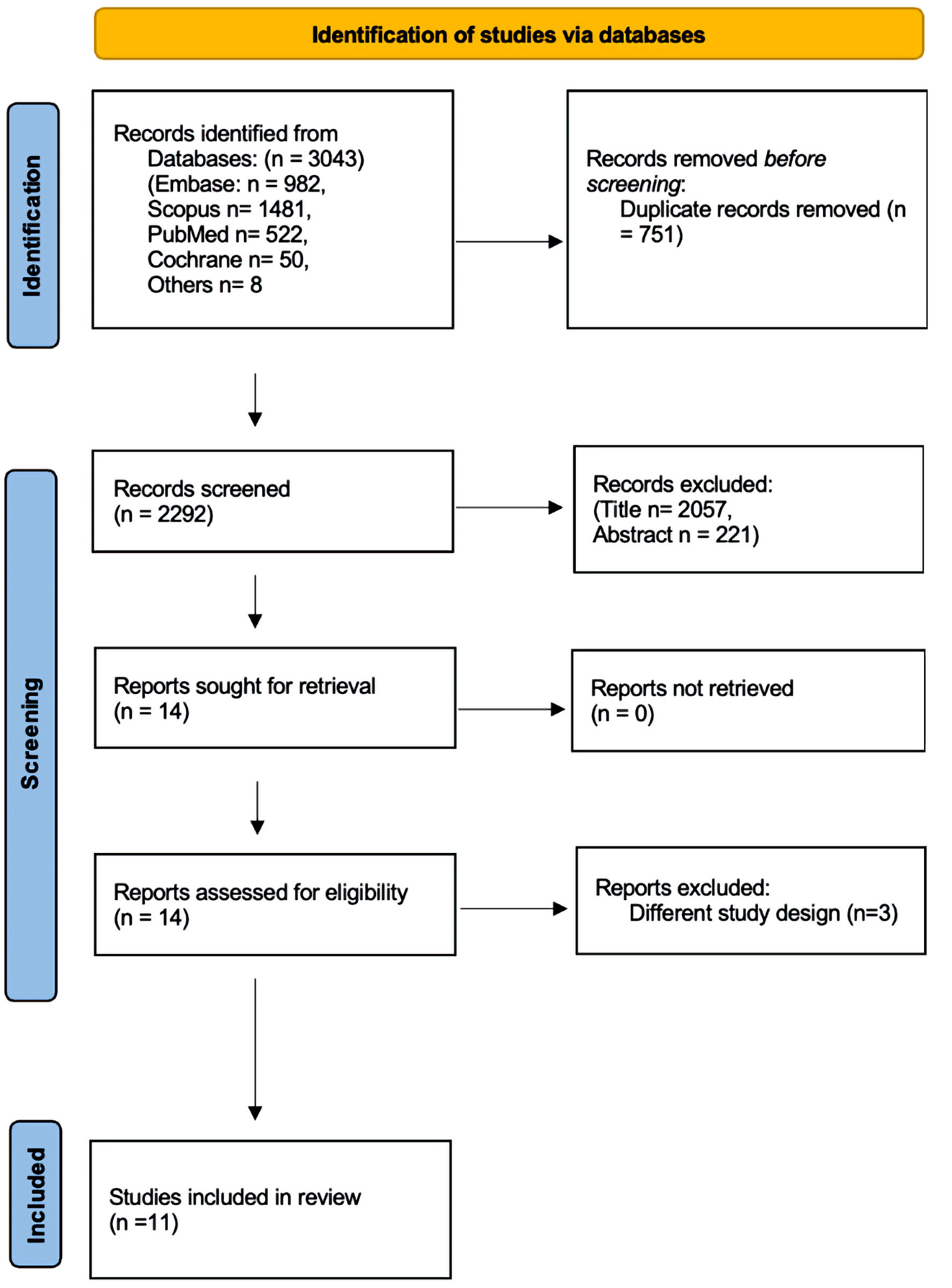
Figure 1. PRISMA flowchart for the selection process. PRISMA: Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses.
