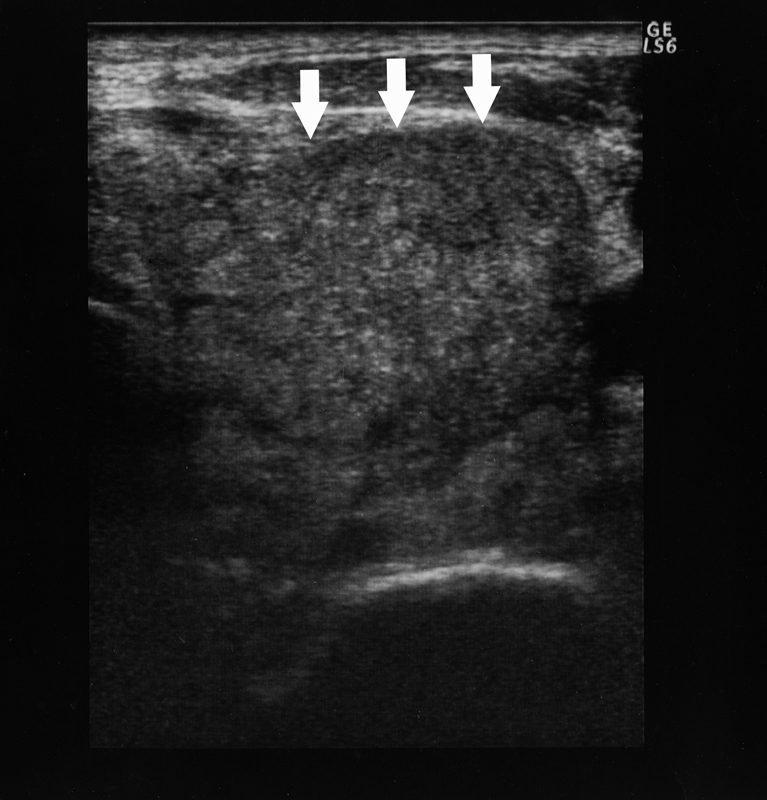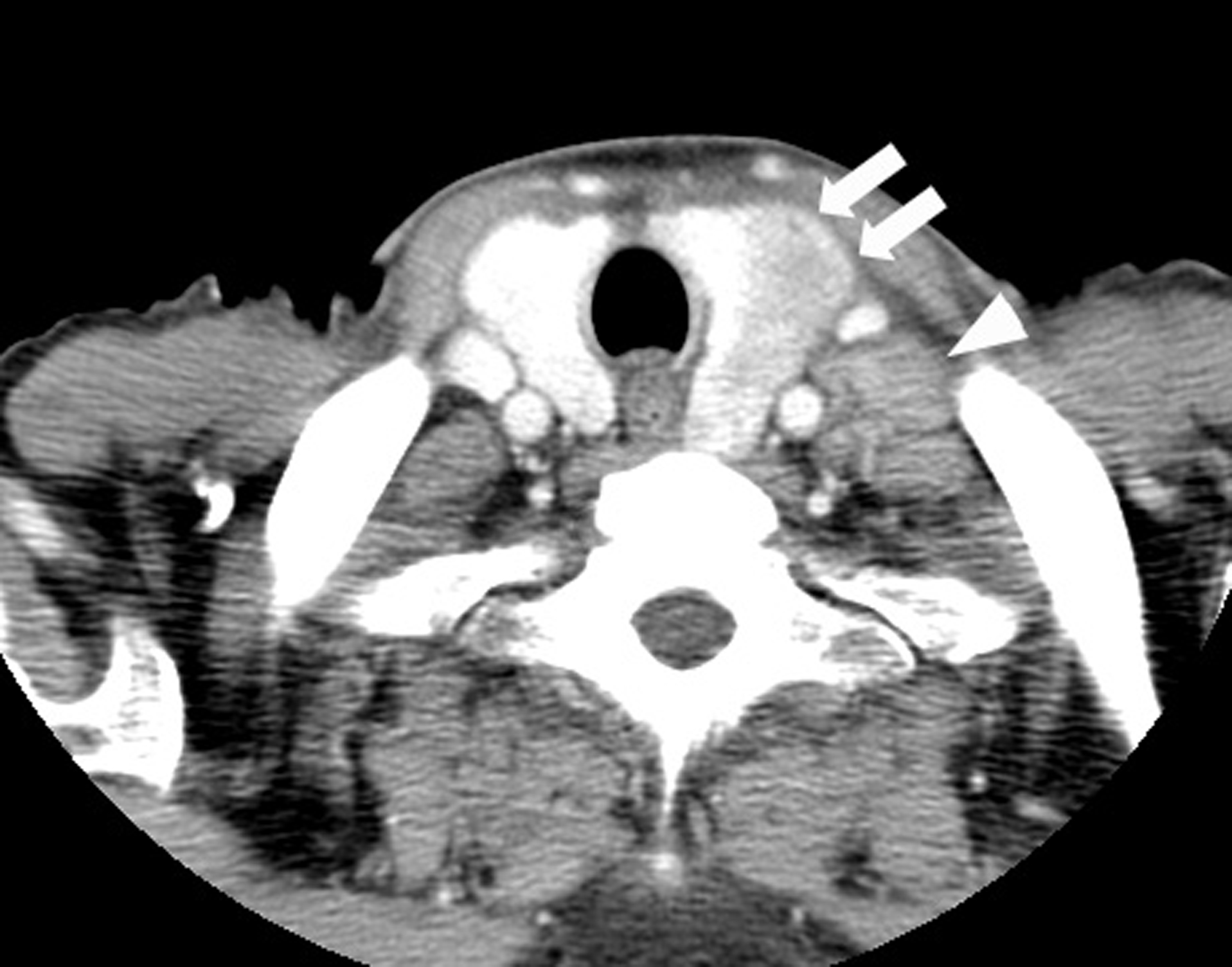
Figure 1. CT findings of the thyroid tumor. Thyroid tumor in the left lobe (arrows) and the left cervical lymph node swelling (arrowhead) are detected in contrast-enhanced CT. This thyroid tumor is a heterogeneously low-density tumor with an unclear border. The trachea is deviated to the right by this tumor.
