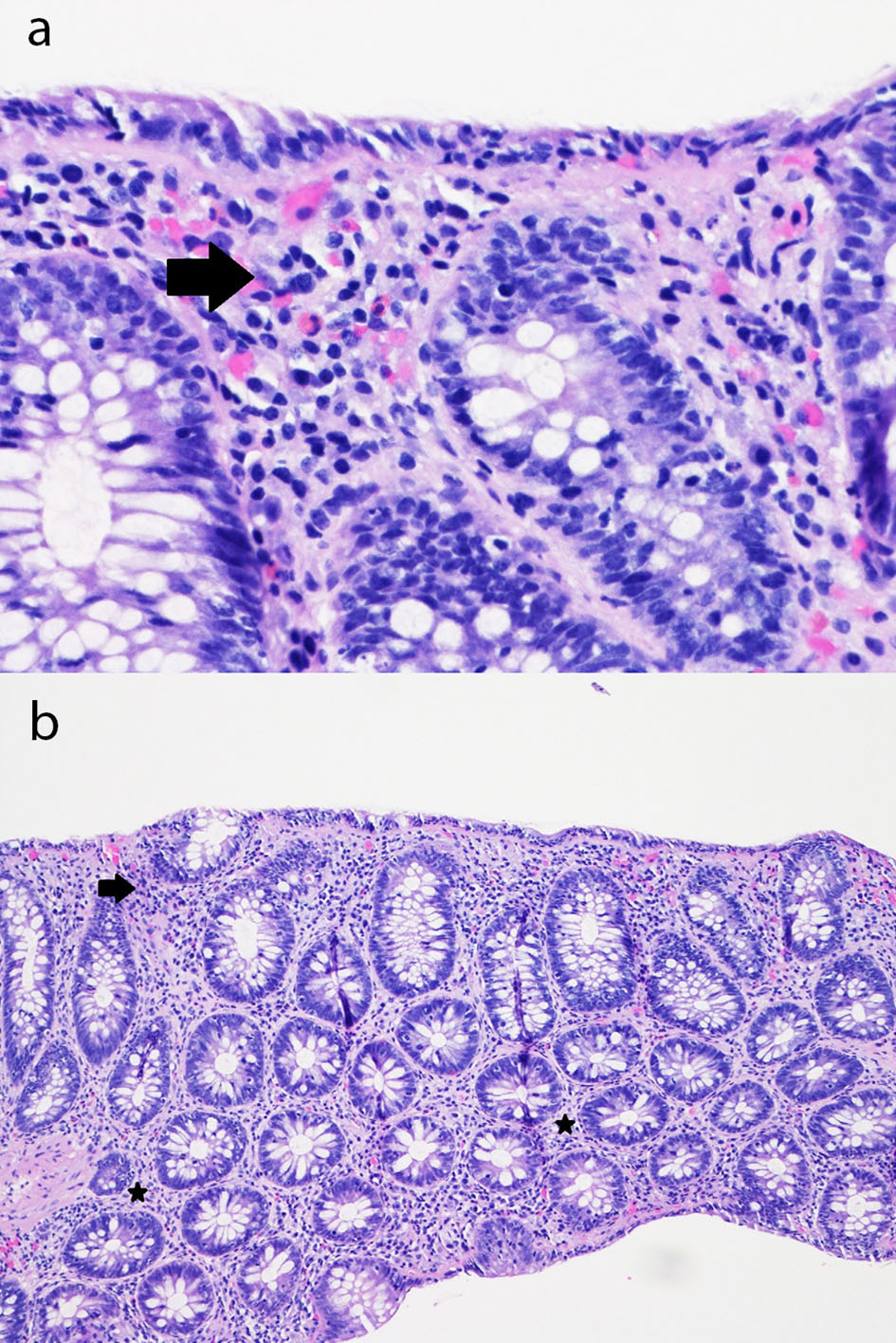
Figure 1. (a) Sigmoid colon mucosa (hematoxylin and eosin, × 400) showing chronic inflammation in the superficial portion of the lamina propria and mild intraepithelial lymphocytosis with surface epithelial injury (lymphocytic colitis-like injury) with rare acute inflammatory cells in the lamina propria and surface epithelium (arrow). (b) Sigmoid colon mucosa (hematoxylin and eosin, × 100) showing chronic inflammation in the superficial portion of the lamina propria and mild intraepithelial lymphocytosis with surface epithelial injury (lymphocytic colitis-like injury) with rare acute inflammatory cells in the lamina propria (stars) and surface epithelium (arrow).