| Gastroenterology Research, ISSN 1918-2805 print, 1918-2813 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, Gastroenterol Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website https://www.gastrores.org |
Original Article
Volume 16, Number 2, April 2023, pages 68-78
Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt With or Without Gastroesophageal Variceal Embolization for the Prevention of Variceal Rebleeding: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Figures

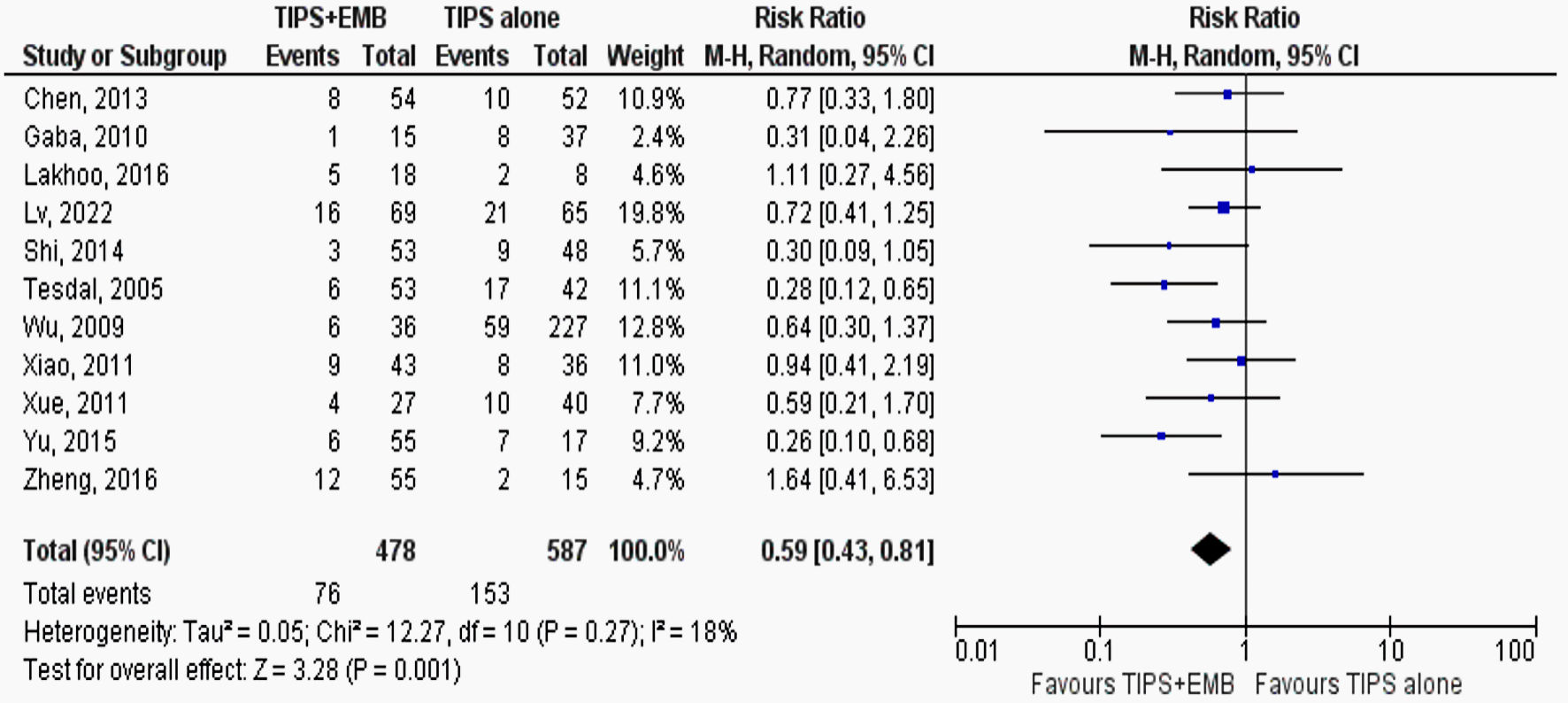
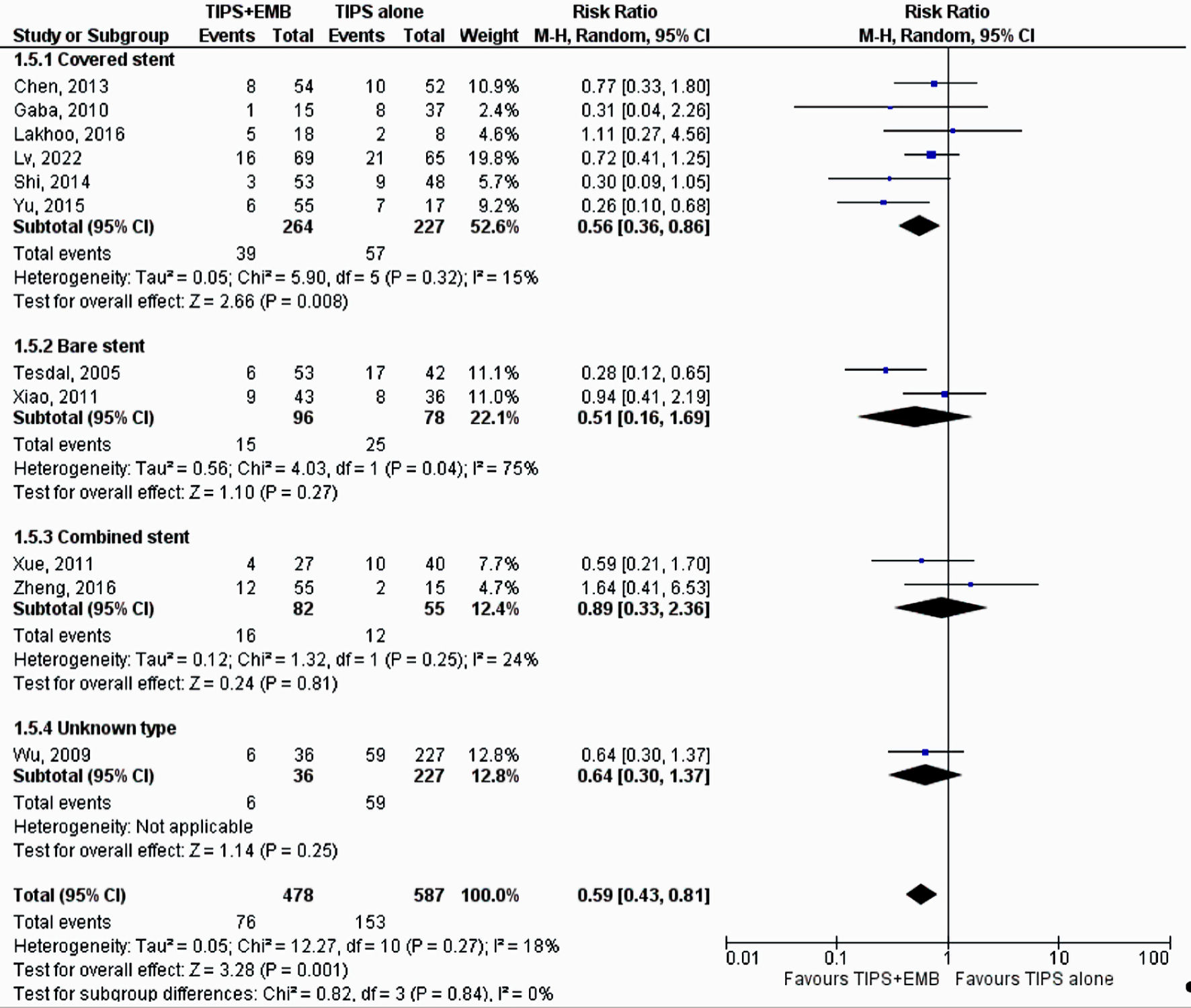
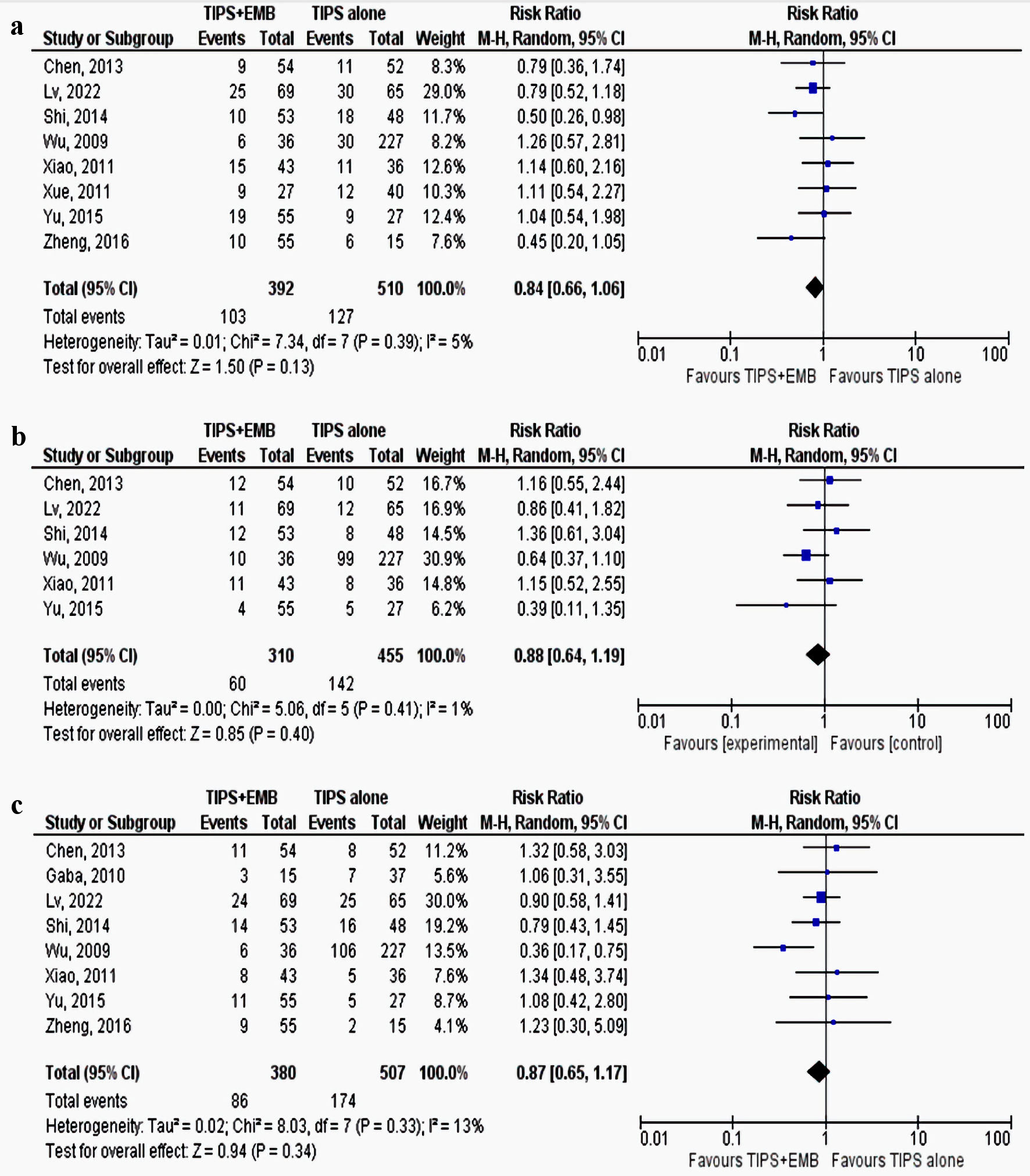
Tables
| Study, year | Country | Study period | Study design | No. of patients included in analysis | Mean age (SD) | Male/female | Study population |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SD: standard deviation; GOV: gastroesophageal varices; IGV: isolated gastric varices; EGVB: esophagogastric variceal bleeding; NA: not available. | |||||||
| Lv et al, 2022 [17] | China | 2014 - 2016 | RCT | 134 | 49.9 (11.6) | 99/35 | 18 - 75 years with cirrhosis and had variceal bleeding in the past 6 weeks despite endoscopic treatment plus non-selective β-blockers for secondary prophylaxis |
