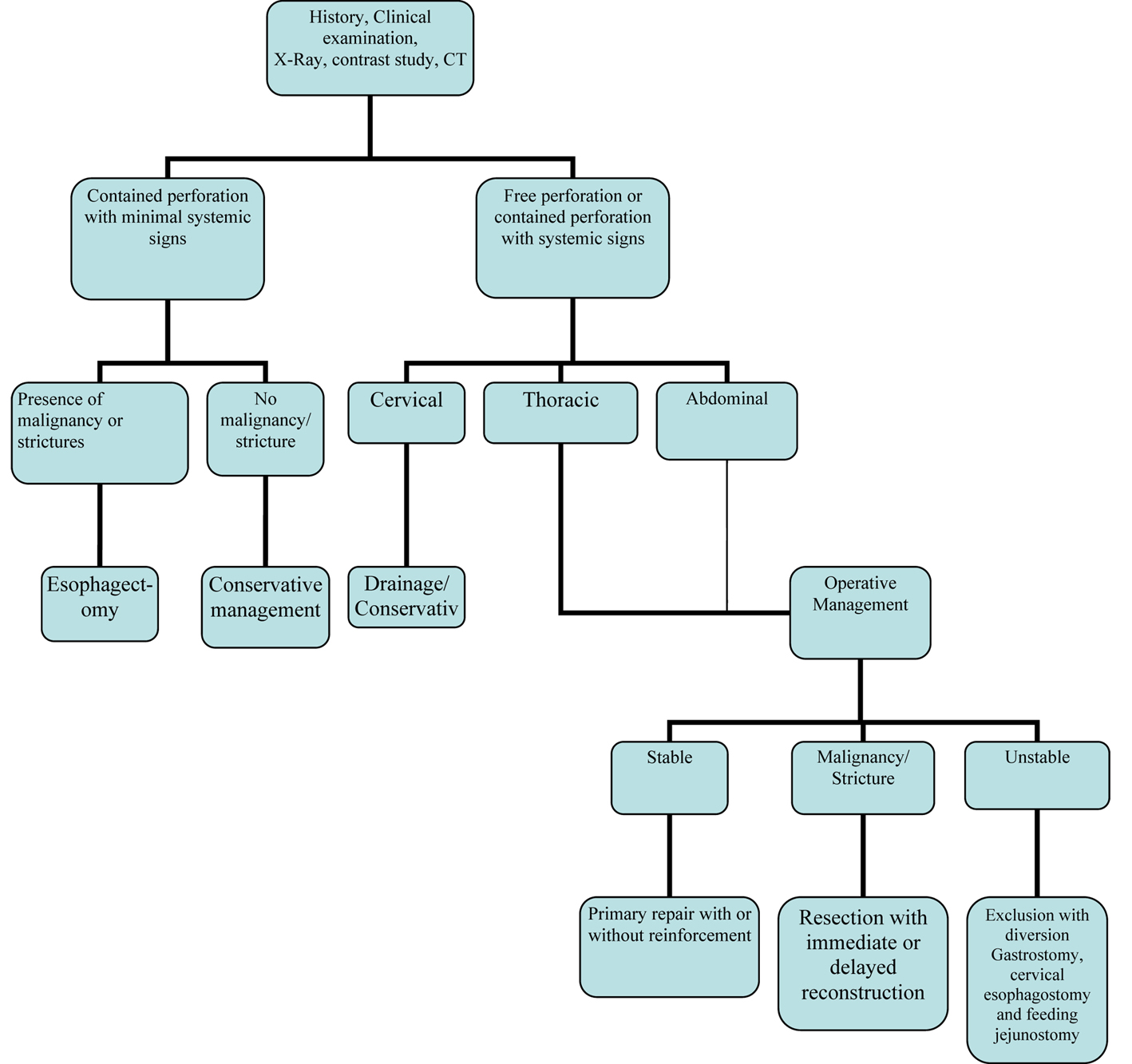
Figure 1. Management algorithm of esophageal perforation
| Gastroenterology Research, ISSN 1918-2805 print, 1918-2813 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, Gastroenterol Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.gastrores.org |
Review
Volume 3, Number 6, December 2010, pages 235-244
Management of Esophageal Perforation in Adults
Figure

Tables
| Endoscopic |
| - Diagnostic endoscopy |
| - Endoscopic biopsy |
| - Endoscopic dilatations |
| - Variceal Sclerotherapy |
| - Endoscopic laser therapy |
| - Endoscopic Photodynamic therapy |
| - Endoscopic Stent Placement |
| Nasogastric tube placement |
| Endotracheal intubations |
| Transesophageal echocardiography |
| Minitracheostomy |
| Foreign bodies- |
| Bones, dentures, button batteries |
| Trauma |
| - Blunt |
| - Penetrating |
| - Sword swallowing |
| Spontaneous or Boerhaave’s syndrome |
| Caustic agents |
| - Acid and alkali |
| Severe Reflux and Mallory-Weiss tear |
| Infective causes |
| - Candida |
| - Herpes |
| - Syphilis |
| - Tuberculosis |
| - Immunodeficiency status |
| Non esophageal surgery – |
| Mediastinal and cervical –Thyroid, Lung, spine and mediastinal tumors |
| Malignancy of esophagus, Lung and other mediastinal structures |
| History |
| Clinical examinations |
| Radiology Plain |
| - Neck X-ray lateral view |
| - Chest X-ray PA view |
| - Abdominal X-ray erect |
| Radiology Contrast |
| - Gastrografin study(water soluble contrast) |
| - Thin barium swallow study |
| - CT scan of chest and abdomen with oral contrast |
| - MRI chest and abdomen |
| - Ventilation perfusion (V/Q) scan |
| ECG |
| Operative | Non operative |
|---|---|
| Primary closure | Conservative management |
| Primary closure with buttressing of repair with | Esophageal stenting |
| - Pleural flap | Fibrin glue applications |
| - Pericardial fat pad | Endoclip application |
| - Diaphragmatic pedicle graft | |
| - Omentum onlay graft | |
| - Rhomboid muscle | |
| - Latissimus dorsi muscle | |
| - Intercostal muscle | |
| T-tube drainage | |
| Drainage only | |
| Esophagectomy with | |
| - Immediate reconstruction | |
| - Delayed reconstruction | |
| Exclusion and diversion |