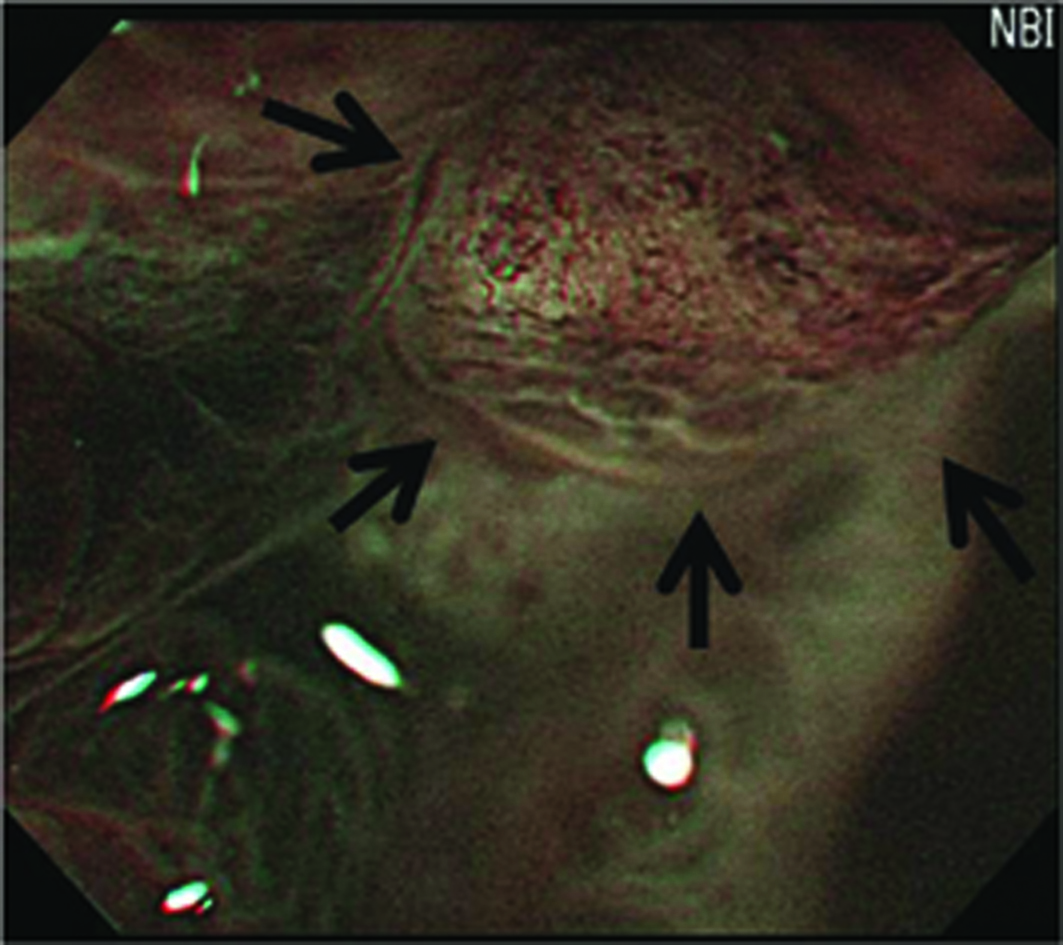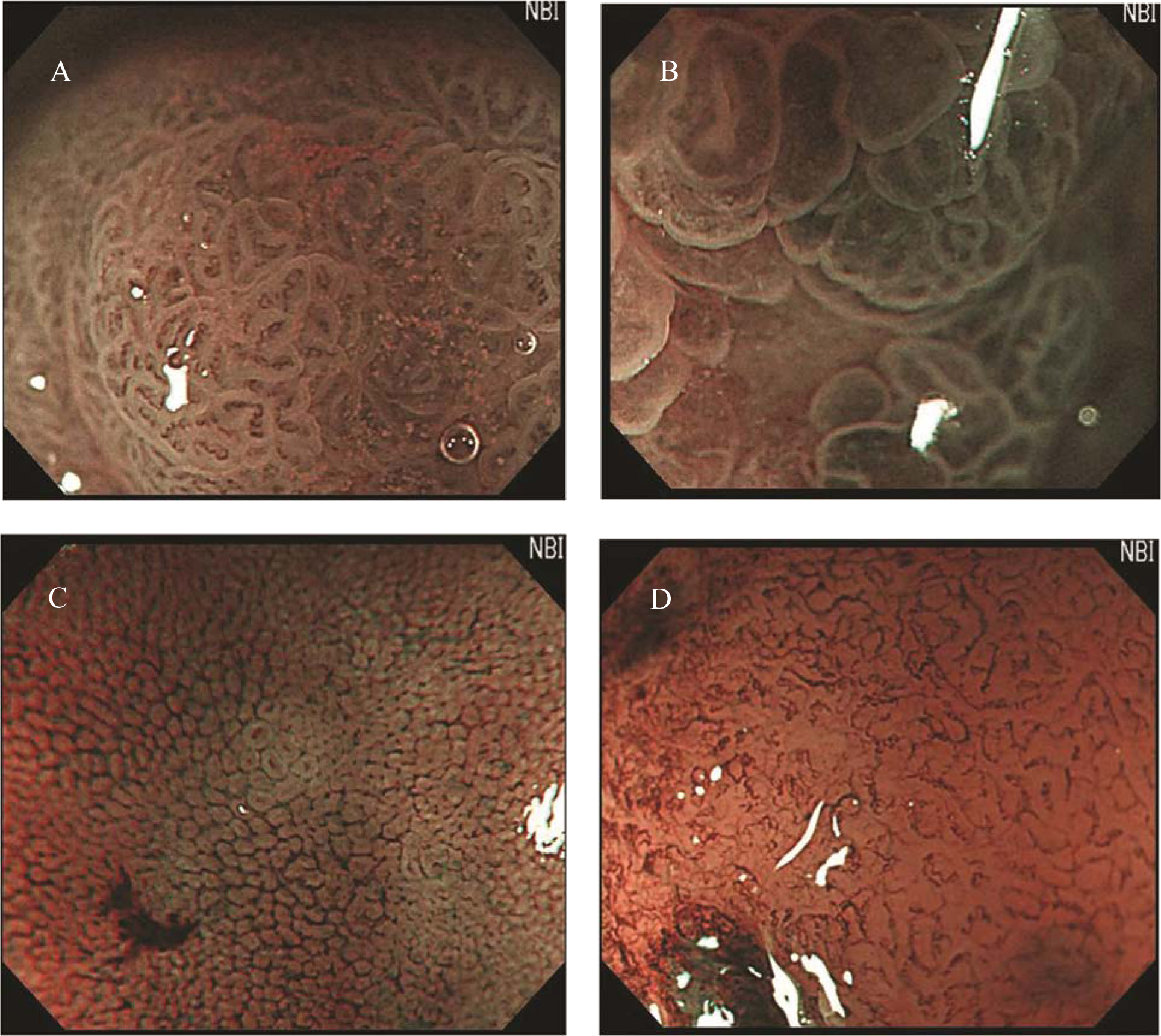
Figure 1. Classification of irregular microvascular patterns observed by MENBI: (A) Slight ISIMVPs, defined by the presence of tiny spiral blood vessels within the fine lobular superficial structure; (B) Severe ISIMVPs, defined by the presence of vertical spiral blood vessels within the coarse lobular superficial structure; (C) Fine networks, defined by fine tubular structures surrounded by a thin microvasculature; (D) Corkscrew patterns, defined by obliterated surface structures and irregular vascular patterns without loop formation. (MENBI: narrow band imaging system in combination with a magnifying endoscope; ISIMVPs: intrastructual irregular microvascular patterns)