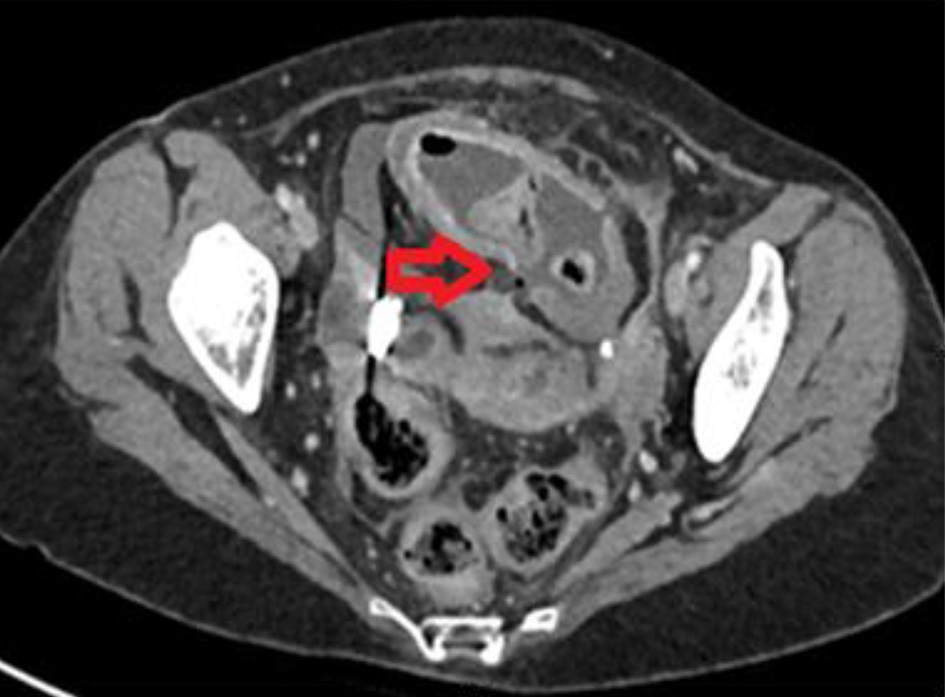
Figure 1. Axial image of contrast-enhanced computed tomography of abdomen with an active flare-up of Crohn’s disease showing a localized perforation at the distal ileum (horizontal red arrow).
| Gastroenterology Research, ISSN 1918-2805 print, 1918-2813 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, Gastroenterol Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website https://www.gastrores.org |
Case Report
Volume 15, Number 2, April 2022, pages 100-105
Extensive Aortic Thrombosis and Renal Infarction in Association With an Active Flare-Up of Crohn’s Disease
Figures

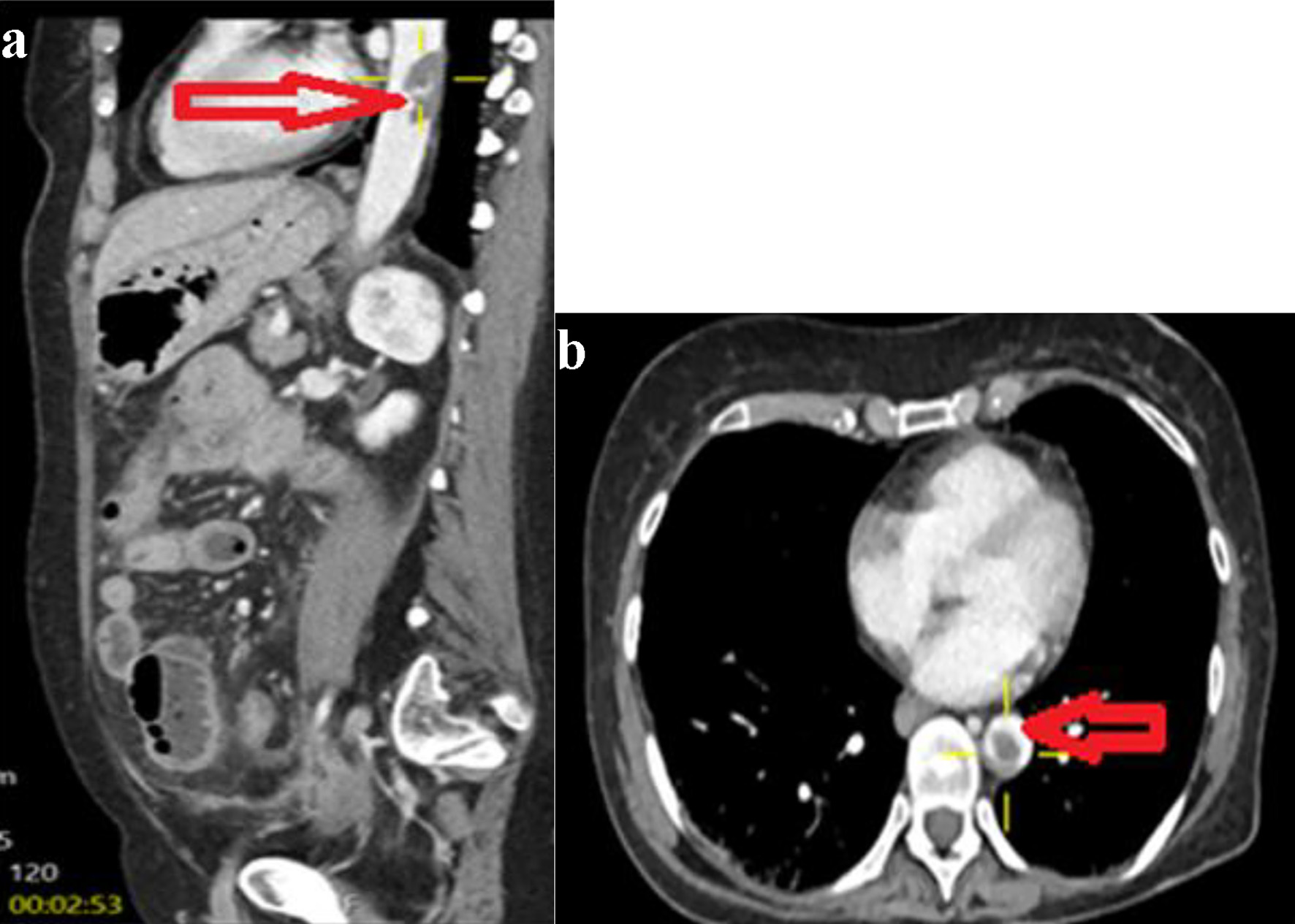
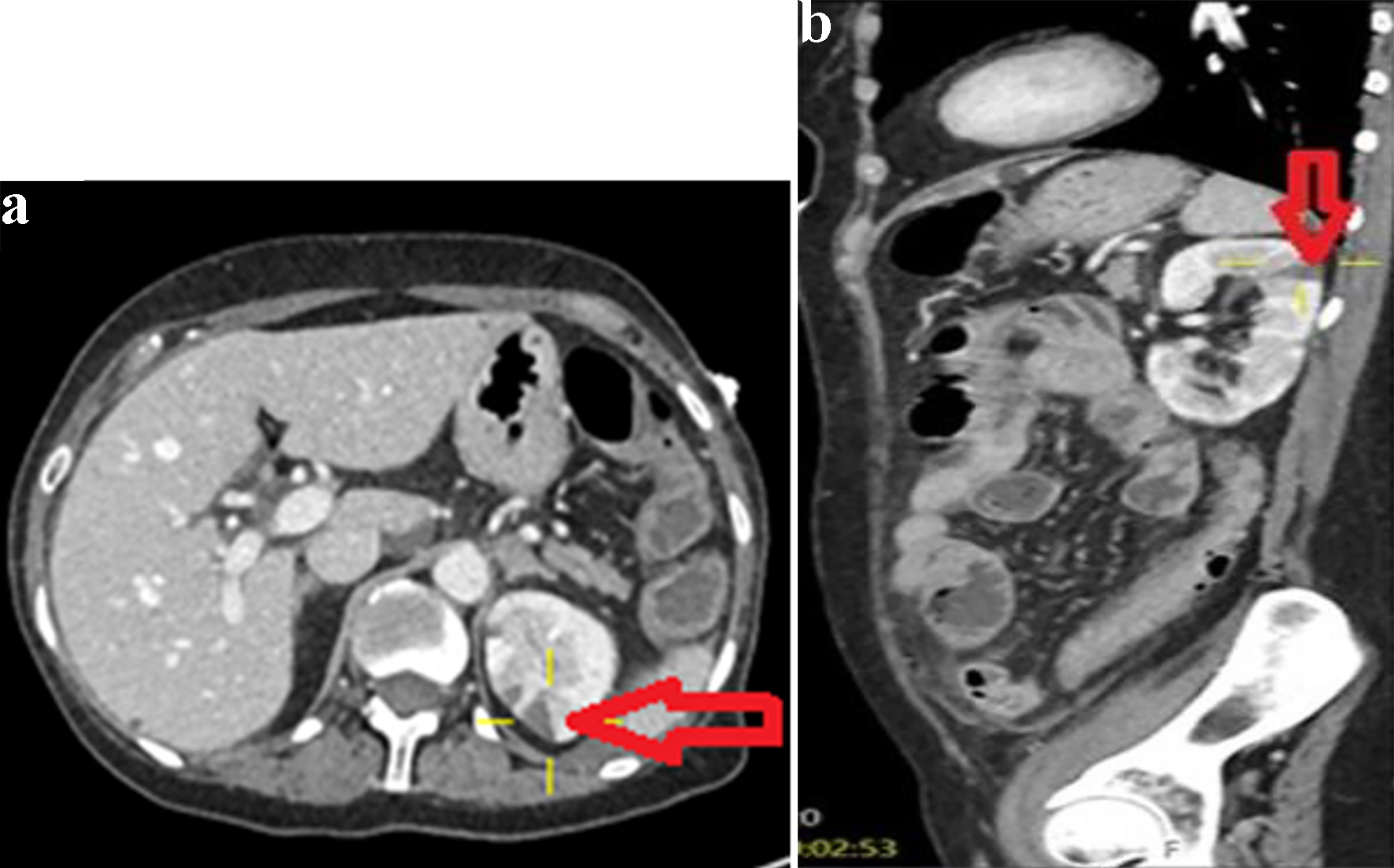
Table
| Authors/publication year | Patient’s age (years)/gender | IBD/activity status | Aortic thrombosis site/embolus site/clinical consequences | Management | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IBD: inflammatory bowel disease; CD: Crohn’s disease; IMA: inferior mesenteric artery; SMA: superior mesenteric artery; UC: ulcerative colitis; IR: interventional radiology. | |||||
| Novacek et al, 2004 [3] | 36/female | UC/active | Distal abdominal aorta with occlusion of the origin of IMA with distal colonic spare due to SMA collaterals | Medical management of UC. Heparin anticoagulation followed by a direct oral anticoagulant | Good outcome with thrombus resolution |
| Novacek et al, 2004 [3] | 41/female | CD/active | Distal abdominal aorta with left iliac embolization and acute left lower extremity ischemia | Thrombectomy with heparin anticoagulation followed by a coumarin derivative | Left leg amputation. Thrombus resolution |
