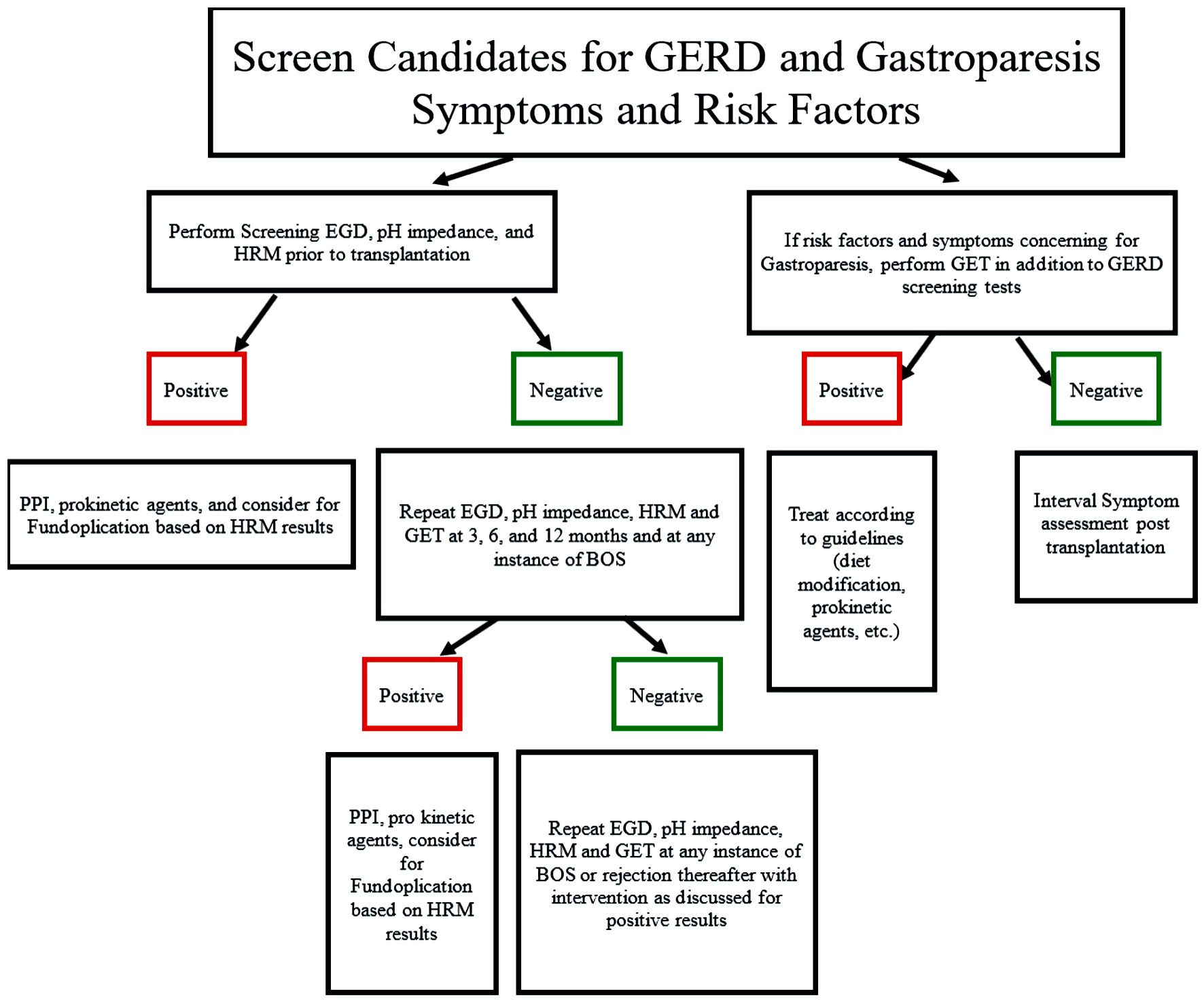
Figure 1. Algorithm for screening, monitoring, and treatment of lung transplant recipients for reflux and gastroparesis. GERD: gastroesophageal reflux disease; EGD: esophagogastroduodenoscopy; HRM: high-resolution manometry; BOS: bronchitis obliterans syndrome.