| Yu et al, 2019 [14] | China | 2011 - 2015 | Retrospective, single study | 82 | 53.9 (11.7) | 54/28 | Bleeding from cardiofundal varices, historical evidence of hemorrhage from the varices refractory to medical or endoscopic therapy; the presence of GOV-2 or IGV-1 |
| Zheng et al, 2016 [21] | China | 2010 - 2015 | Retrospective, single study | 70 | 56.3 (11.3) | 52/18 | Acute EGVB is ineffective after drug or endoscopic treatment, or multiple recurrences after bleeding is temporarily controlled |
| Lakhoo et al, 2016 [15] | USA | 1999 - 2014 | Retrospective, single study | 26 | 54, median | 16/10 | Gastric varix hemorrhage refractory to medical therapy |
| Shi et al, 2014 [16] | China | 2006-2011 | Retrospective, single study | 101 | 50.4 (10) | 53/48 | Esophageal variceal bleeding refractory to endoscopic therapy |
| Chen et al, 2013 [10] | China | 2007 - 2011 | RCT | 106 | 52.4 (12.6) | 66/40 | Recurrent gastroesophageal variceal bleeding who had undergone failed endoscopic and medical therapy |
| Xiao et al, 2011 [9] | China | 2002 - 2008 | Retrospective, single study | 79 | 44.3 (8.5) | 59/20 | Historical evidence of repeated bleeding or episode of massive bleeding |
| Xue et al, 2011 [13] | China | 2002 - 2009 | Retrospective, single study | 67 | 51 (12.83), median | 52/28 | Esophageal variceal bleeding refractory to endoscopic therapy |
