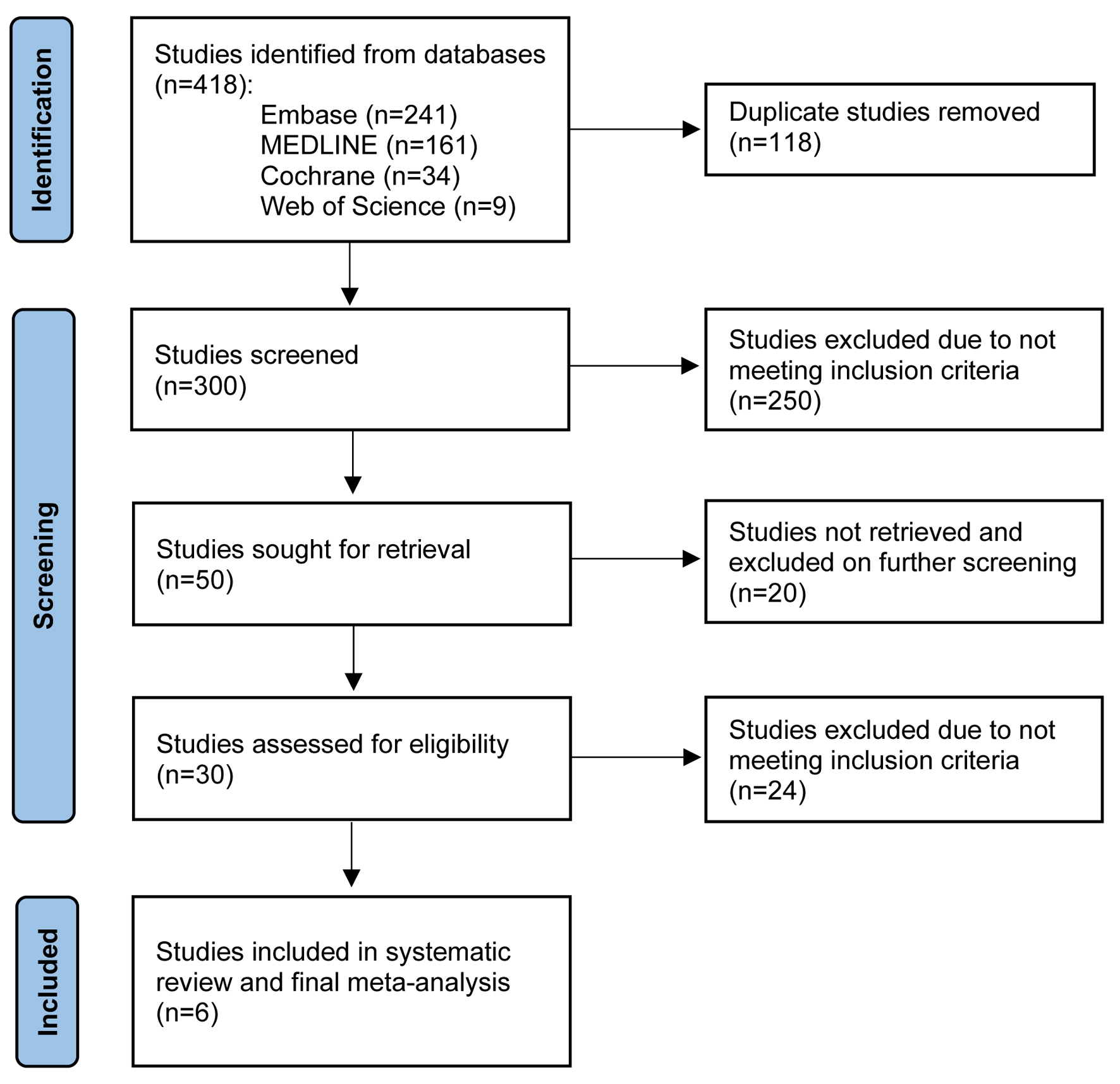
Figure 1. PRISMA flow diagram of the literature review process.