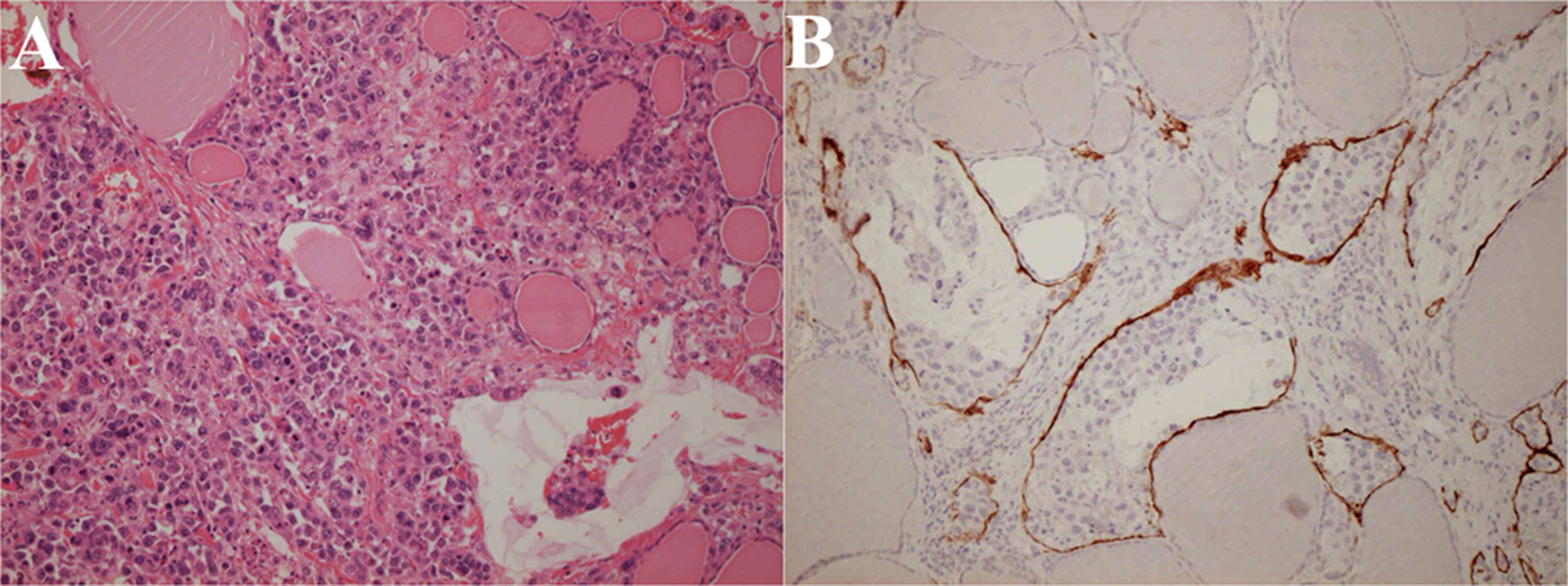
Figure 4. Histopathology of the thyroid gland at autopsy. The thyroid gland is destructed by extensive tumor invasion and colloid content is diminished (A: Hematoxylin and eosin stain; × 200). Lymph vessels are filled with tumor cells (B: Immunohistochemical stain using D2-40 monoclonal antibodies that specifically stain lymph vessels; × 200).