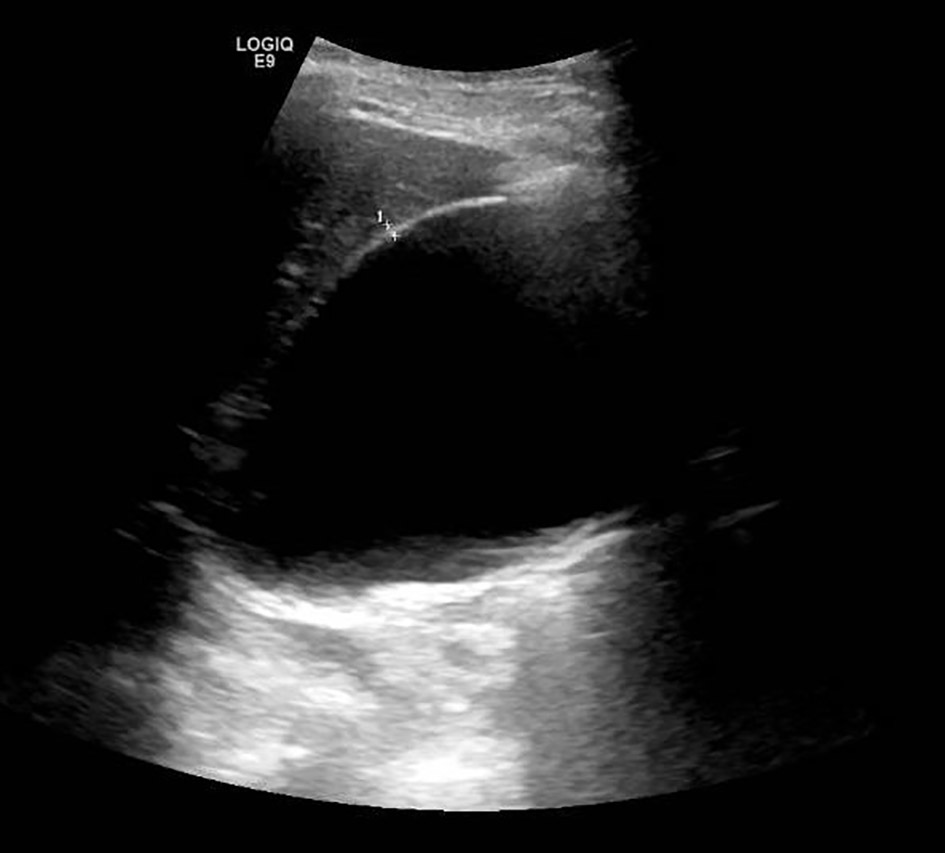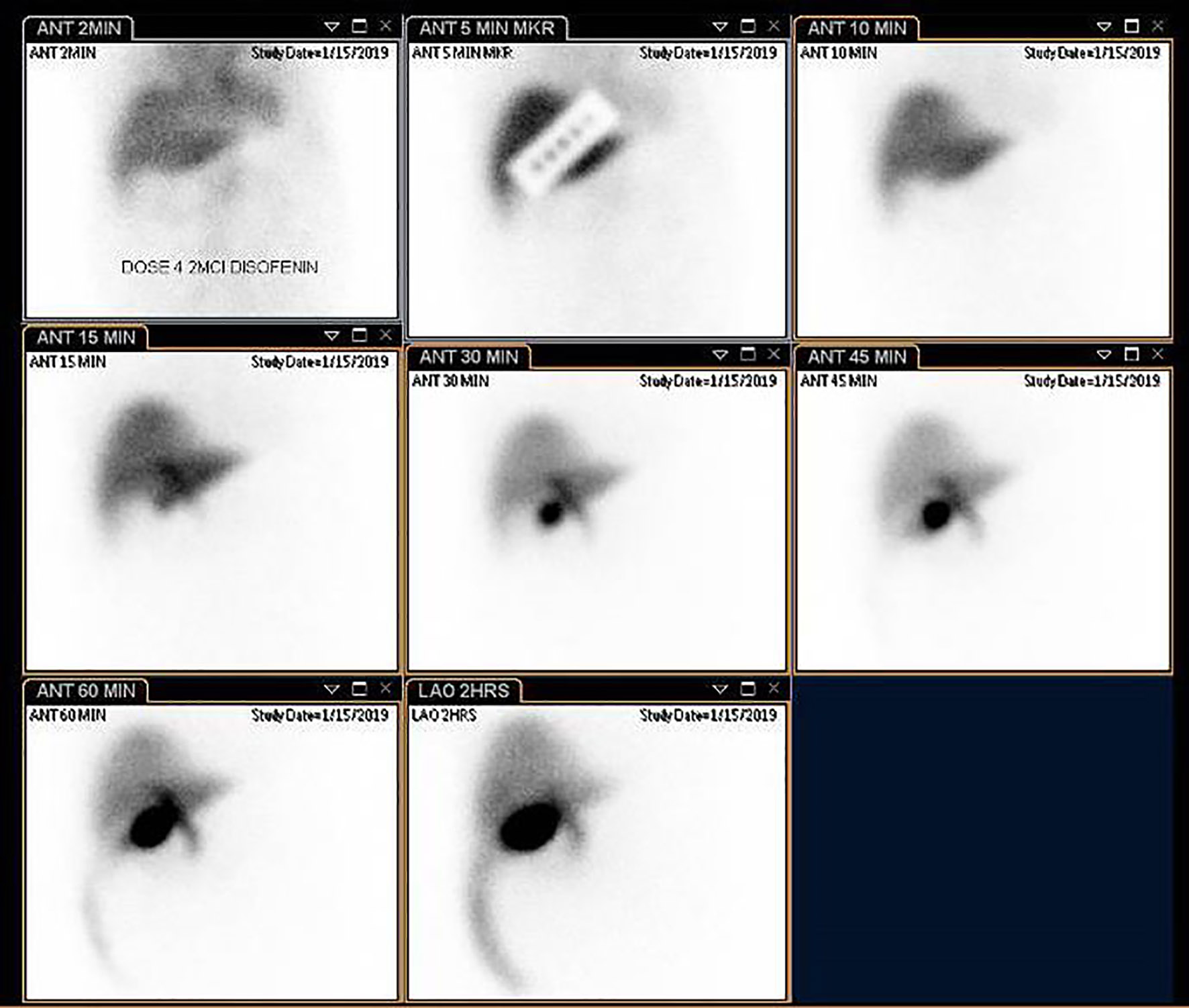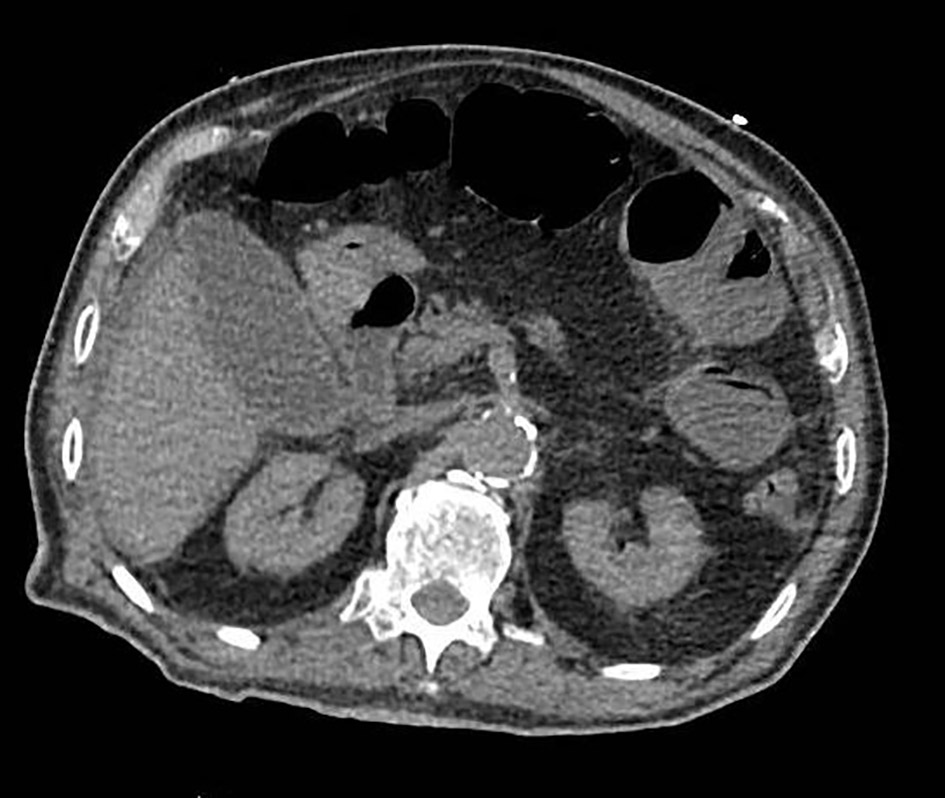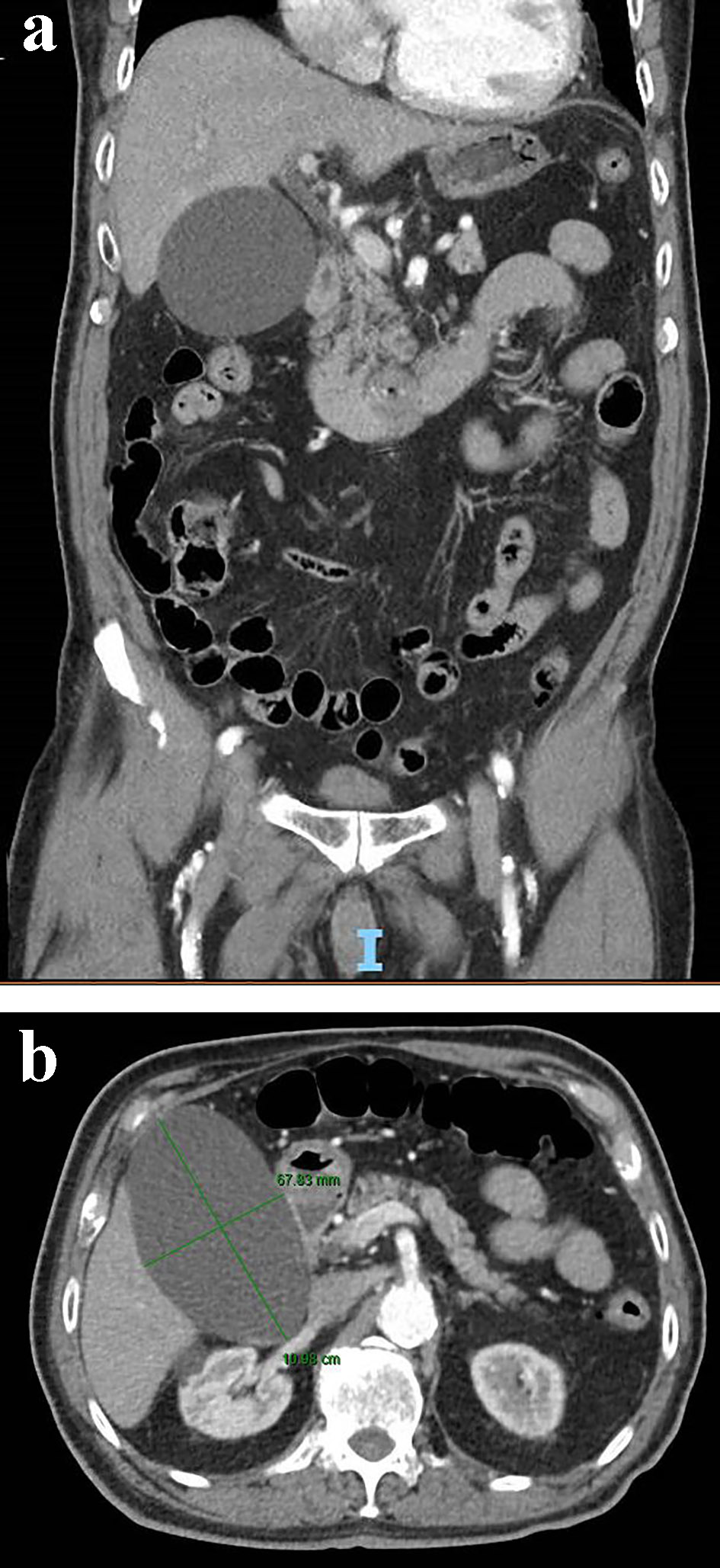
Figure 1. Coronal (a) and axial view (b) of a contrast-enhanced abdominal CT scan showing an acalculous hydropic gallbladder. CT: computed tomography.
| Gastroenterology Research, ISSN 1918-2805 print, 1918-2813 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, Gastroenterol Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.gastrores.org |
Case Report
Volume 12, Number 6, December 2019, pages 315-319
Spontaneous Perforation of an Acalculous Hydropic Gallbladder in a Diabetic Patient With Neuropathy: An Underdiagnosed Entity
Figures