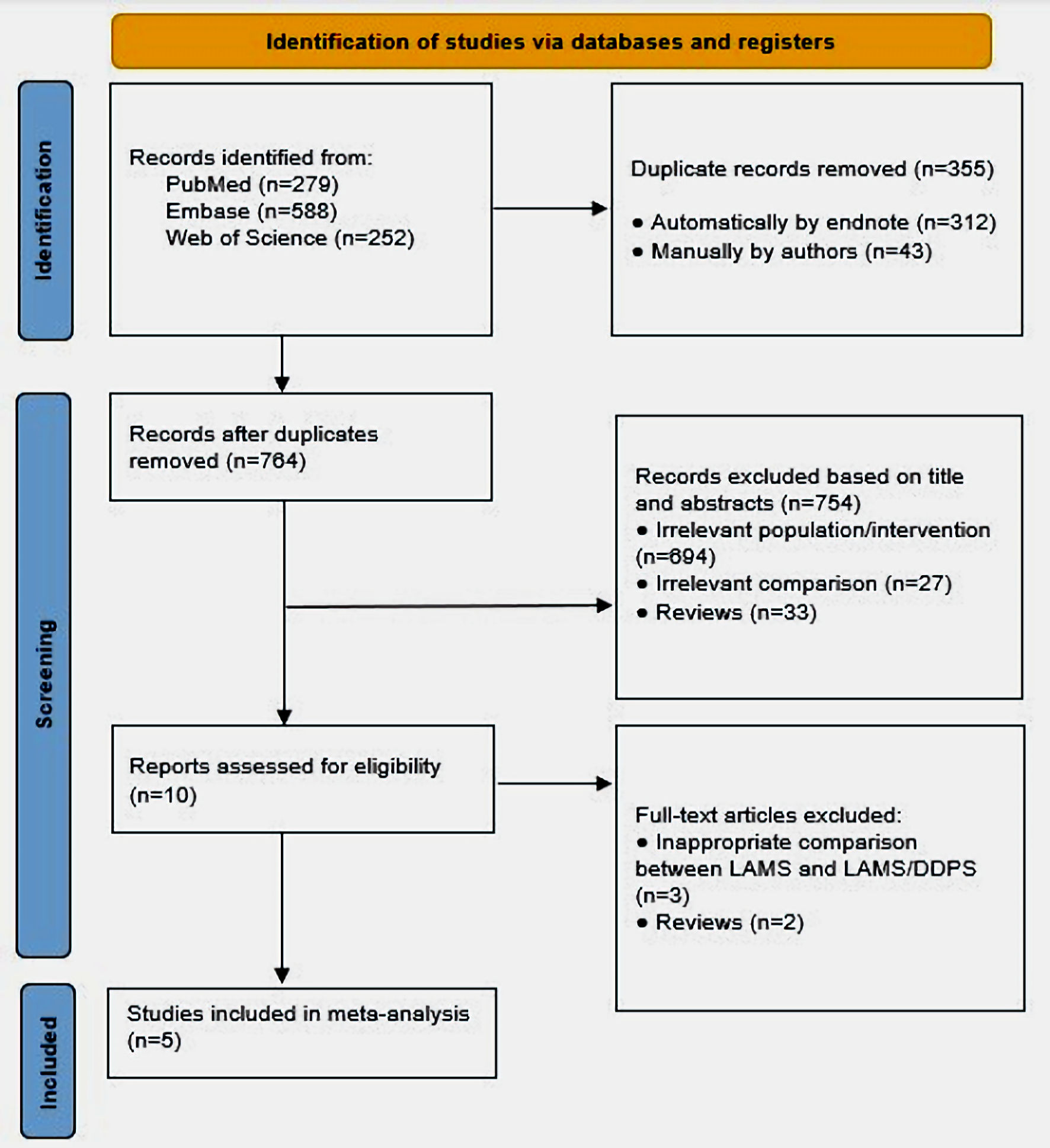
Figure 1. PRISMA flow diagram of included studies. PRISMA: preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses; DPPS: double-pigtail plastic stent; LAMS: lumen-apposing metal stent.