| Gaba et al, 2010 [12] | USA | 2003 - 2008 | Retrospective, single study | 52 | 52, median | 29/23 | Acute (within 24 h) or recent (more than 24 h prior) hemorrhage from GOV refractory to endoscopic therapy |
| Wu et al, 2009 [22] | China | 1993 - 2008 | Retrospective, single study | 263 | NA | NA | Portal hypertension with variceal bleeding |
| Tesdal et al, 2006 [11] | Germany | 1991 - 2002 | Prospective, single study | 95 | 55.9 (11.3) | 61/34 | Severe bleeding that had failed to respond to endoscopic sclerotherapy of esophageal varices or had gastric varices not amenable to sclerotherapy |
| Study, year | No. of patients | TIPS alone (n) | TIPS + embolization (n) | Child score in TIPS alone (A/B/C) | Child score in TIPS + embolization (A/B/C) | Varices location | Stent type | Embolic agents | Time of embolization in relation to TIPS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TIPS alone | TIPS + embolization | |||||||||
| aInclude both groups. GEV: gastroesophageal varices; TIPS: transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt; IGV: isolated gastric varices; NA: not available. | ||||||||||
| Lv et al, 2022 [17] | 134 | 65 | 69 | 31/26/8 | 38/27/4 | Esophagus: 21/GEV1: 33/GEV2: 11 | Esophagus: 23 /GEV1: 34/GEV2: 12 | Covered | Coils | After TIPS |
| Yu et al, 2019 [14] | 82 | 27 | 55 | 14/11/2 | 21/24/10 | GEV2: 22/IGV1: 5 | GEV2: 34/IGV1: 21 | Covered | Combined (coils, vascular plug, sclerosing agent) | After TIPS |