| Khan et al, 2009 [5] | 41/male | CD/active (post-operative) | Extensive proximal abdominal aorta occluding the ostia of celiac, SMA, and left renal artery with left renal infarction and diffuse small bowel and colonic ischemia. Aortic arch thrombus | Heparin anticoagulation with failed IR attempts to cannulate blocked visceral and mesenteric vessels | Death from visceral ischemia and sepsis |
| Kok et al, 2012 [6] | 48/female | UC/active | Large proximal abdominal aorta thrombus with splenic artery embolization and splenic infarction | Heparin anticoagulation followed by warfarin | Good outcome |
| Talbot et al,1986 [7] | 47/male | CD/active | Infra-renal abdominal aorta with colonic ischemia | Unspecified | Death due to colonic ischemia |
| Perler et al, 1991 [8] | 34/female | CD/unspecified | Infra-renal abdominal aorta with distal embolization | Thrombo-embolectomy with heparin anticoagulation | Good outcome |
| Novotny et al, 1992 [9] | 35/female | UC/unspecified | Aorto-iliac thrombosis | Unspecified | Leg amputation |
| Novotny et al, 1992 [9] | 22/female | UC/unspecified | Aorto-bifemoral thrombosis | Unspecified | Unspecified |
| Novotny et al, 1992 [9] | 34/female | UC/unspecified | Aorto-iliac thrombosis | Thrombectomy with heparin anticoagulation | Good outcome |
| Hahn et al, 1999 [10] | 34/male | CD/active (post-operative) | Infra-renal abdominal aorta with distal embolization resulting in blue toe syndrome | Lower extremity embolectomy with heparin anticoagulation followed by warfarin | Good outcome with thrombus resolution |
