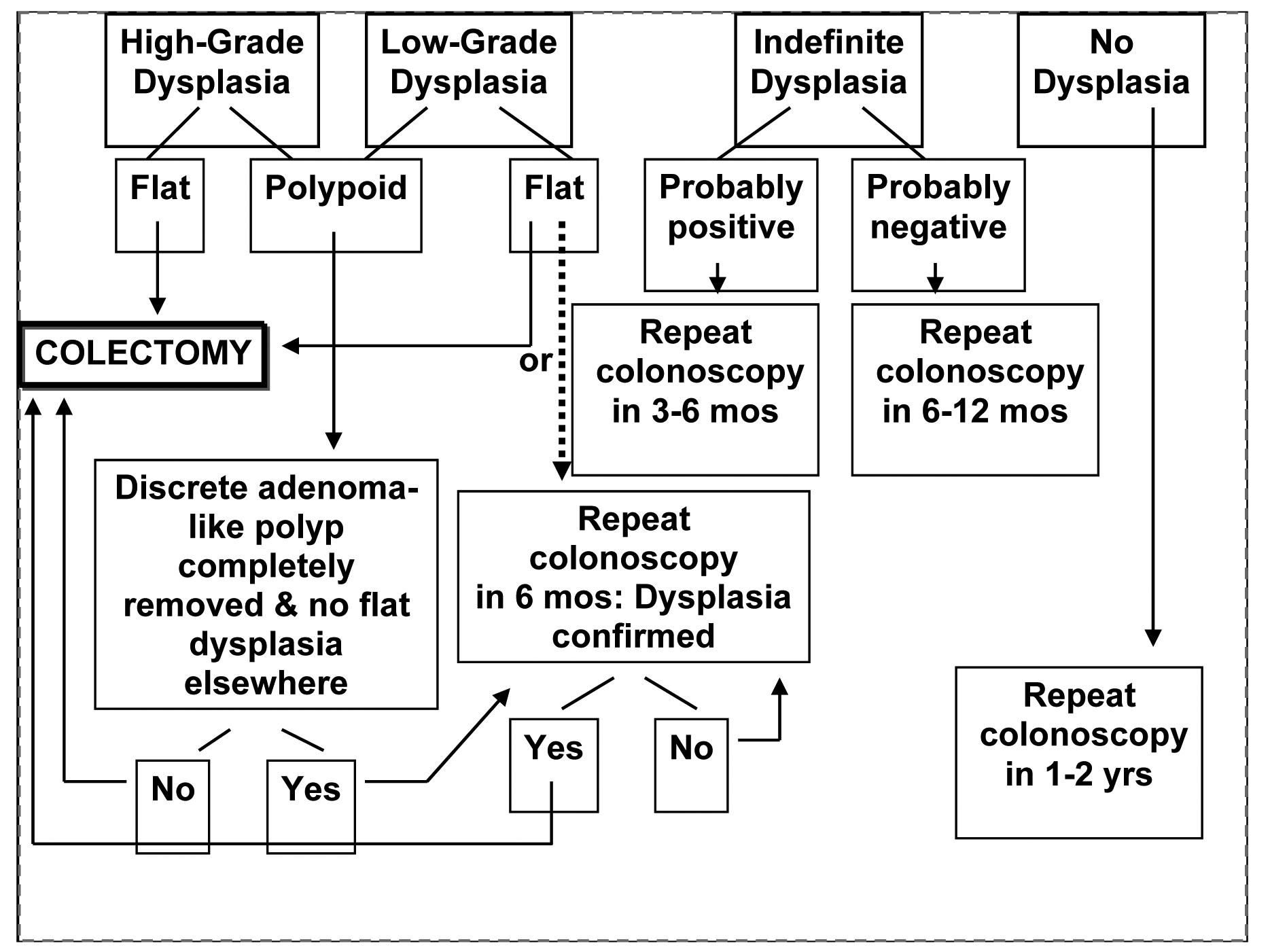
Figure 1. The suggested management of dyplasia in IBD
| Gastroenterology Research, ISSN 1918-2805 print, 1918-2813 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, Gastroenterol Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.gastrores.org |
Review
Volume 2, Number 4, August 2009, pages 200-208
Common Pitfalls in Management of Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Figure

Tables
| Class | Examples | Indications |
|---|---|---|
| Sulfasalazine and 5-amino salicylates | Azulfidine-Olsalazine, Asacol, Pentasa, Balsalazide | Mild to moderate UC and CD |
| Corticosteroids | Hydrocortisone, Prednisone, Budesonide | UC and CD |
| Immunosuppressives | Azathioprine, 6-Mercaptopurine, Methotrexate | Evidence for CD > UC. MTX-no role in UC |
| Anti-TNFα Antibody | Infliximab, Adalimumab, Certolizumab pegol | Severe UC (Infliximab)/ all 3 for CD |
| Antibiotics | Metronidazole, Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, Ciprofloxacin, Clarithromycin, | Ancillary in treatment of IBD |
| Sulfasalazine and 5-ASA compounds | Hypersensitivity, sperm abnormalities, blood dyscrasias |
| Corticosteroids | Adrenal insufficiency, hyperglycemia, edema, osteonecrosis, cataracts myopathy, peptic ulcer disease, hypokalemia, osteoporosis, euphoria, psychosis, altered cell mediated immunity |
| Azathioprine/ Methotrexate | Blood dyscrasia, drug induced hepatitisand pancreatitis. AZA implied in T cell lymphoma, MTX in Hodgkin’s lymphoma |
| Metronidazole | Seizures, peripheral neuropathy, disulfiram reaction with alcohol |
| TNF–Alpha inhibitors | Anaphylaxis, superinfections, chest pain or rash, risk of reactivation of tuberculosis, rare occurrence of multifocal leucoencephalopathy |
| 1. Bile acid diarrhea |
| 2. Increased NSAID use |
| 3. Short gut syndrome |
| 4.Infectious |
| 5. Ischemic |
| 6. Irritable bowel syndrome |
| Crohn’s disease | Ulcerative colitis |
|---|---|
| 1. Intra-abdominal/ perianal abcess | 1. Dysplasia complicating long standing UC |
| 2. Complex fistulae | 2. Recurrent, frequent relapses with poor quality of life despite optimal therapy |
| 3. Mechanical complications like fibrotic strictures | 3. Fulminant UC unreponsive to medical therapy |
| 4. Fulminant CD unreponsive to medical therapy |