| Zheng et al, 2016 [21] | 70 | 15 | 55 | NA | NA | Esophageal and gastric fundus varices | Combined (covered and bare) | Combined (coils, sclerosing agent) | After TIPS | |
| Lakhoo et al, 2016 [15] | 26 | 8 | 18 | NA | NA | Covered | Combined (coils, vascular plug) | After TIPS | ||
| Shi et al, 2014 [16] | 101 | 48 | 53 | 11/28/9 | 16/29/8 | Esophageal and gastric fundus varices | Covered | Sclerosing agents | Before TIPS | |
| Chen et al, 2013 [10] | 106 | 52 | 54 | 9/40/3 | 12/37/5 | NA | Covered | Coils | Before TIPS | |
| Xiao et al, 2011 [9] | 79 | 36 | 43 | 14/18/4 | 15/20/8 | Esophageal: 23/fundus: 13 | Esophageal: 25/fundus: 18 | Bare | Combined (coils, α-cyanoacrylate) | After TIPS |
| Xue et al, 2011 [13] | 67 | 40 | 27 | 37/22/21a | Esophageal: 29/fundus: 11 | Esophageal: 10/fundus: 17 | Combined (covered and bare) | Coils or ethanol | unspecified | |
| Gaba et al, 2010 [12] | 52 | 37 | 15 | 6/28/18a | Esophageal: 24/gastric: 13 | Esophageal: 7/gastric: 8 | Covered | Coils | After TIPS | |
| Wu et al, 2009 [22] | 263 | 227 | 36 | 66/175/117a | NA | NA | NA | Combined (coils, gelatin sponge) | After TIPS | |
| Tesdal et al, 2006 [11] | 95 | 42 | 53 | 13/22/7 | 21/26/6 | NA | NA | Bare | Combined (coils, sclerosing agent) | After TIPS |