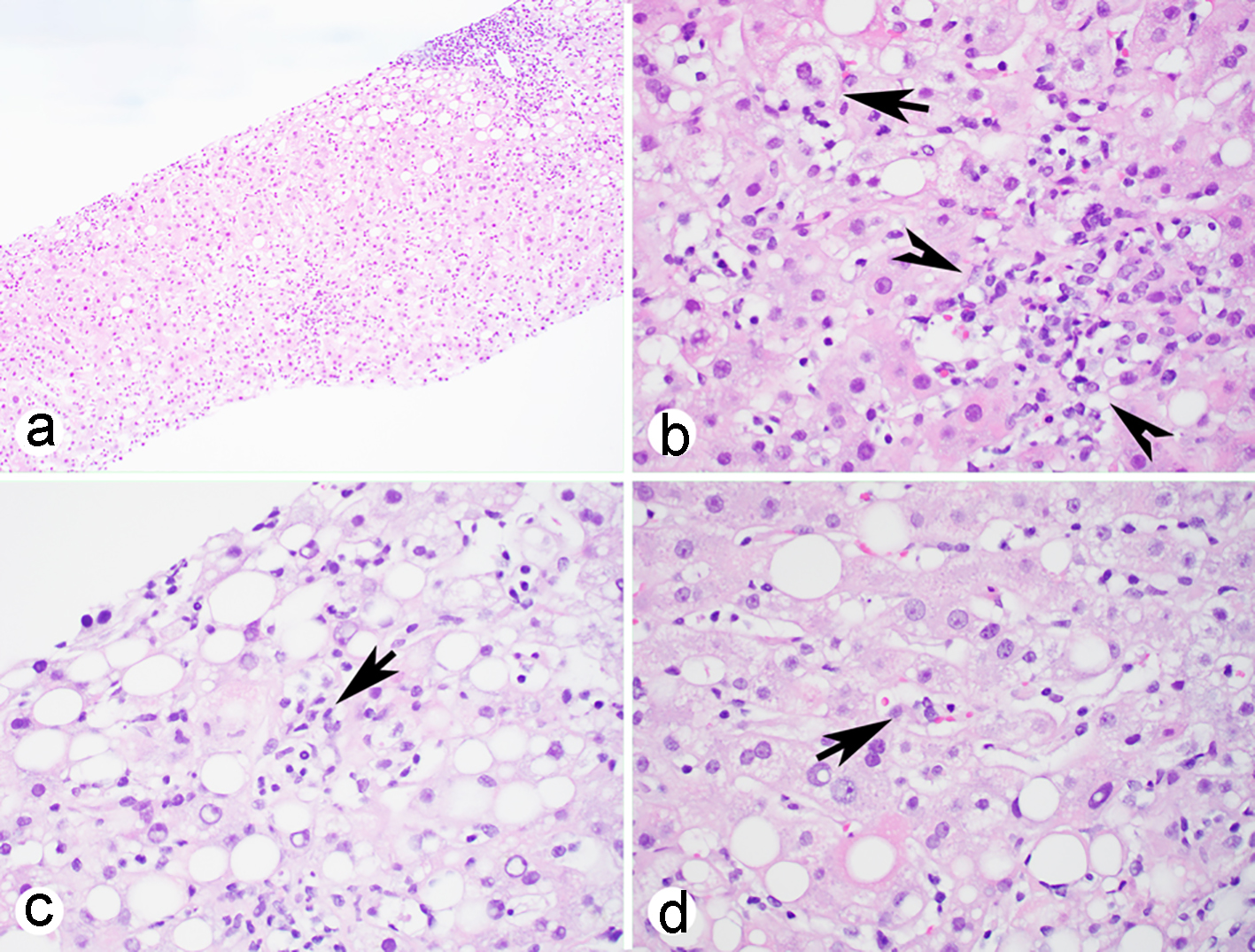
Figure 1. Liver biopsy shows acute hepatitis with portal inflammation (a), lobular confluent necrosis (b, arrow heads), mild steatosis and occasional ballooning hepatocytes (b, arrow) and atypical lymphoid cells in the sinusoids (c, arrow) with phagocytosis (d, arrow) (H&E stain: a, × 100, b-d, × 400). H&E: hematoxylin-eosin.
