| 1 | 28 | M | Abdominal cramps, diarrhea, jaundice | Diffuse narrowing and strictures of biliary system (PSC-compatible) | Cholangitis with eosinpophilic infiltration (PSC-like) | Steroid hydroxyurea | Colitis with eosinophilic infiltration | Scheurlen et al [16] |
| 2 | 41 | M | Abdominal pain, fever, jaundice | Stricture and dilatation in extrahepatic bile duct (PSC-compatible) | Eosinophilic sclerosing cholangitis | Steroid | | Grauer et al [6] |
| 3 | 58 | M | Jaundice, fatigue, abdominal pain | Normal | Eosinophilic cholangitis | Steroid | | Dillon et al [17] |
| 4 | 20 | M | Jaundice, fever | Hepatomegaly, diffuse irregular appearance (PSC-like) | Eosinophilic cholangitis | Steroid, aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA) | Colitis with eosinophilic infiltration (UC-like) | Schoonbroodt et al [18] |
| 5 | 52 | M | Diarrhea, jaundice | NS | Eosinophilic cholangitis | NS | Colitis with eosinophilic infiltration | Sussman et al [19] |
| 6 | 20 | M | Fatigue, myalgia, night sweat | NS | Chronic active hepatitis with eosinophilic infiltration | Steroid | AMA (NS)
ANA (+) | Croffy et al [20] |
