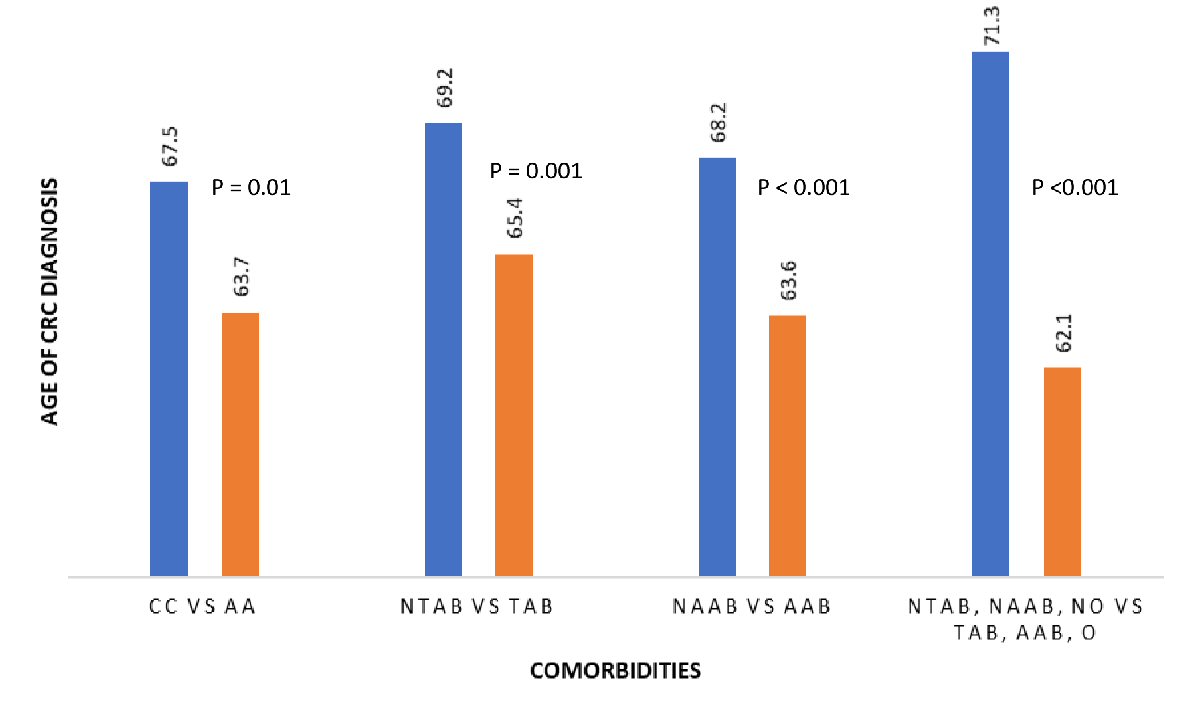
Figure 1. Relationship between race and comorbidity and age of CRC diagnosis. CC: Caucasian; AA: African American; NTAB: non-tobacco abuse; TAB: tobacco abuse; NAAB: non-alcohol abuse; AAB: alcohol abuse; NO: non-obese; O: obese; CRC: colorectal cancer.