 6 | 12 | 0.13 |
| Size of CBD stones > 10 mm | 4 | 9 | 0.33 |
| Elevation of AST or ALT | 4 | 15 | 0.55 |
| Elevation of ALP or γ-GTP | 5 | 20 | 0.41 |
| OR (95% CI) | P value | |
|---|---|---|
| CBD, common bile duct; OR, odds ration; CI, confidence interval. | ||
| CBD dilation | 10.18 (1.09-94.73) | 0.042 |
| No. of CBD stones > 2 | 3.89 (0.58-26.12) | 0.13 |