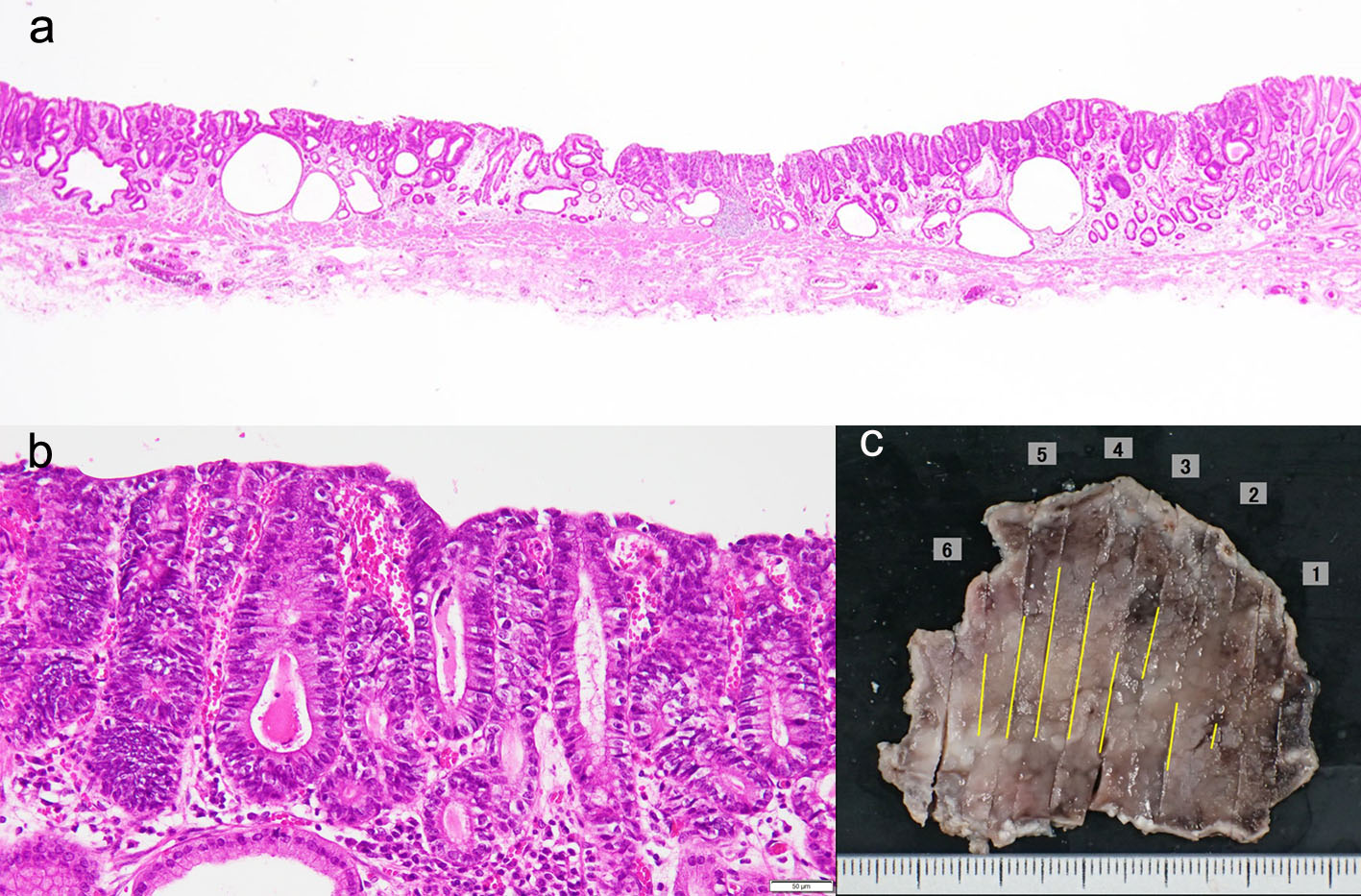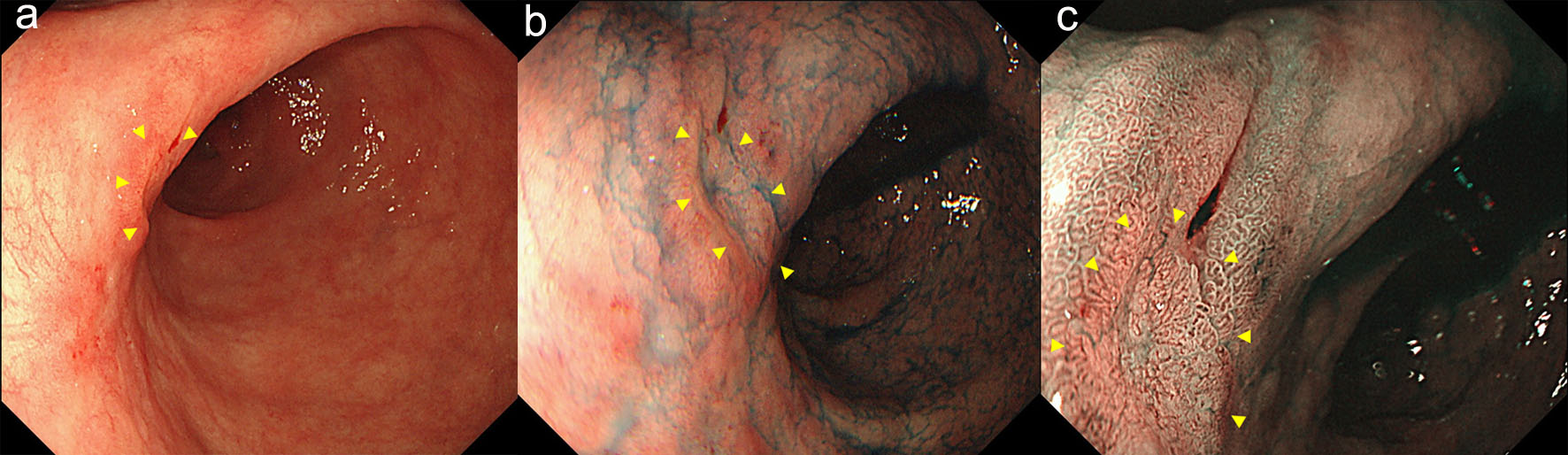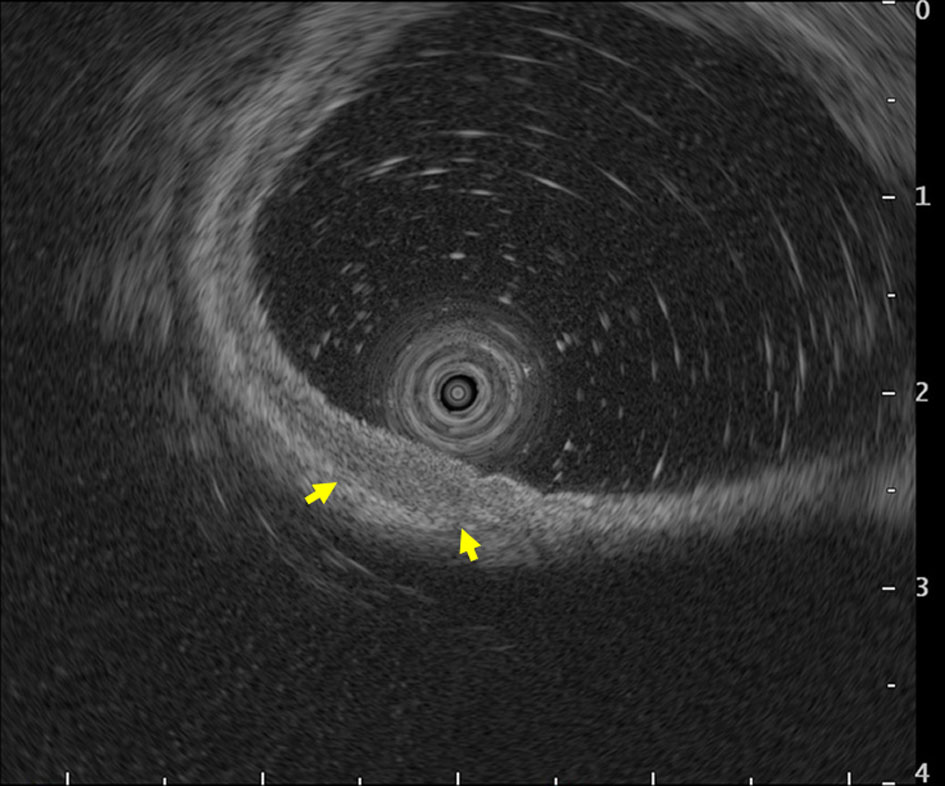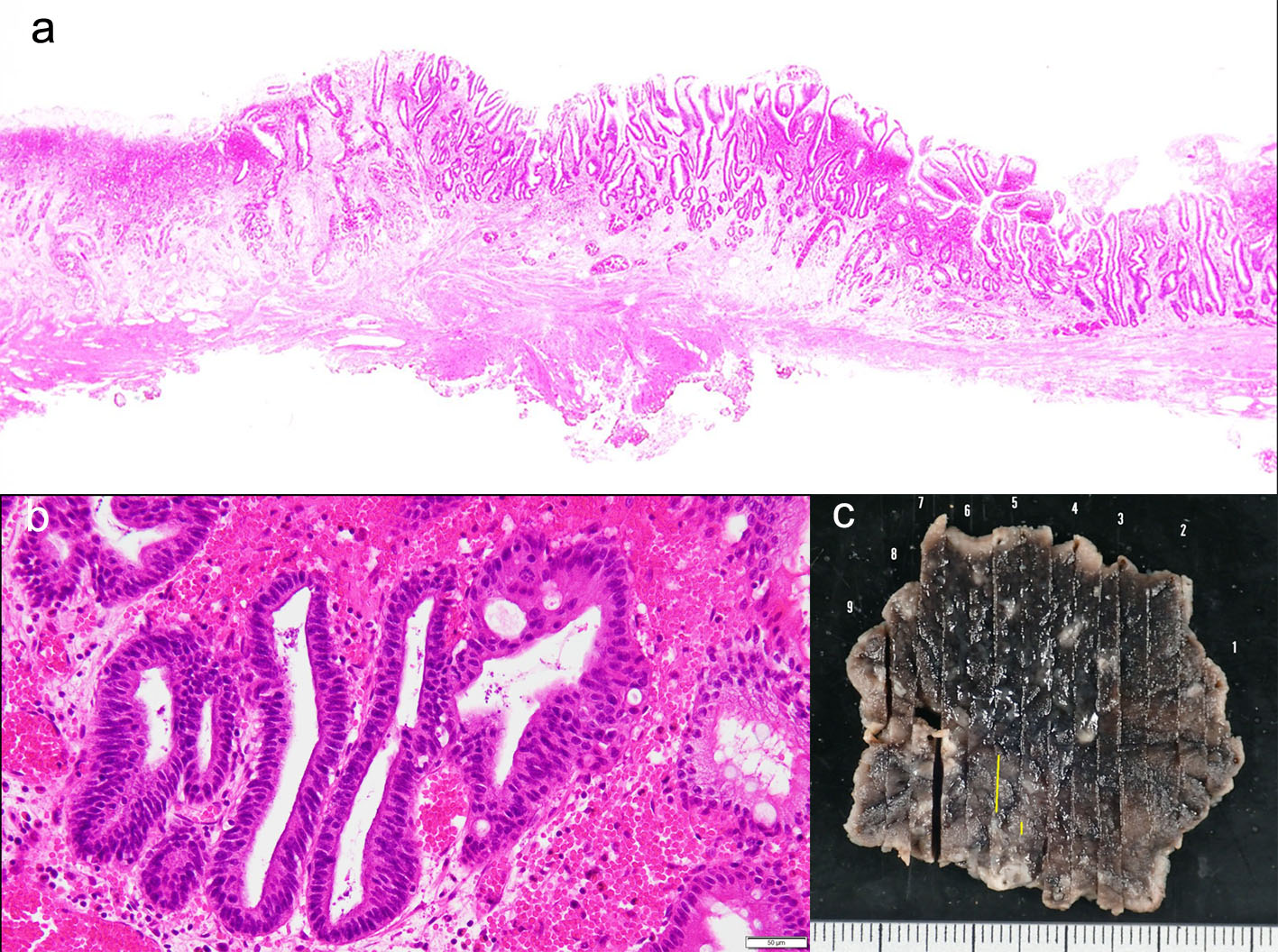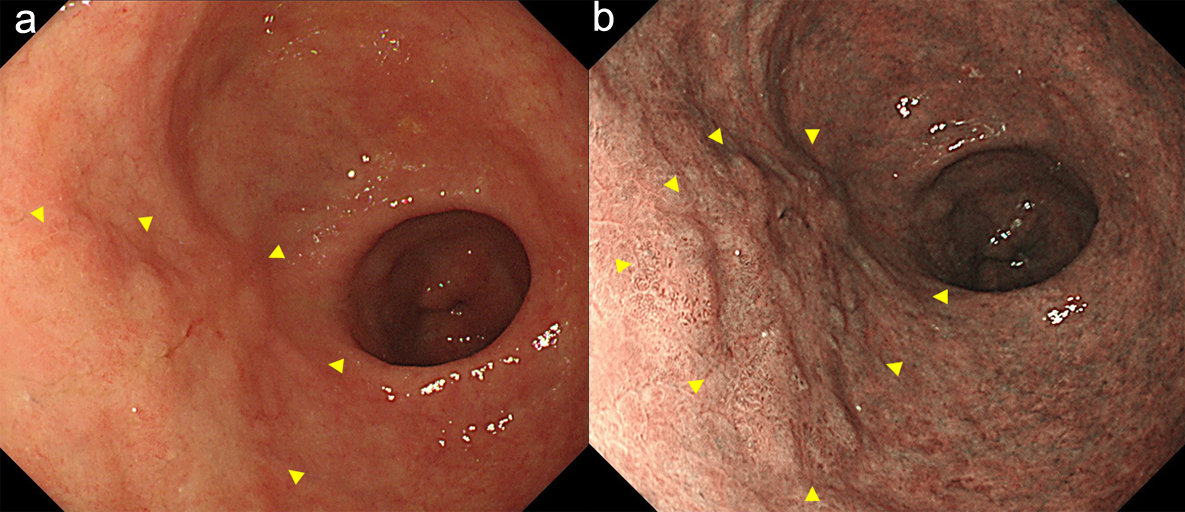
Figure 1. Endoscopy showed a type 0-IIa early gastric cancer in the anterior wall of the antrum (arrow heads). (a) white light image, and (b) NBI image. NBI: narrow band imaging (c).
| Gastroenterology Research, ISSN 1918-2805 print, 1918-2813 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, Gastroenterol Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.gastrores.org |
Case Report
Volume 12, Number 2, April 2019, pages 103-106
A Rare Case of Local Recurrence Following Curative Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection of Intramucosal Differentiated-Type Gastric Cancer
Figures