| Hahn et al, 1999 [10] | 74/male | CD/active (post-operative) | Peripancreatic aorta with severe pancreatitis and distal embolization with blue toe syndrome | Heparin anticoagulation followed by warfarin | Toe amputation. Thrombus resolution |
| Lehmann et al, 2001 [11] | 50/female | CD/active | Infra-renal abdominal aorta with distal embolization to the right popliteal artery resulting in acute lower extremity ischemia | Thrombolysis with urokinase then lower extremity embolectomy with heparin anticoagulation followed by warfarin | Good outcome |
| Szychta et al, 2001 [12] | 42/female | UC/active | Infra-renal abdominal aorta with right renal artery embolization with a right renal infarction | Renal thrombectomy with heparin anticoagulation followed by a coumarin derivative | Good outcome |
| Grothues et al, 2002 [13] | 49/male | UC/active | Aortic arch thrombus in a critically ill UC patient with systemic aspergillosis infection | UC management with antifungal therapy | Death from systemic sepsis |
| Delay et al, 2014 [14] | 33/female | CD/quiescent | Extensive infra-renal abdominal aortic thrombosis extending to both iliac arteries. Extensive workup negative for underlying etiology | The initial IR attempt failed. Aorto-bifemoral bypass with heparin anticoagulation followed by life-long aspirin | Good outcome. Histology showed non-specific occlusive aortitis. |