| 7 | 34 | M | Nausea, jaundice | NS | Chronic active hepatitis with eosinophilic infiltration | Steroid | AMA (NS)
ANA (-) | Croffy et al [20] |
| 8 | 19 | M | Jaundice, pruritic rash | Hepatomegaly | Chronic active hepatitis with eosinophilic infiltration | Steroid | AMA (-)
ANA (-) | Foong et al [7] |
| 9 | 65 | F | Arthralgias | Normal | Chronic hepatitis with confluent eosinophilic centrilobular necrosis | Steroid | AMA (+), ANA (-) | Ung et al [21] |
| 10 | 52 | M | Malaise, nausea, dizziness, weight loss | Hepatomegaly | NRH, portal eosinophilic infiltration | Steroid, hydroxyurea, thiaguanine | Esophageal varix | Bennie et al [9] |
| 11 | 27 | M | Abdominal fullness | Obstruction of the hepatic veins and stricture of the inferior vena cava (Budd-Chiari syndrome) | Obstructive thrombophlebitis with eiosinophilic infiltration | Interventinal therapy, steroid | Fusion of the FIP1L1 and PDGFRA gene (+) | Inoue et al [8] |
| 12 | 52 | F | Abdominal pain | Liver masses | Hepatic eosinophilic infiltration | Steroid | | Lai et al [22] |
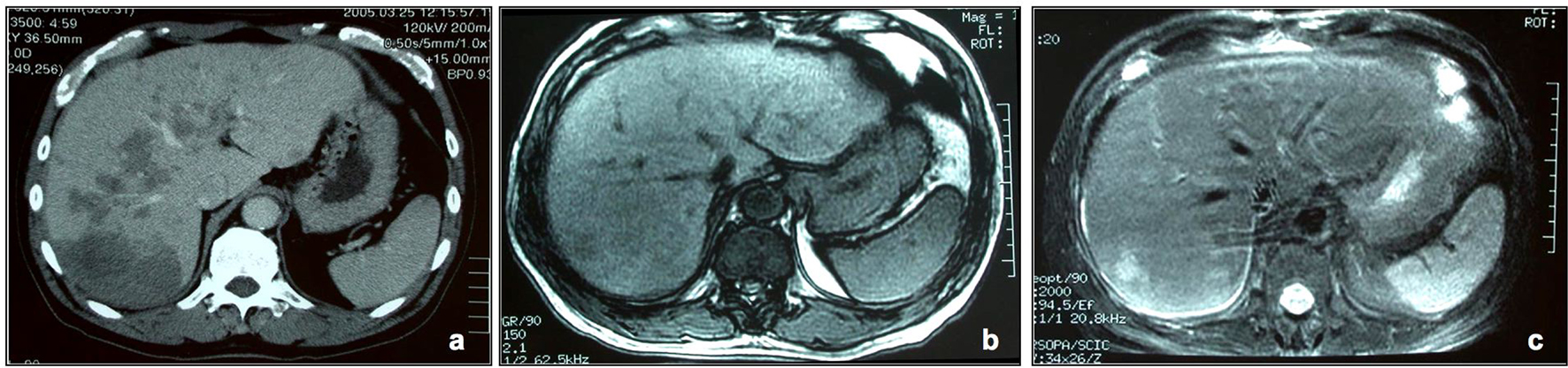
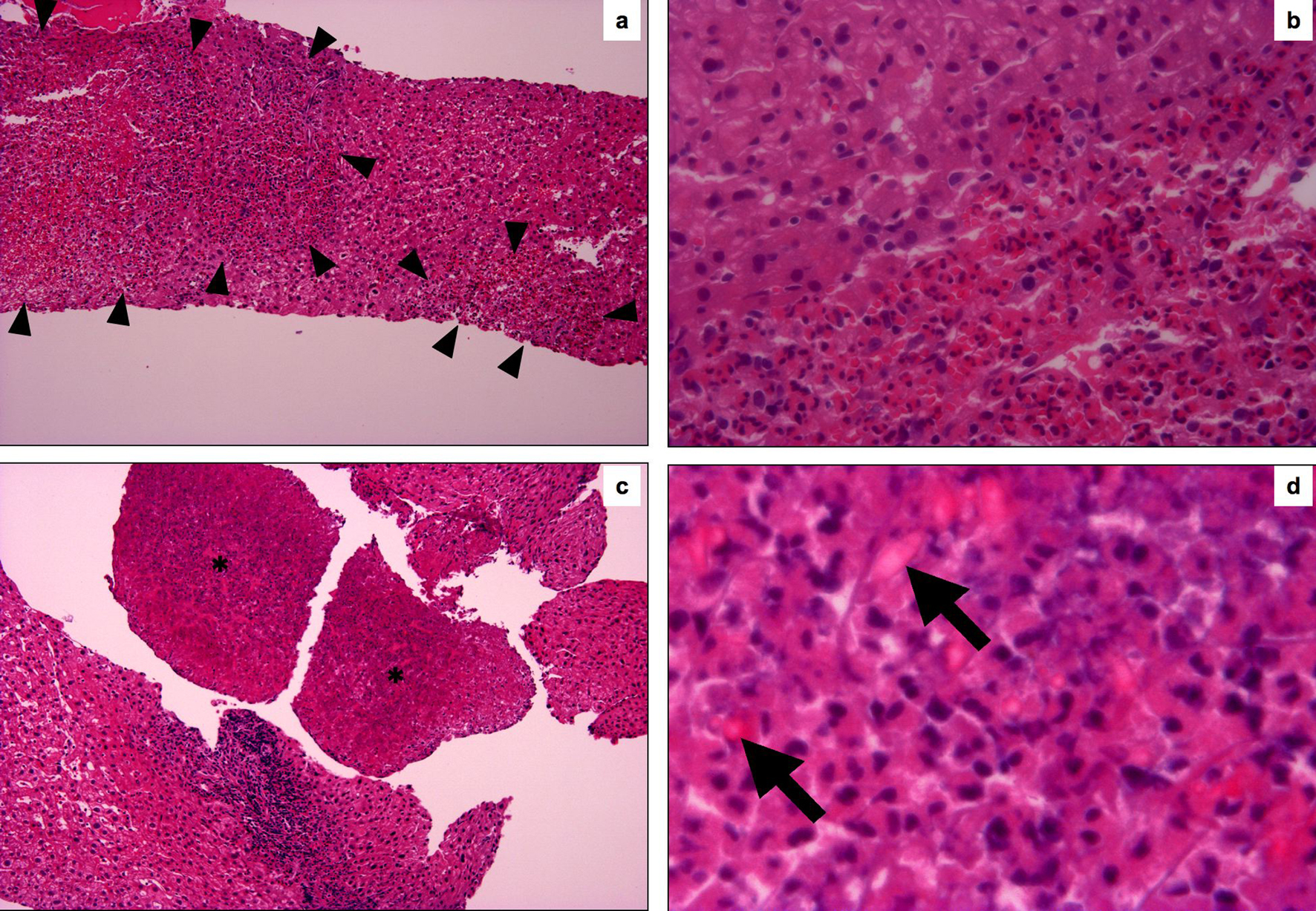
| 13 | 70 | M | Back pain, fever | Liver masses | Hepatic eosinophilic infiltration | Steroid | | Our case |