| Gastroenterology Research, ISSN 1918-2805 print, 1918-2813 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, Gastroenterol Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website https://www.gastrores.org |
Original Article
Volume 15, Number 6, December 2022, pages 325-333
Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt Outcomes in the Elderly Population: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Figures

Tables
| Studies | Clearly stated aim | Consecutive patient inclusion | Prospective data collection | Appropriate end-points | Unbiased study end-point assessment | Appropriate follow-up period | Attrition bias (< 5%) | Sample size | Adequate control group | Contemporary groups | Baseline equivalence of groups | Statistical analysis | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MINORS: Methodological Index for Non-Randomized Studies. | |||||||||||||
| Madhok et al [29] | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 19 |
| Saad et al [33] | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 19 |
| Kus et al [28] | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 18 |
| Adlakha and Russo [32] | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 19 |
| Stockhoff et al [31] | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 19 |
| Bisht et al [30] | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 19 |
| Study | Design | Demographics | Total number | Number of patients | MELD score | Indications for TIPS | Etiology of liver cirrhosis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| < 70 years | > 70 years | < 70 years | > 70 years | < 70 years | > 70 years | < 70 years | > 70 years | ||||
| MELD: Model for End-Stage Liver Disease; SD: standard deviation; TIPS: transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt; HCV: hepatitis C virus; IQR: interquartile range; NASH: non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. | |||||||||||
| Adlakha and Russo [32] | Retrospective | Median age (IQR) in 50 - 59 years group = 55 (± 4) years; Median age (IQR) in 70 - 84 years group = 73 (± 6) years | 100 | 50 | 50 | Median (IQR) = 11 (± 6) | Median (IQR) = 11 (± 5) | Ascites = 16 (32%); Variceal bleed = 45 (90%); Hydrothorax = 6 (12%) | Ascites = 26 (52%); Variceal bleed = 38 (76%); Hydrothorax = 2 (4%) | HCV = 26 (52%); Alcohol = 13 (26%); NAFLD = 5 (10%); Other | NAFLD = 28 (56%); Alcohol = 8 (16%); Other |
| Saad et al [33] | Retrospective | Mean age (SD) in < 70 years group = 53.9 (± 8.9), range 24 - 69 years; Mean age (SD) in ≥ 70 years group = 75 (± 4.3), range 70 - 89 years | 539 | 474 | 65 | Mean (SD) = 11 (± 4) | Mean (SD) = 11 (± 3) | Ascites/hydrothorax = 338 (71%); -Variceal bleed = 126 (27%) | Ascites/hydrothorax = 42 (65%); Variceal bleed = 22 (34%) | HCV = 178 (38%); Alcohol = 142 (30%); NASH = 41 (9%); Other | Alcohol = 15 (23%); NASH = 12 (19%); HCV = 7 (11%); Other |
