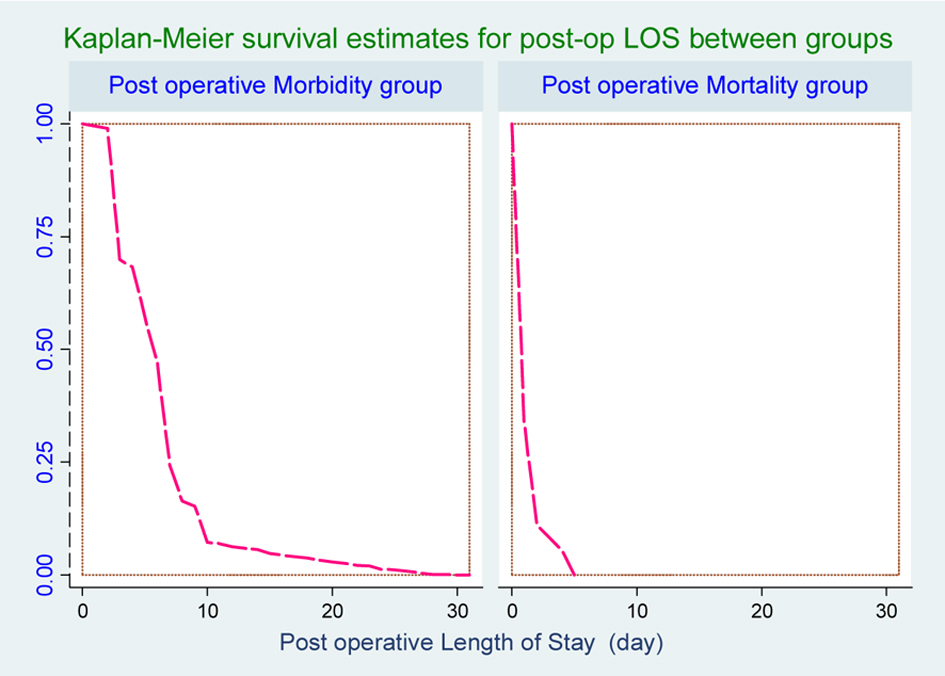
Figure 1. Survival curve for post-operative length of stay (PLOS) between groups.
| Gastroenterology Research, ISSN 1918-2805 print, 1918-2813 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, Gastroenterol Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.gastrores.org |
Original Article
Volume 7, Number 1, February 2014, pages 5-11
Prognostic Factors and Complications in Patients With Operational Peptic Ulcer Perforation in Northern Thailand
Figure

Tables
| Patient characteristics | Complications (n = 87, 9.54%) | Recovered (n = 825, 90.46%) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| *PUP: peptic ulcer perforation. | |||
| Gender | |||
| Male | 64 (73.56) | 645 (78.18) | 0.325 |
| Age (years) | |||
| Median (IQR) | 78.5 (15 - 92) | 66 (15 - 87) | < 0.001 |
| Underlying illnesses | |||
| Diabetes mellitus | 11 (12.64) | 46 (5.58) | 0.010 |
| Hypertension | 27 (31.03) | 168 (20.36) | 0.021 |
| Lung disease | 38 (43.68) | 64 (7.76) | < 0.001 |
| Liver disease | 13 (14.94) | 22 (2.67) | < 0.001 |
| Heart disease | 33 (37.93) | 114 (13.82) | < 0.001 |
| Kidney disease | 20 (22.99) | 57 (6.91) | < 0.001 |
| Systolic blood pressure ≤ 90 mmHg | 68 (78.16) | 44 (5.33) | < 0.001 |
| Referred from lower level hospitals | 60 (68.97) | 640 (77.58) | 0.071 |
| Duration of operation > 3 h | 33 (37.93) | 54 (6.55) | < 0.001 |
| Prolonged ventilation > 24 h | 33 (37.93) | 54 (6.55) | < 0.001 |
| Unplanned admission to ICU | 70 (80.46) | 630 (76.36) | 0.390 |
| Post-operational complications | Number (n=912) | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Surgical site infection | 32 | 3.51 |
| Re-operation | 11 | 1.21 |
| Pneumonia | 74 | 8.11 |
| Death | 18 | 1.97 |
| Associated outcomes | Outcomes presence | Mortality | IRR (95%CI) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surgical site infection | No | 8 (44.44%) | Reference | 0.158 |
| Yes | 10 (55.56%) | 2.00 (0.76 - 5.27) | ||
| Re-operation | No | 15 (82.33%) | Reference | 0.137 |
| Yes | 3 (16.67%) | 2.65 (0.73 - 9.62) | ||
| Pneumonia | No | 0 (0.00%) | Reference | 0.958 |
| Yes | 18 (100.00%) | 6.97 (6.30 - 7.70) |
| Associated outcomes | PLOS (days) | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Without complications (n = 825) | With complications (n = 87) | ||
| Surgical site infection | |||
| Median (IQR) | 7 (1 - 29) | 10 (7 - 31) | 0.004 |
| Re-operation | |||
| Median (IQR) | 6 (1 - 22) | 11 (1 - 31) | 0.002 |
| Pneumonia | |||
| Median (IQR) | 6 (1 - 25) | 15 (1 - 31) | < 0.001 |
| Death | |||
| Median (IQR) | 6 (1 - 31) | 1 (1 - 5) | < 0.001 |
| Prognostic factors | Multivariable RR | 95%CI | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | |||
| Male | 0.35 | 0.06 - 1.96 | 0.235 |
| Age (years) | |||
| ≥ 60 | 0.11 | 0.013 - 0.84 | 0.034 |
| Underlining illnesses | |||
| Diabetes mellitus | 2.15 | 0.53 - 8.73 | 0.281 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 1.12 | 0.34 - 3.74 | 0.851 |
| Lung disease | 1.33 | 0.29 - 6.05 | 0.715 |
| Liver disease | 5.41 | 1.36 - 21.56 | 0.015 |
| Heart disease | 1.23 | 0.28 - 5.29 | 0.784 |
| Kidney disease | 4.72 | 1.05 - 21.11 | 0.042 |
| Systolic blood pressure ≤ 90 mmHg | 2.42 | 0.30 - 19.41 | 0.407 |
| Duodenal ulcer perforation | 3.52 | 0.31 - 40.50 | 0.313 |
| Elective surgery | 2.02 | 0.42 - 9.88 | 0.383 |
| Duration of perforation > 3 h | 9.83 | 1.61 - 59.66 | 0.013 |
| Referred from lower level hospitals | 0.97 | 0.18 - 5.10 | 0.969 |
| Unplanned admission to ICU | 9.22 | 1.55 - 54.68 | 0.014 |
| Prolonged ventilation > 24 h | 9.02 | 0.42 - 9.88 | 0.038 |