| Gastroenterology Research, ISSN 1918-2805 print, 1918-2813 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, Gastroenterol Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website https://www.gastrores.org |
Original Article
Volume 16, Number 2, April 2023, pages 59-67
Lumen-Apposing Metal Stent With and Without Concurrent Double-Pigtail Plastic Stent for Pancreatic Fluid Collections: A Comparative Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Figures

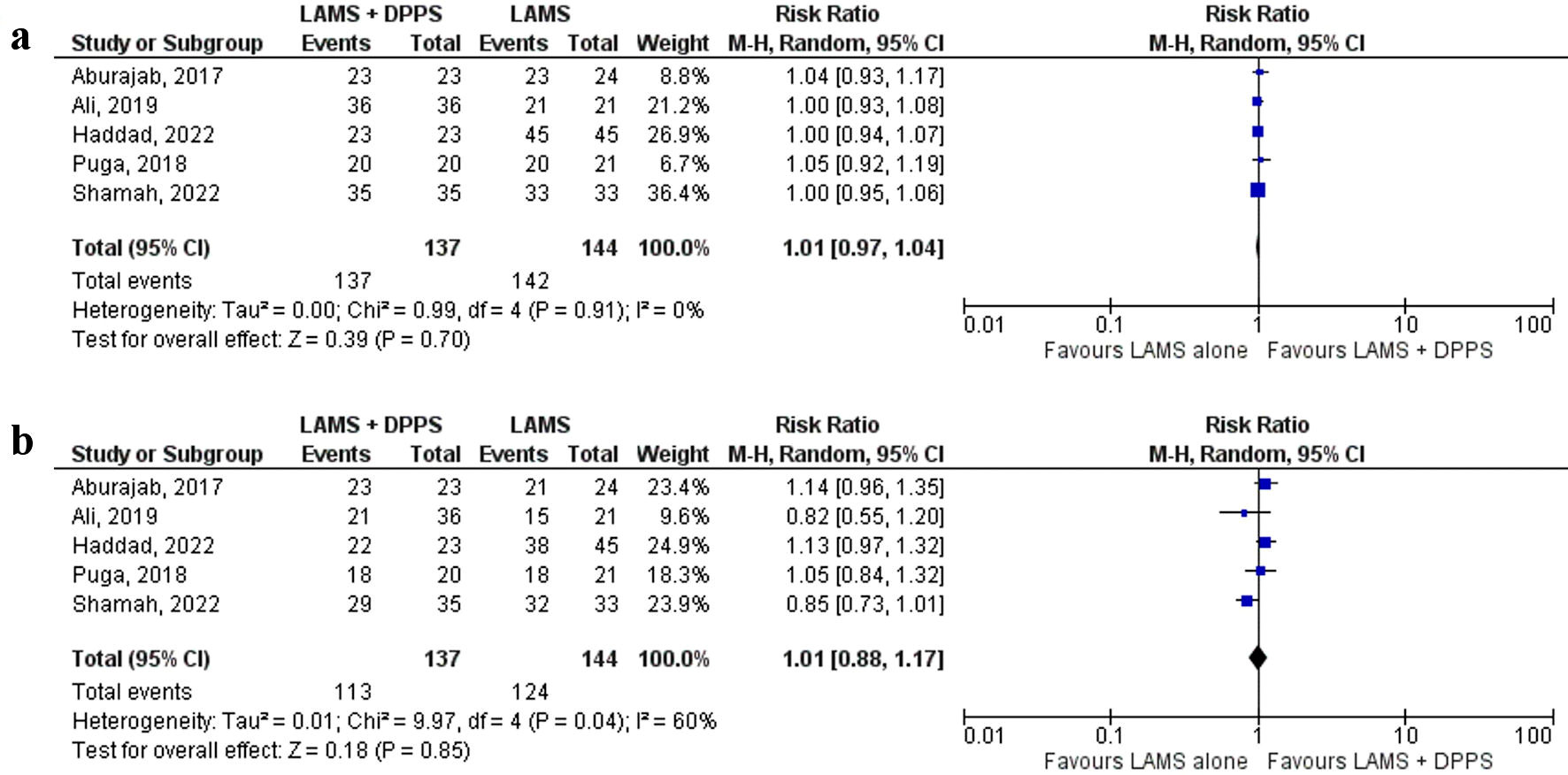
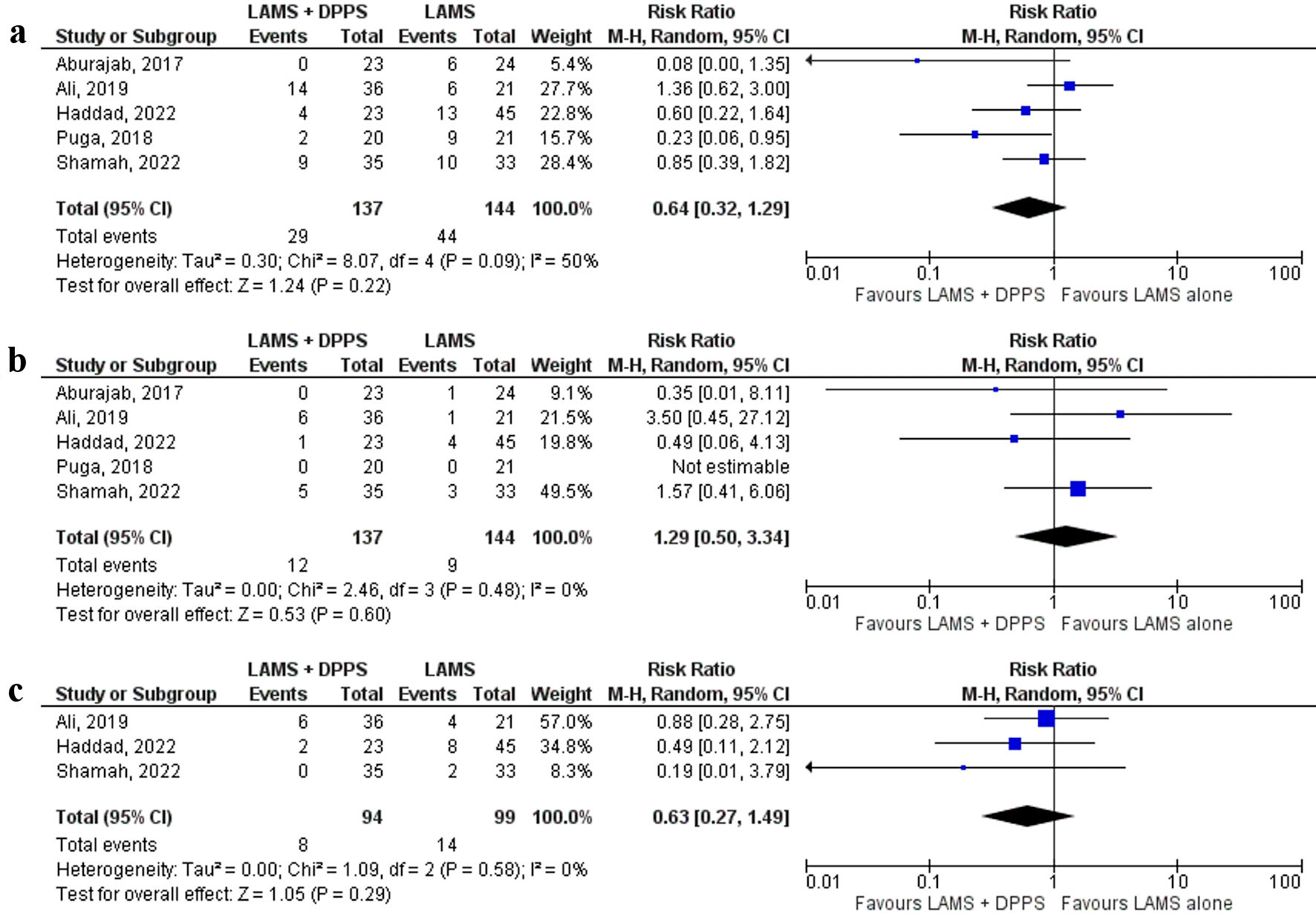
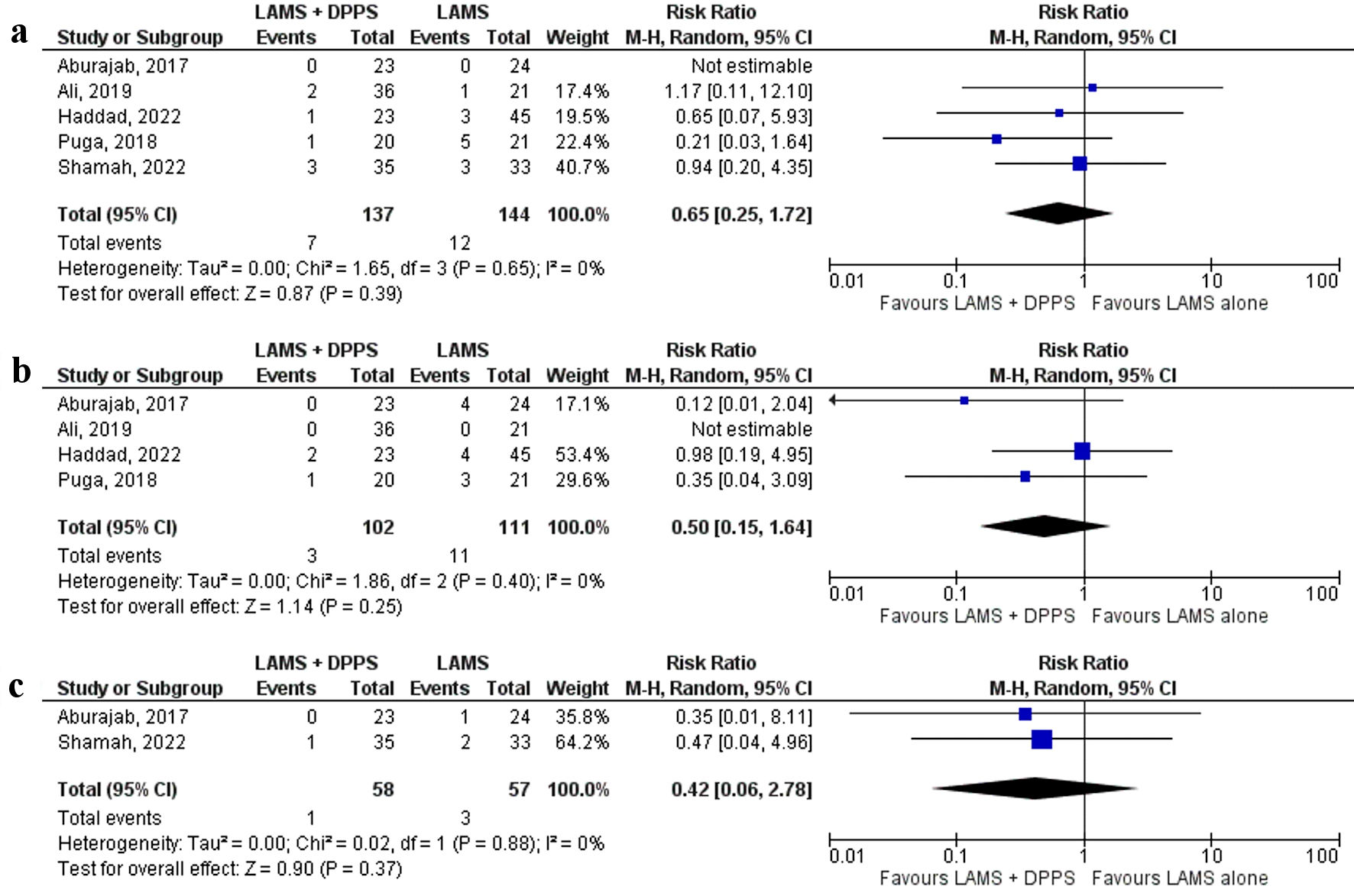
Tables
| Study characteristics | Aburajab et al, 2018 [18] | Ali et al, 2019 [21] | Haddad et al, 2022 [20] | Puga et al, 2018 [17] | Shamah et al, 2022 [19] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DPPS: double-pigtail plastic stent; LAMS: lumen-apposing metal stent; NR: not reported; PFC: pancreatic fluid collection; SD: standard deviation. | |||||
| Study design | Retrospective cohort, single-center | Retrospective cohort, single-center | Retrospective cohort, single-center | Retrospective cohort, single-center | Retrospective cohort, multi-center |
