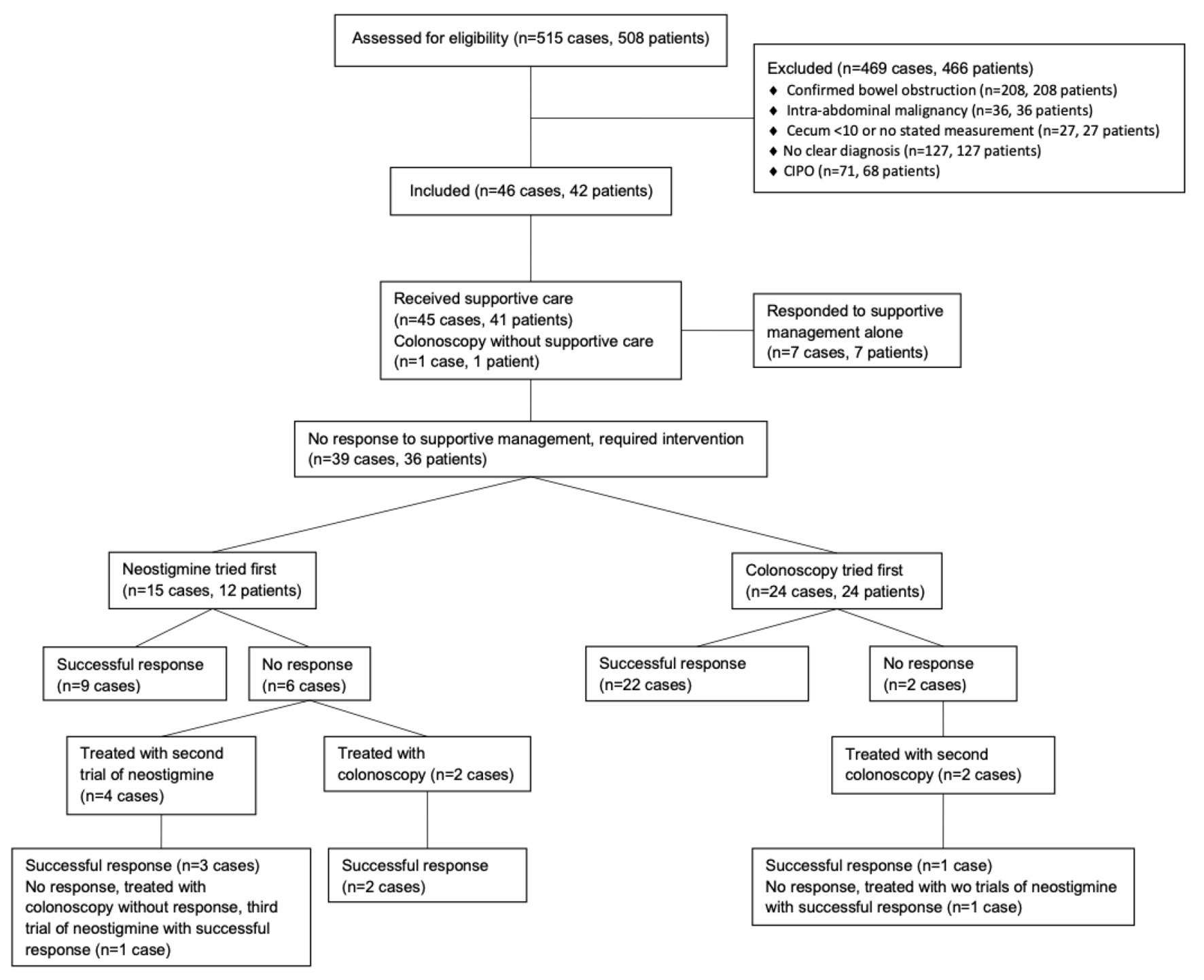
Figure 1. Patient flow and treatments for management of ACPO. A total of 515 cases in 508 patients (as some patients had repeat hospitalizations for ACPO) were initially identified. Some excluded patients did receive neostigmine or underwent colonoscopy during their hospitalization. Excluded patients receiving neostigmine: intra-abdominal malignancy (n = 1), cecum < 10 cm or no stated measurement (n = 4 in 4 patients), CIPO (n = 5 in 3 patients) for a total of 10 episodes in 8 patients. Excluded patients undergoing colonoscopy: confirmed bowel obstruction (n = 3 in 3 patients), intra-abdominal malignancy (n = 2 in 2 patients), cecum < 10 cm or no stated measurement (n = 11 in 11 patients), CIPO (n = 7 in 4 patients) for a total of 23 episodes in 20 patients. Among included cases (n = 46 in 42 patients), all but one patient who underwent a colonoscopy initially received supportive care. Because this patient underwent colonoscopy, they were included in the group of cases that received colonoscopy first. In the group of cases that received supportive care (n = 45 in 41 patients), there was one patient who responded to supportive care alone during one hospitalization and required neostigmine during a second hospitalization. This patient and their demographic information at time of hospitalization was included in both the group of cases receiving neostigmine first as well as in the group of cases responding to supportive care alone. ACPO: acute colonic pseudo-obstruction.