| Kus et al [28] | Retrospective | Mean age in 50 - 59 years group = 55 years; Mean age in ≥ 70 years group = 74 years | 136 | 101 | 35 | Mean MELD-Na = 21.8 | Mean MELD-Na = 15.2 | Complications of portal hypertension | Not reported | ||
| Study | Design | Demographics | Total number | Number of patients | MELD score | Indications for TIPS | Etiology of liver cirrhosis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| < 65 years | > 65 years | < 65 years | > 65 years | < 65 years | > 65 years | < 65 years | > 65 years | ||||
| MELD: Model for End-Stage Liver Disease; SD: standard deviation; TIPS: transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt; HCV: hepatitis C virus; IQR: interquartile range; NASH: non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. | |||||||||||
| Madhok et al [29] | Retrospective | Mean age (SD) in < 65 years group = 57.75 (± 6.91) years; Mean age (SD) in ≥ 65 years group = 72.06 (± 5.98) years | 254 | 127 | 127 | Mean (SD) = 15.45 (± 4.95) | Mean (SD) = 14.87 (± 4.91) | Refractory ascites = 73 (57.4%); Variceal bleeding = 40 (31.5%) | Refractory ascites = 78 (61.4%); Variceal bleeding = 35 (27.1%) | Alcohol = 66 (52%); HCV = 49 (38.6%) | Alcohol = 78 (61.4%); HCV = 35 (27.6%) |
| Stockhoff et al [31] | Retrospective | Median age (IQR) in < 65 years group = 55 (49 - 59) years; Median age (IQR) in ≥ 65 years group = 70 (68 - 75) years | 160 | 107 | 53 | Median (IQR) = 12.7 (10.1 - 15.6) | Median (IQR) = 12.6 (10.8 - 15.9) | Refractory ascites | Viral = 12 (11%); Alcohol = 71 (66%); NASH = 6 (6%); Others = 22 (21%) | Viral = 7 (13%); Alcohol = 26 (49%); NASH = 6 (11%); Others = 14 (27%) | |
| Bisht et al [30] | Retrospective | Mean age (SD) in ≤ 65 years group = 53 (± 9) years; Mean age (SD) in > 65 years group = 70 (± 5) years | 402 | 300 | 102 | Mean (SD) = 17.9 (± 8.07) | Mean (SD) = 16.2 (± 5.76) | Acute bleeding; Ascites; Hydrothorax | Alcohol; Viral hepatitis; NASH | ||
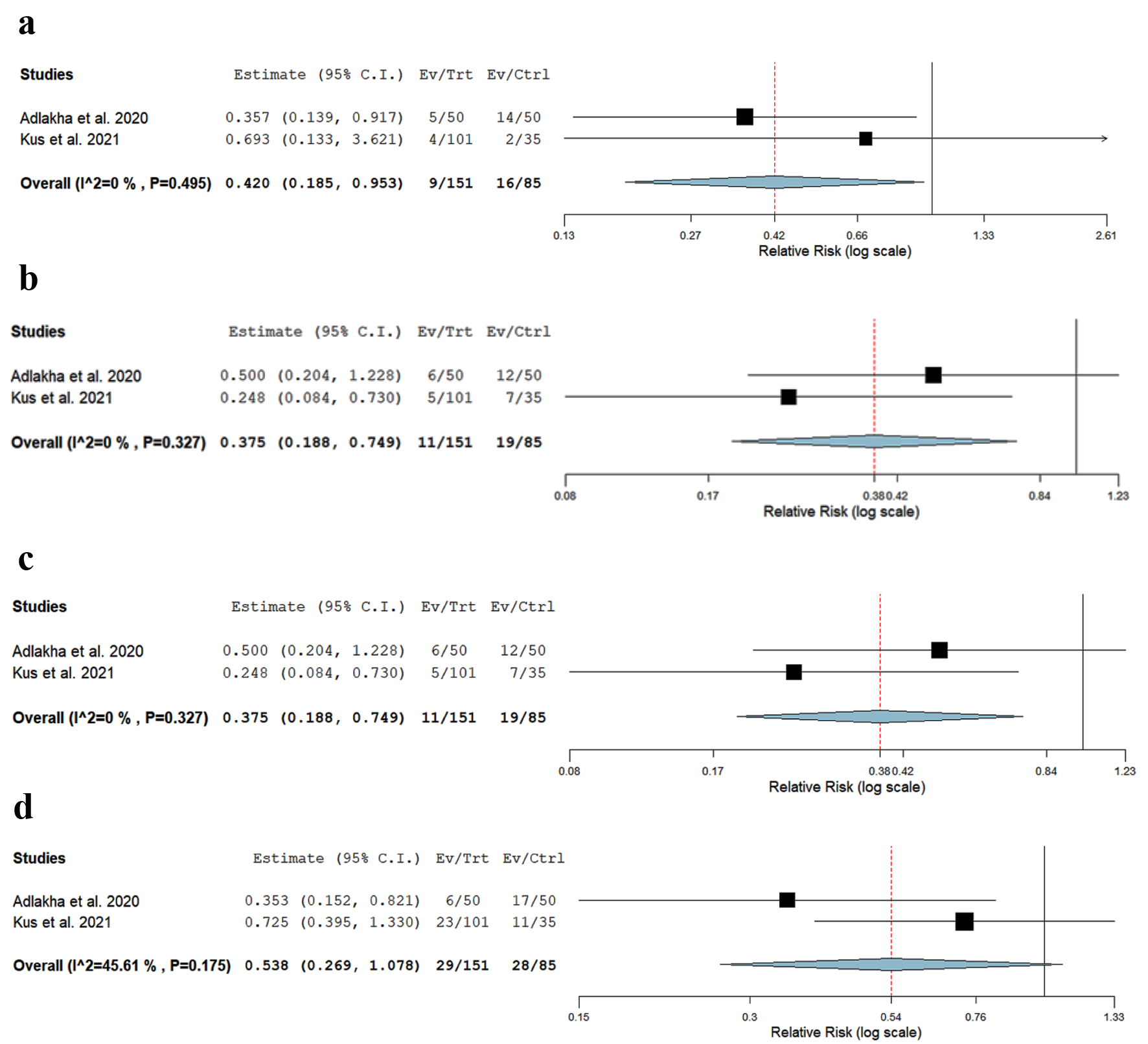
| Outcome | Relative risk | 95% confidence interval | P-value | I2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HE: hepatic encephalopathy; TIPS: transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt. | ||||
| Post-TIPS HE | 0.42 | 0.185 - 0.953 | 0.03 | 49% |
| 30-day mortality | 0.37 | 0.188 - 0.74 | 0.005 | 0% |
| 90-day mortality | 0.35 | 0.24 - 0.49 | 0.001 | 0% |
| 30-day readmission due to HE | 0.538 | 0.269 - 1.078 | 0.08 | 45% |
| Outcome | Relative risk | 95% confidence interval | P | I2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HE: hepatic encephalopathy; TIPS: transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt. | ||||
| Post-TIPS HE | 0.923 | 0.632 - 1.43 | 0.680 | 34% |
| 30-day mortality | 0.87 | 0.35 - 2.1 | 0.76 | 81% |
| 90-day mortality | 0.67 | 0.413 - 1.1 | 0.115 | 63% |
| 30-day readmission due to HE | 0.907 | 0.75 - 1.095 | 0.308 | 0% |