| Country of origin | USA | USA | USA | Spain | USA |
| Total number (LAMS/LAMS + DPPS) | 47 (24/23) | 57 (21/36) | 68 (45/23) | 41 (21/20) | 68 (33/35) |
| Male, n (%) | 35 (74.5%) | 34 (60%) | 36 (53%) | 32 (78%) | 44 (65%) |
| Age (years), mean ± SD | 50.6 ± 12.1 | NR | 46.5 ± 16.2 | 58.7 ± 14.1 | 54.8 ± 13.2 |
| PFC size (cm), mean ± SD (LAMS/LAMS + DPPS) | 9.5 ± 4 (10 ± 4/9 ± 4) | (9/10.5) | 14.7 ± 5.9 (15 ± 5.7/14.2 ± 6.2) | 9.6 ± 1.3 (10 ± 1.06/9.1 ± 1.3) | 10.9 ± 3.8 (11.4 ± 4/10.37 ± 3.5) |
| LAMS size | 15 mm | 10 or 15 mm | 15, 10, and 20 mm | 10 or 15 mm | 10 or 15 mm |
| Number of necrosectomies, mean (LAMS/LAMS/DPPS) | NR | NR | 1.14/1.56 | NR | NR |
| Stent duration, median (weeks), (LAMS/LAMS + DPPS) | NR | NR | 7.38/7.86 | NR | NR |
| Outcomes reported | Technical success, clinical success, overall adverse events, stent migration, bleeding, infection, and perforation | Technical success, clinical success, overall adverse events, stent migration, stent occlusion, bleeding, and infection | Technical success, clinical success, overall adverse events, stent