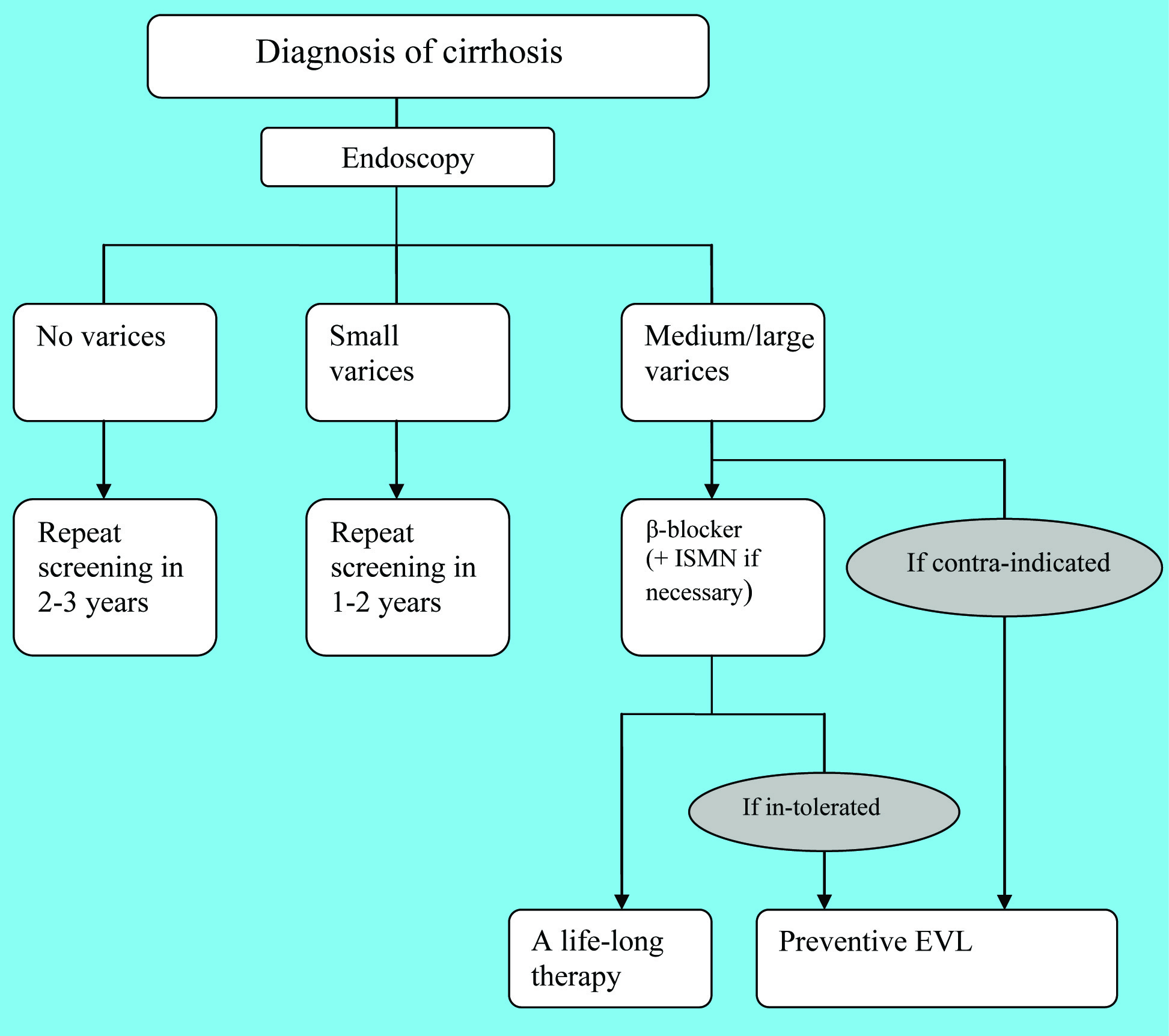
Figure 1. The management of primary prophylaxis
| Gastroenterology Research, ISSN 1918-2805 print, 1918-2813 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, Gastroenterol Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.gastrores.org |
Review
Volume 2, Number 1, February 2009, pages 8-19
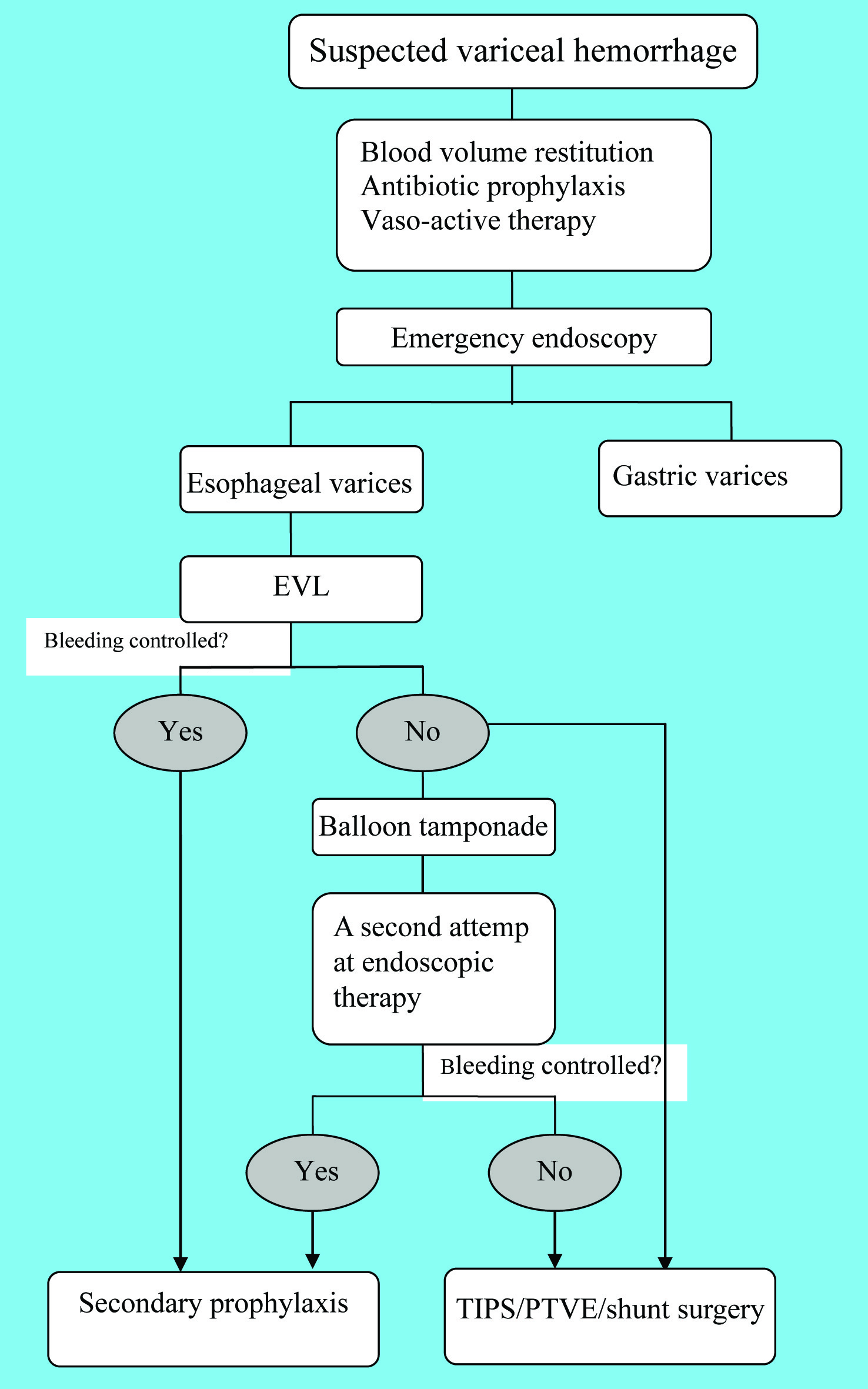
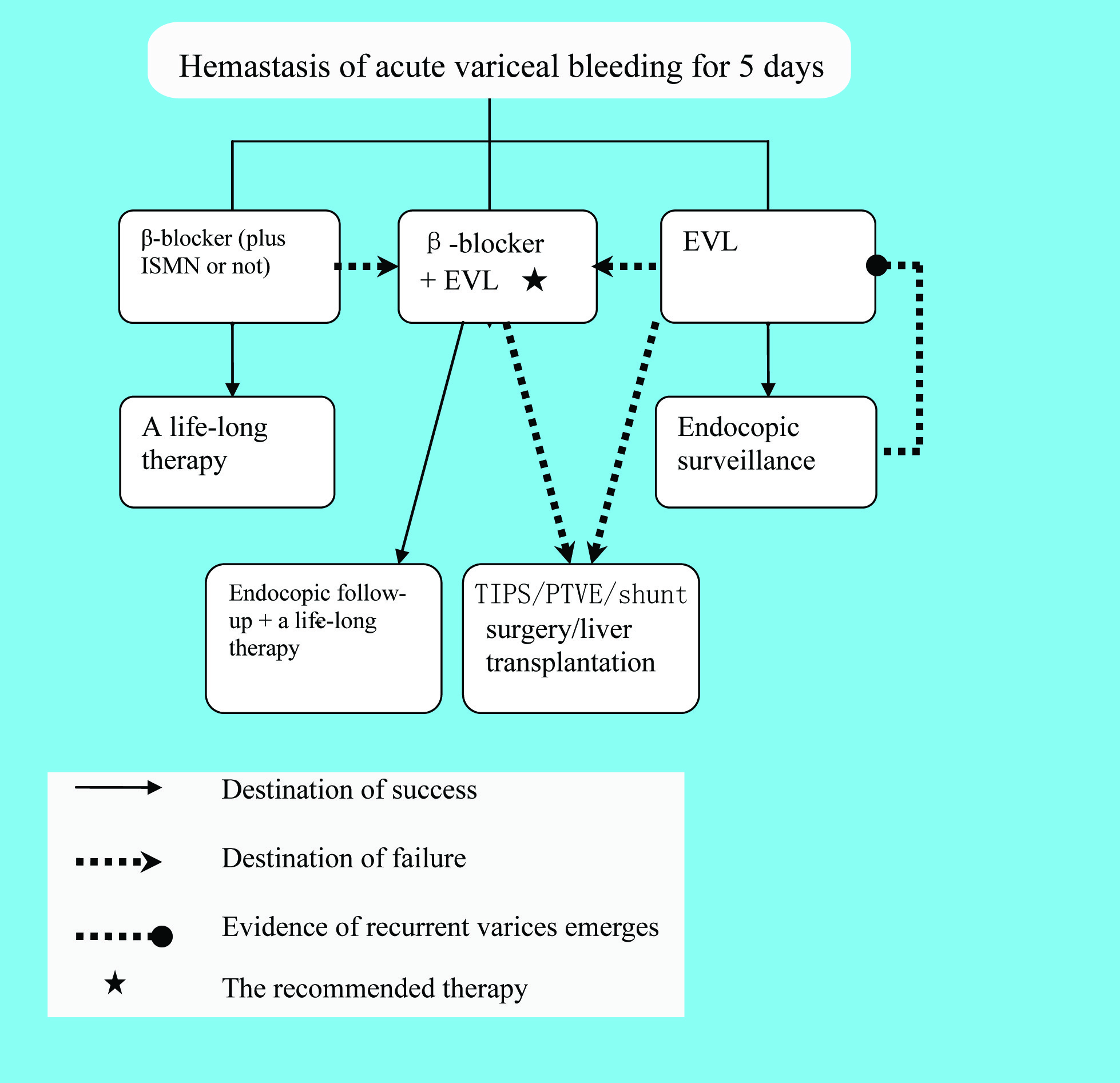
Management of Variceal Hemorrhage
Figures

Tables
| Liquid forbidden use | Reasons |
|---|---|
| Normal saline | Worsen the formation of ascites as well as other extra-vascular fluid accumulation |
| Dextrans | Side-effect on bleeding times |
| Hydroxyethyl starch | Worsen hepatic function |
| Ringer’s lactate solution | Contraindicated in case of liver dysfunction |
| Sclerosant | Concentration | Volume/site (ml) | The max value of volume/session (ml) | Special points |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sodium morrhuate | 5% | 4-6 | 20 | Commonly used in China |
| Ethanolamine oleate | 5% | 2-3 | 25 | Commonly used in China |
| Polidocanol | 1% | 1-2 | 20 | n/a |
| Sodium tetradecyl sulphate | 0.5%-1.5% | 5 | n/a | Associated with more complications and seldom used now |
| Time frame | Intervals between re-endoscopy |
|---|---|
| ≤ 2 years after eradication | 3 - 6 months |
| > 2 and ≤ 3 years after eradication | 6 - 12 months |
| > 3 years after eradication till death | 12 months |