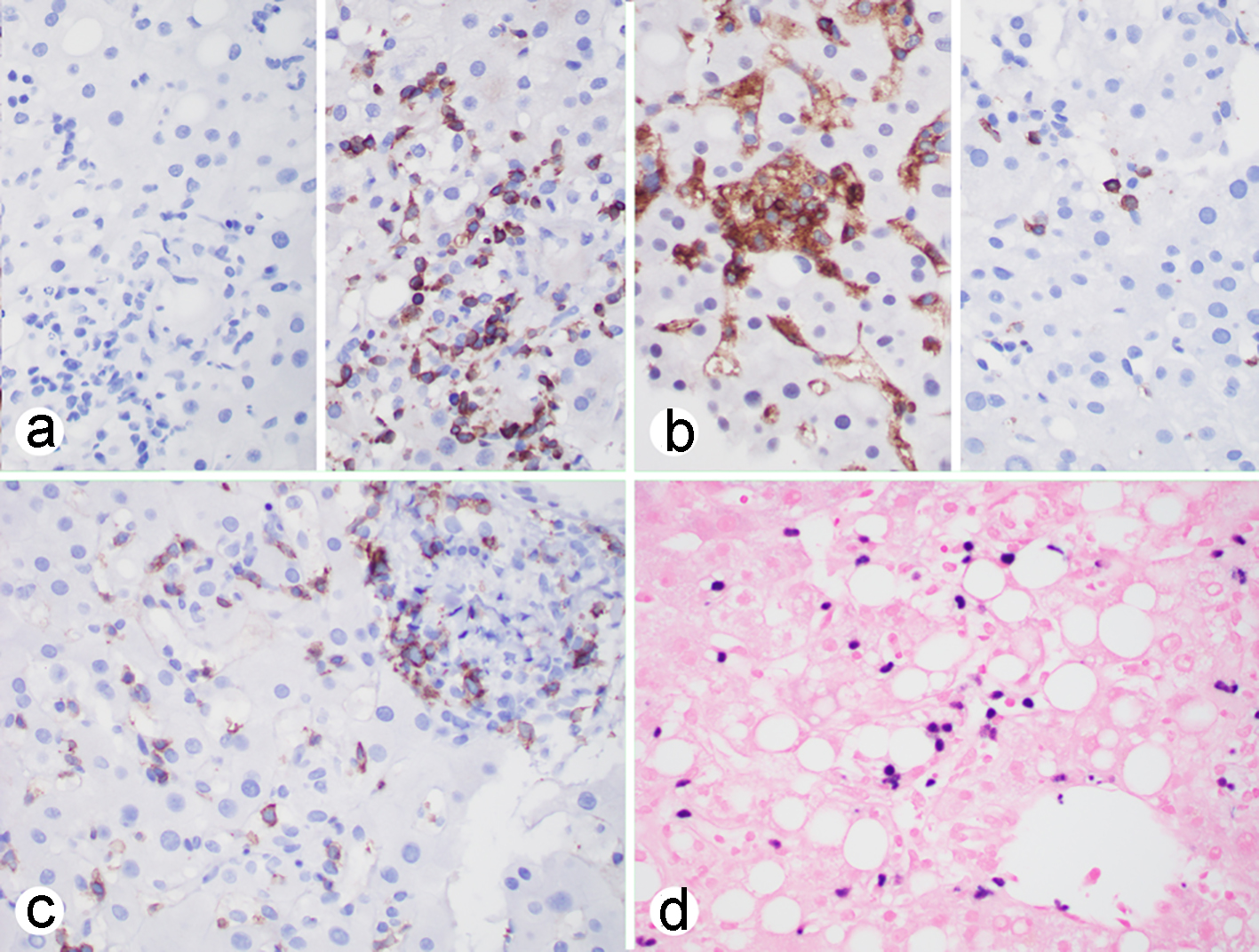
Figure 2. EBV-associated hepatitis: (a-c) immunohistochemistry showing that the atypical lymphoid cells are negative for CD20 (a, left), positive for CD3 (a, right), CD4 (b, left), rarely positive for CD8 (b, right), positive for CD56 (c); (d) EBER in situ hybridization showing that individual lymphoid cells are positive. (a-d, × 400). EBV: Epstein-Barr virus; EBER: Epstein-Barr virus encoding RNA.