migration, stent occlusion, bleeding, and infection | Technical success, clinical success, overall adverse events, stent migration, bleeding, and infection | Technical success, clinical success, overall adverse events, stent migration, stent occlusion, bleeding, and perforation |
| Clinical success definition | Symptom improvement with resolution of PFC on imaging to < 2 cm and without further intervention | Symptom improvement with resolution of PFC on imaging to < 2 cm without further intervention | Symptom resolution or PFC resolution on imaging | Decrease in PFC size by at least 50% on imaging at 4 - 6 weeks’ follow-up with symptom resolution | Symptom resolution and complete resolution of PFC on imaging at 3-month follow-up |
| Follow-up duration | NR | NR | 189 days | NR | 90 days |
| Number of studies | All patients (n = 281) | LAMS (n = 144) | LAMS + DPPS (n = 137) | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DPPS: double-pigtail plastic stent; LAMS: lumen-apposing metal stent; NS: not significant; PFC: pancreatic fluid collection; PP: pancreatic pseudocyst; PPI: proton pump inhibitor; SD: standard deviation; WOPN: walled-off pancreatic necrosis. | |||||
| Age, year | 4 | 52.1 ± 14.7 | 51 ± 13.8 | 53.5 ± 15.8 | NS (0.21) |
| Male gender | 5 | 64.4% (181/281) | 65% (78/120) | 68.4% (78/114) | NS (0.58) |
| PPI use | 2 | 49% (51/104) | % (25/45) | 44.1% (26/59) | NS (0.24) |
| PFC size, cm (mean ± SD) | 4 | 11.5 ± 4.8 | 12.2 ± 4.9 | 10.7 ± 4.5 | 0.02 |
| PFC type | 5 | ||||
| PP | 51.2% (144/281) | 47.5% (57/120) | 35.1% (40/114) | NS (0.06) | |
| WOPN | 44.5% (125/281) | 50% (60/120) | 57% (65/114) | NS (0.28) | |
| PFC etiology | 4 | ||||
| Alcohol | 31% (74/240) | 30% (37/123) | 31.6% (37/117) | NS (0.79) | |
| Gallstones | 33% (79/240) | 38.2% (47/123) | 27.4% (32/117) | NS (0.08) | |
| PFC location | 4 | ||||
| Head | 10% (23/224) | 8% (10/123) | 13% (13/101) | NS (0.25) | |
| Body | 60% (134/224) | 62% (76/123) | 57% (58/101) | NS (0.51) | |
| Tail | 18% (40/224) | 18% (22/123) | 18% (18/101) | NS (0.99) | |
| Drainage site | 4 | ||||
| Transgastric | 85% (181/213) | 89% (88/99) | 82% (93/114) | NS (0.13) | |
| Transduodenal | 11% (24/213) | 10% (10/99) | 12% (14/114) | NS (0.62) | |