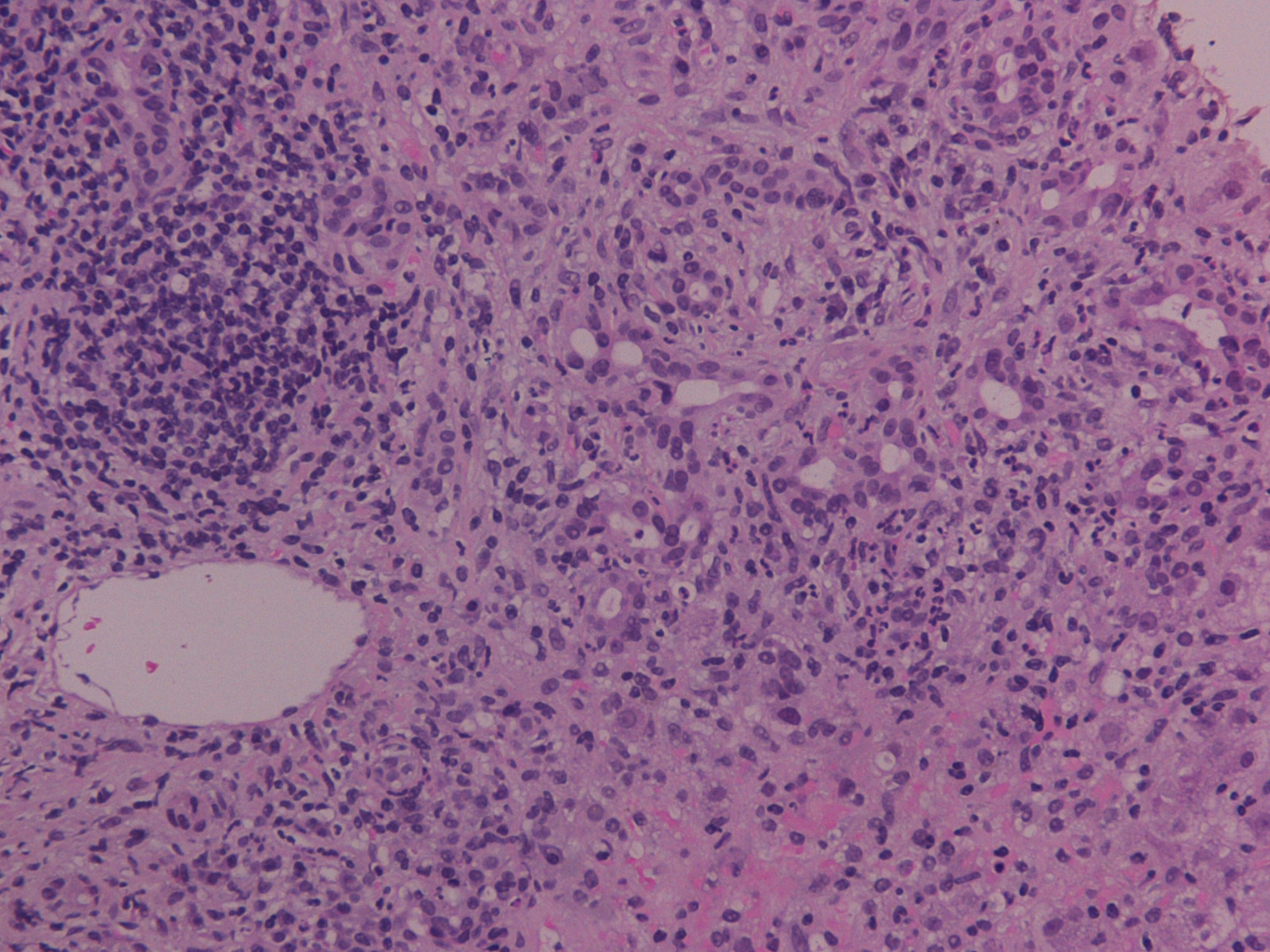
Figure 1. Inflammatory infiltration of intra-hepatic bile ducts with the presence of endoepithelial lymphocytes and plasma cells, periductal fibrosis, portal inflammation and canalicular cholestasis (H-E stain, × 200).
| Gastroenterology Research, ISSN 1918-2805 print, 1918-2813 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, Gastroenterol Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.gastrores.org |
Case Report
Volume 2, Number 3, June 2009, pages 183-187
Facing the Challenge of Acute Autoimmune Liver Disease: Report of a Case and Review of the Literature
Figures

Table
| Variable | Cutoff | Points |
|---|---|---|
| ANA: Antinuclear antibody; SMA: Smooth muscle antibody; LKM: Liver/Kidney microsome type; SLA: Soluble liver antigen. Resulting in: ≥ 6: Probable AIH and ≥ 7: Definite AIH. *Addition of points achieved for all autoantibodies (maximum, 2 points). | ||
| ANA or SMA | ≥ 1:40 | 1 |
| ANA or SMA | ≥ 1:80 | |
| or LKM | ≥ 1:40 | 2* |
| or SLA | Positive | |
| IgG | > Upper normal limit | 1 |
| > 1.10 times upper normal limit | 2 | |
| Liver histology (evidence of hepatitis is a common condition) | Compatible with AIH | 1 |
| Typical AIH | 2 | |
| Absence of viral hepatitis | Yes | 2 |