| Singh et al, 2012 [15] | 28/female | CD/active | Aortoiliac thrombosis. Saddle aortic thrombus at aortic bifurcation extending to both common iliac | Bilateral aorto-iliofemoral bypass surgery. Heparin anticoagulation followed by warfarin for six months | Good outcome with complete thrombus resolution |
| Elder et al, 2010 [16] | 40/male | UC/active | Aortic arch thrombus with distal lower extremity embolization resulting in acute ischemia of the left lower extremity | Limb salvage with embolectomy. Anticoagulation with heparin | Good outcome |
| Leblanc et al, 2011 [17] | 25/female | CD/active | Abdominal aorta thrombus with distal embolization to the left popliteal artery and acute ischemia of the left lower extremity | Embolectomy and revascularization surgery with heparin anticoagulation | Good outcome |
| Leblanc et al, 2011 [17] | 24/female | CD/active | Abdominal aorta thrombus extending into IMA with distal colon sparing by multiple SMA collaterals | Heparin anticoagulation | Good outcome with complete thrombus resolution |
| Sinapi et al, 2010 [18] | 47/male | UC/active | Distal descending thoracic aorta thrombus and aortic arch thrombus | Heparin anticoagulation and medical management for UC | Good outcome |
| Stordiau et al, 2011 [19] | 56/male | CD/active | Aortic arch thrombus with distal embolization to the left subclavian and axillary arteries resulting in acute ischemia of the left upper extremity | Embolectomy, followed by a series of revascularization surgeries and eventually upper extremity amputation. Bowel resection for perforated ileal disease | Amputation of left upper extremity |