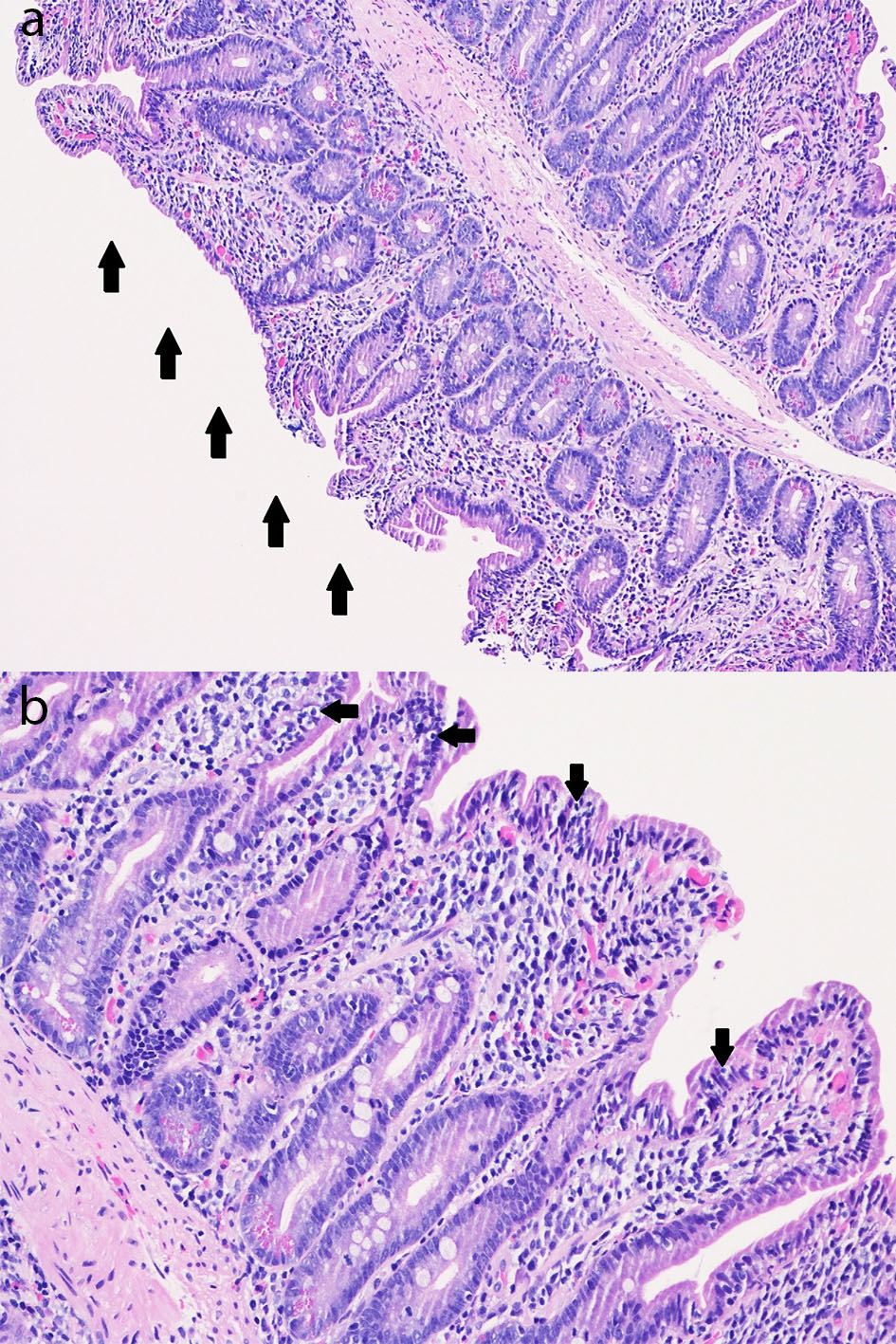
Figure 2. (a) Duodenal mucosa (hematoxylin and eosin, × 100) with subtotal villous blunting (arrows) with chronic duodenitis with an increase in chronic inflammation of the lamina propria consisting of a mixed population of lymphocytes, plasma cells, and eosinophils as well as an increase in intraepithelial lymphocytes (intraepithelial lymphocytosis). (b) Duodenal mucosa (hematoxylin and eosin, × 200) with subtotal villous blunting with chronic duodenitis with an increase in chronic inflammation of the lamina propria consisting of a mixed population of lymphocytes, plasma cells, and eosinophils as well as an increase in intraepithelial lymphocytes (intraepithelial lymphocytosis; arrows).

