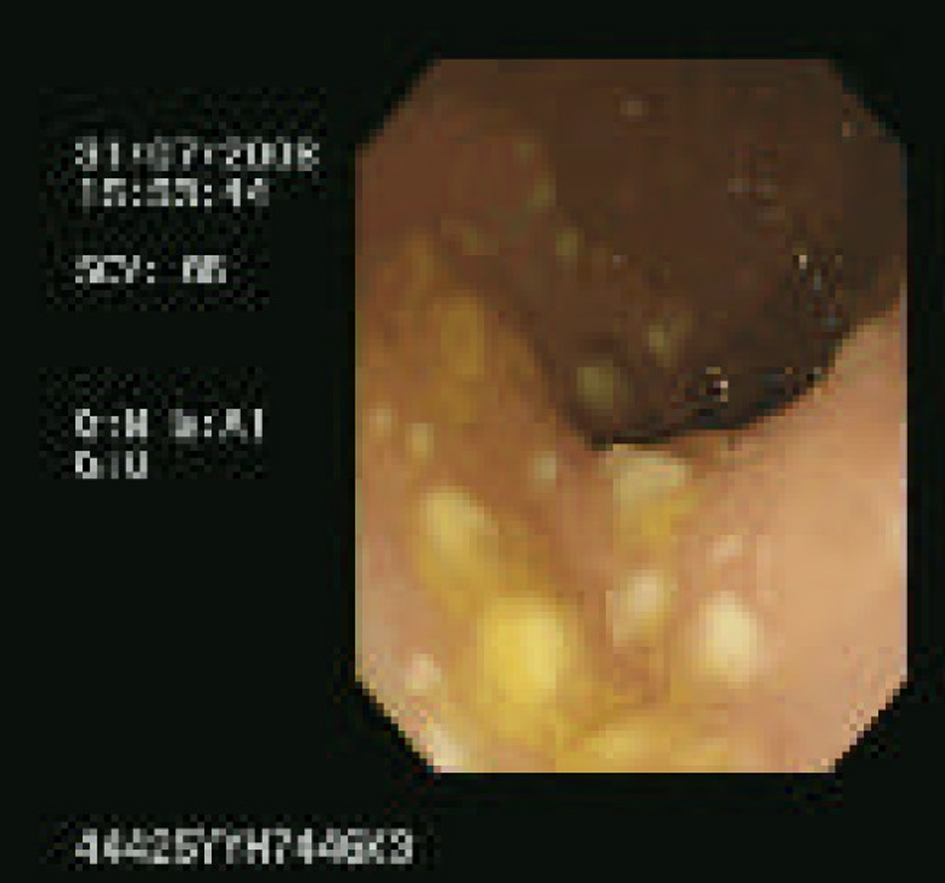
Figure 1. Endoscopy showing a classic pseudomembranous appearance, with multiple plaques from the rectum to the distal sigmoid.
| Gastroenterology Research, ISSN 1918-2805 print, 1918-2813 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, Gastroenterol Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.gastrores.org |
Case Report
Volume 5, Number 5, October 2012, pages 211-214
Corticosteroids in the Treatment of Pseudomembranous Colitis: A Report of 3 Cases
Figure

Table
| Severity of Disease | Definition | Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Mild | ≤ 3 stools a day and a normal White cell count (WCC) | Oral metronidazole 400 - 500 mg tds for 10 - 14 days |
| Moderate | 3-5 stools a day and raised WCC (< 15 × 109/L) | Oral metronidazole 400 - 500 mg tds for 10 - 14 days |
| Severe | WCC > 15 × 109/L, temperature > 38.5 °C, acute rising creatinine, or abdominal or radiological signs of acute colitis | Oral vancomycin 125 mg QDS 10 - 14 days. If not responding, high dose vancomycin (max 500 mg QDS) via NGT +/- IV metronidazole 500 mg TDS or IV immunoglobulins 400 mg/kg |
| Life threatening | Hypotension, partial or complete ileus, toxic megacolon or evidence of severe disease on computed tomography | Vancomycin 500 mg QDS 10 - 14 days via NGT or PR + IV metronidazole 500 mg QDS. Consider colectomy |
| First recurrence | Repeat same antibiotic as initial episode (If first treatment was with metronidazole and the recurrence is severe use vancomycin) | |
| Subsequent recurrence | Oral vancomycin 125 mg QDS |