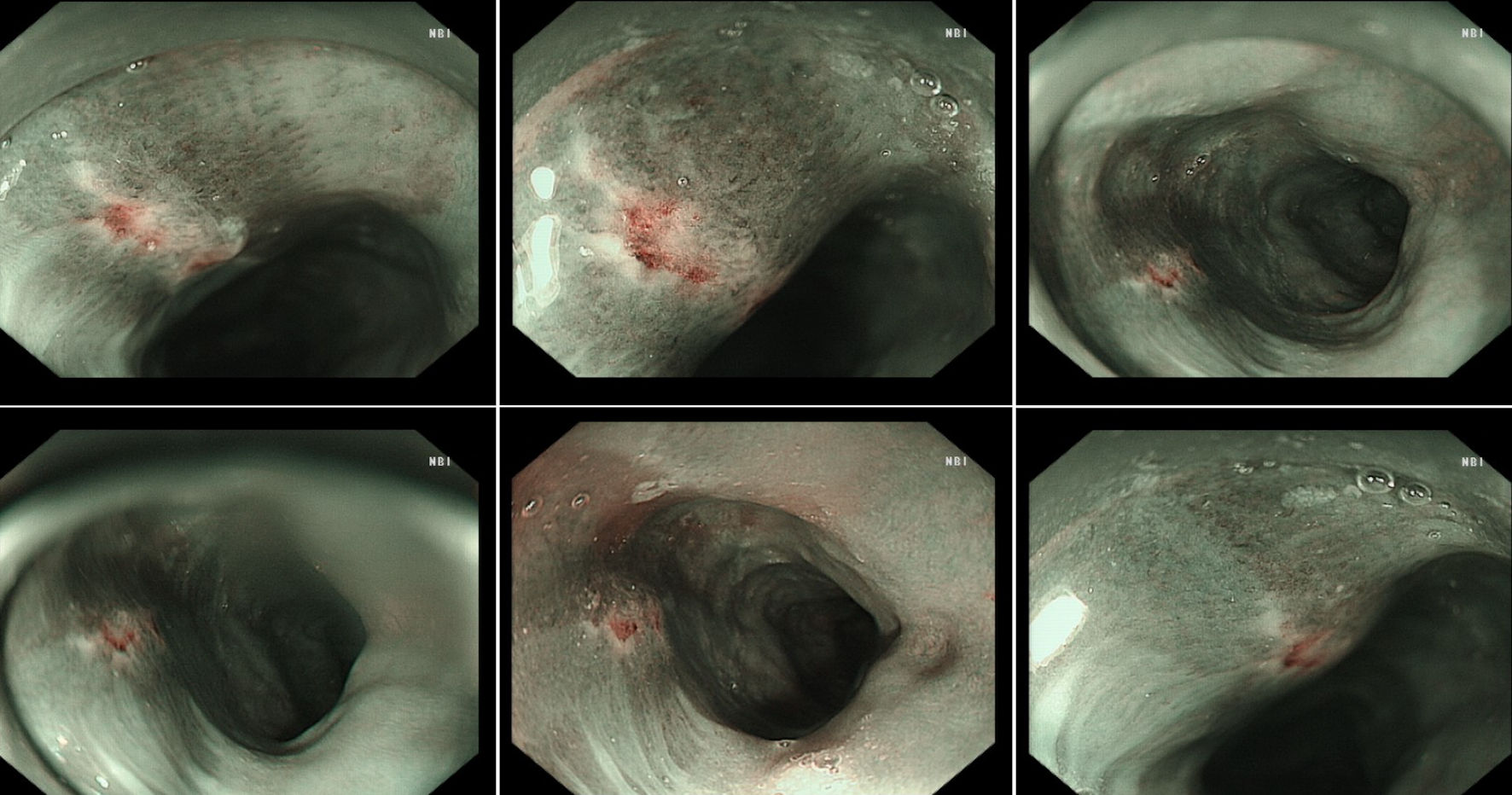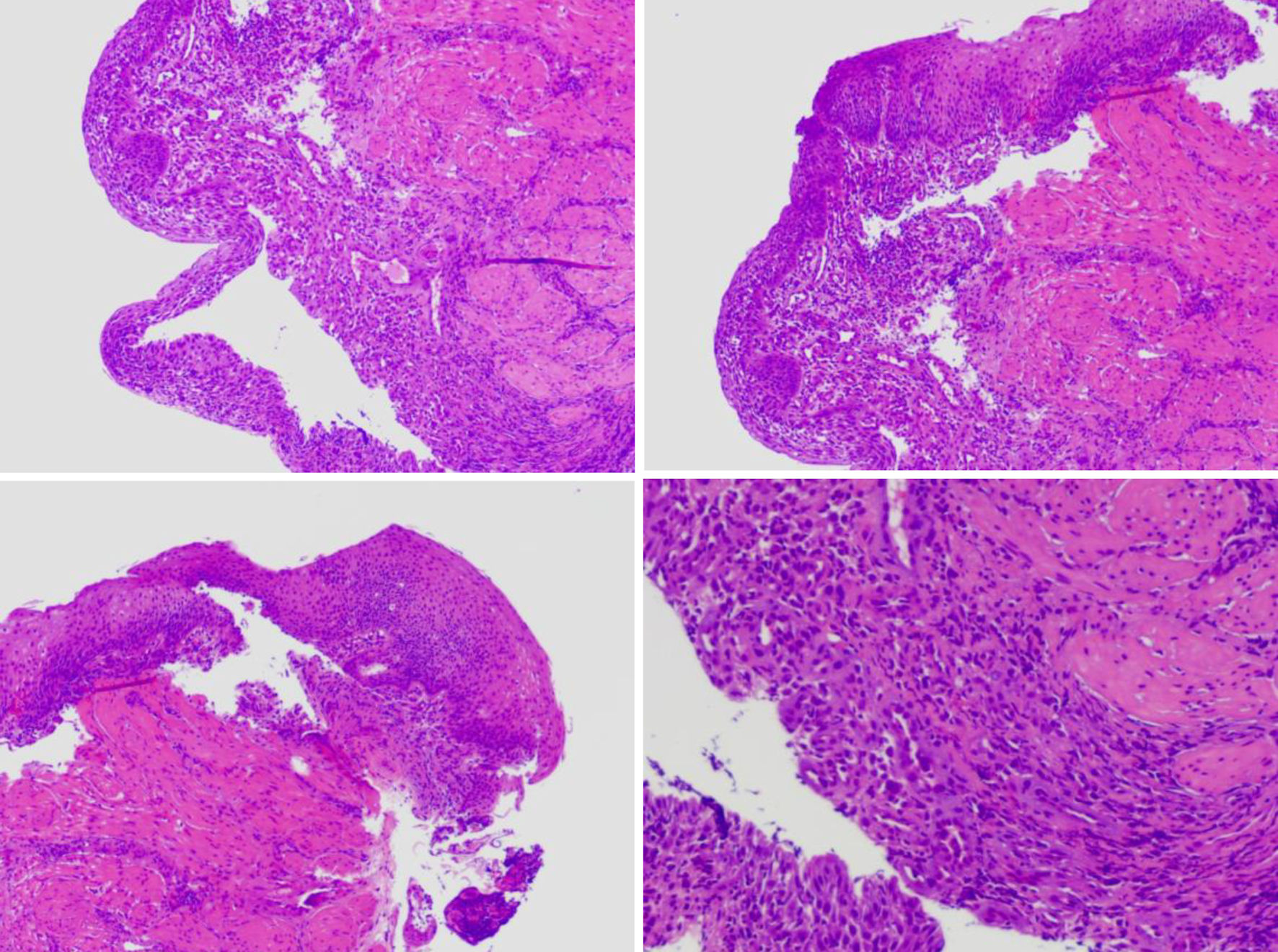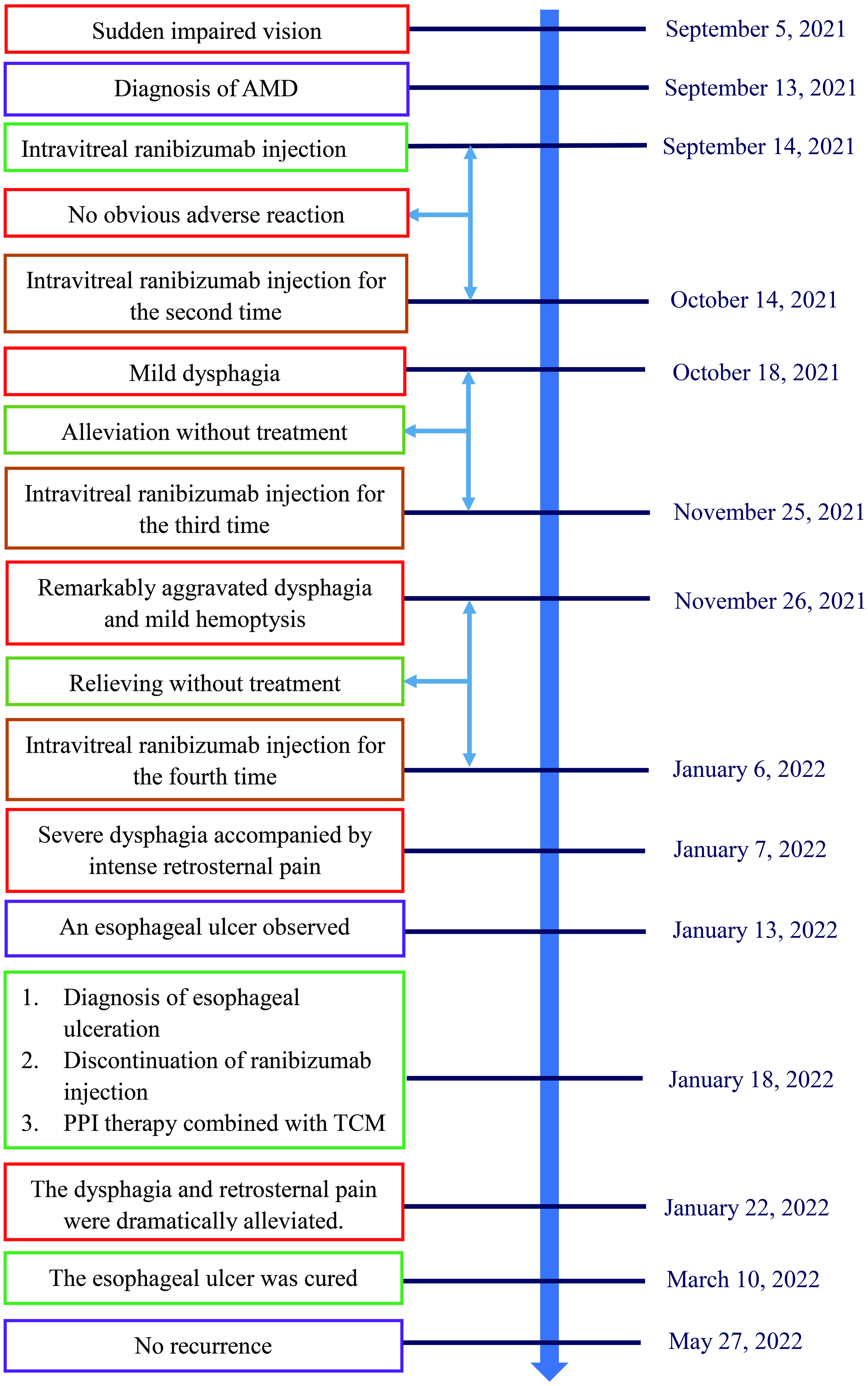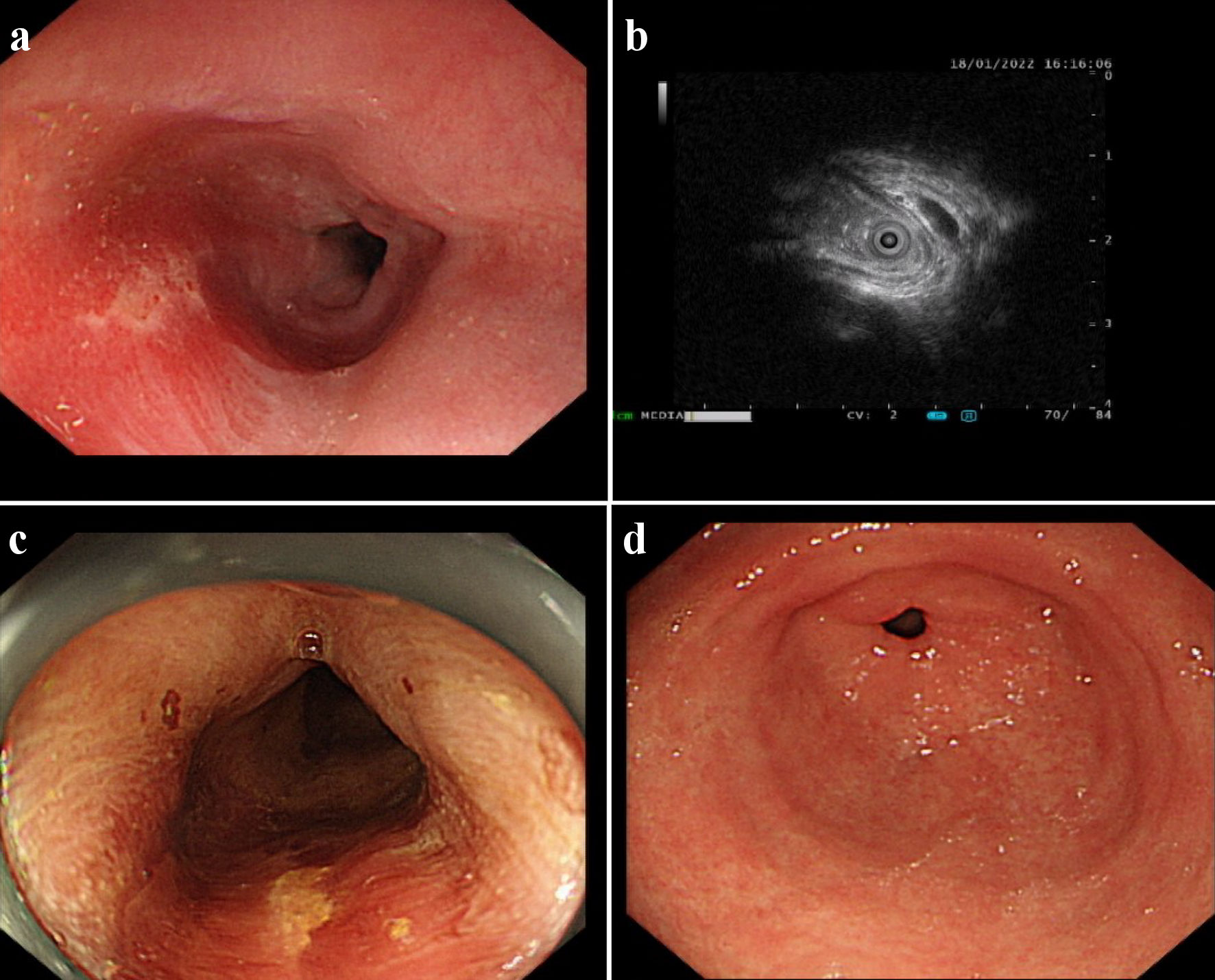
Figure 1. An esophageal surface ulcer occurred after intravitreal ranibizumab injection. (a) Ultrasound gastroscopy showed an esophageal surface ulcer 20 - 24 cm from the incisor. The central of ulcer was covered with fibrinous tissue, and the surrounding mucosae were flushing and congestive. (b) Ultrasonography revealed that the mucosae were slightly incrassated with a hypoechoic variation in the lesion area. (c) The fibrinous tissue was stained by Lugol solution. (d) Ultrasound gastroscopy showed that the mucosae in the gastric antrum were smooth.