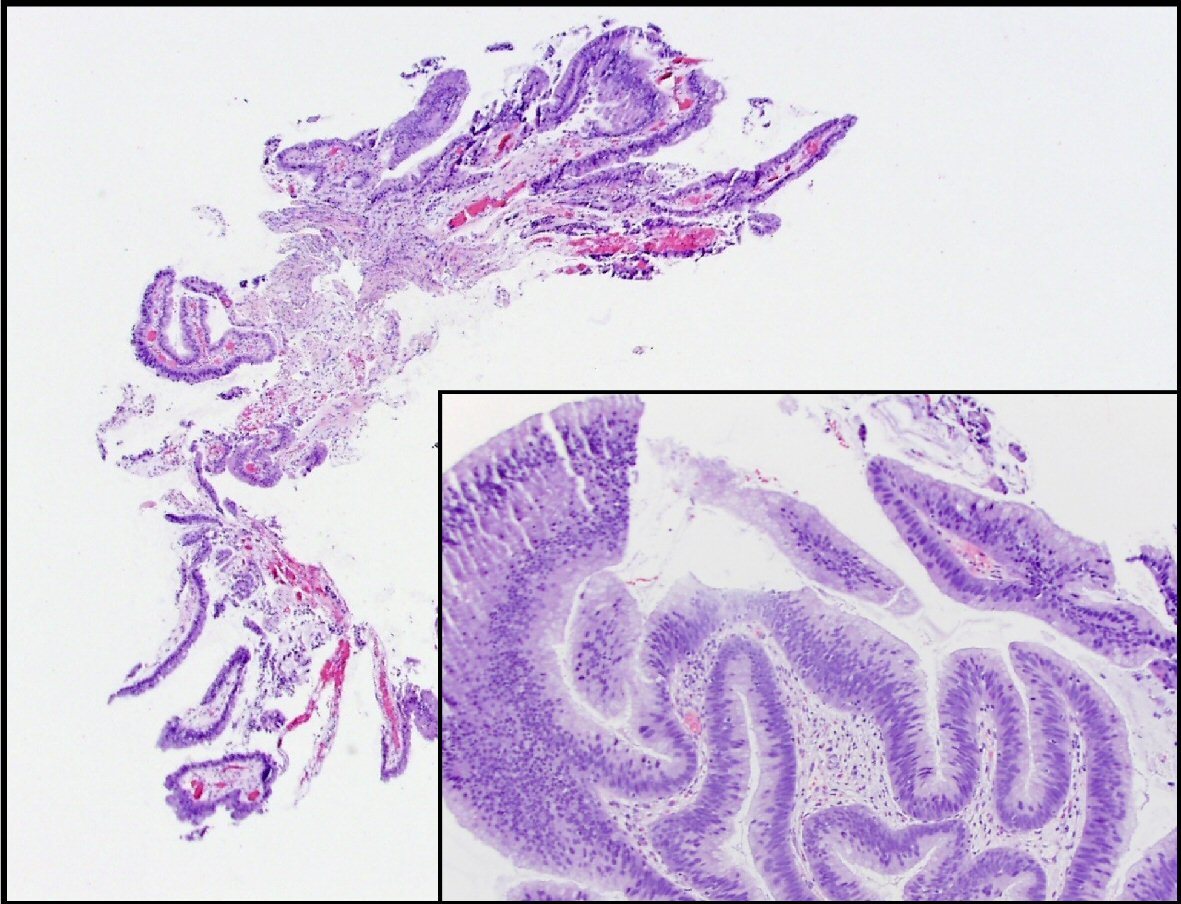
Figure 1. This is a section of the pancreatic duct biopsy showing mucinous epithelium with a papillary architecture. The higher power view (inset) shows areas with nuclear hyperchromasia and crowding, consistent with intermediate grade dysplasia.
| Gastroenterology Research, ISSN 1918-2805 print, 1918-2813 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, Gastroenterol Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.gastrores.org |
Case Report
Volume 12, Number 1, February 2019, pages 43-47
Formation of Pancreatoduodenal Fistula in Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm of the Pancreas Decreased the Frequency of Recurrent Pancreatitis
Figures

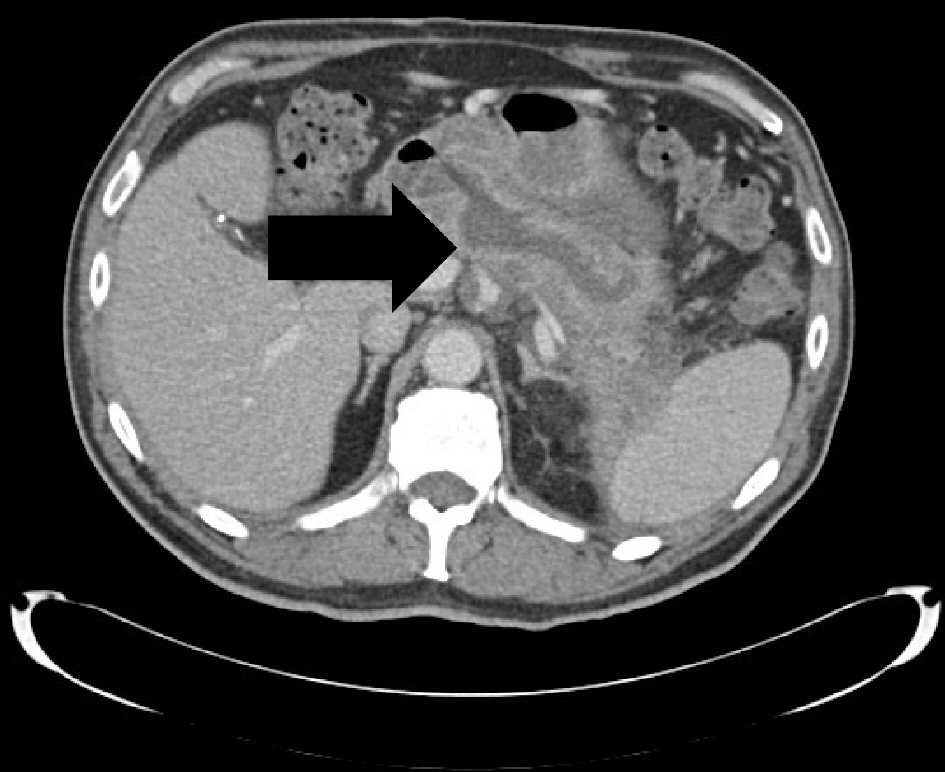
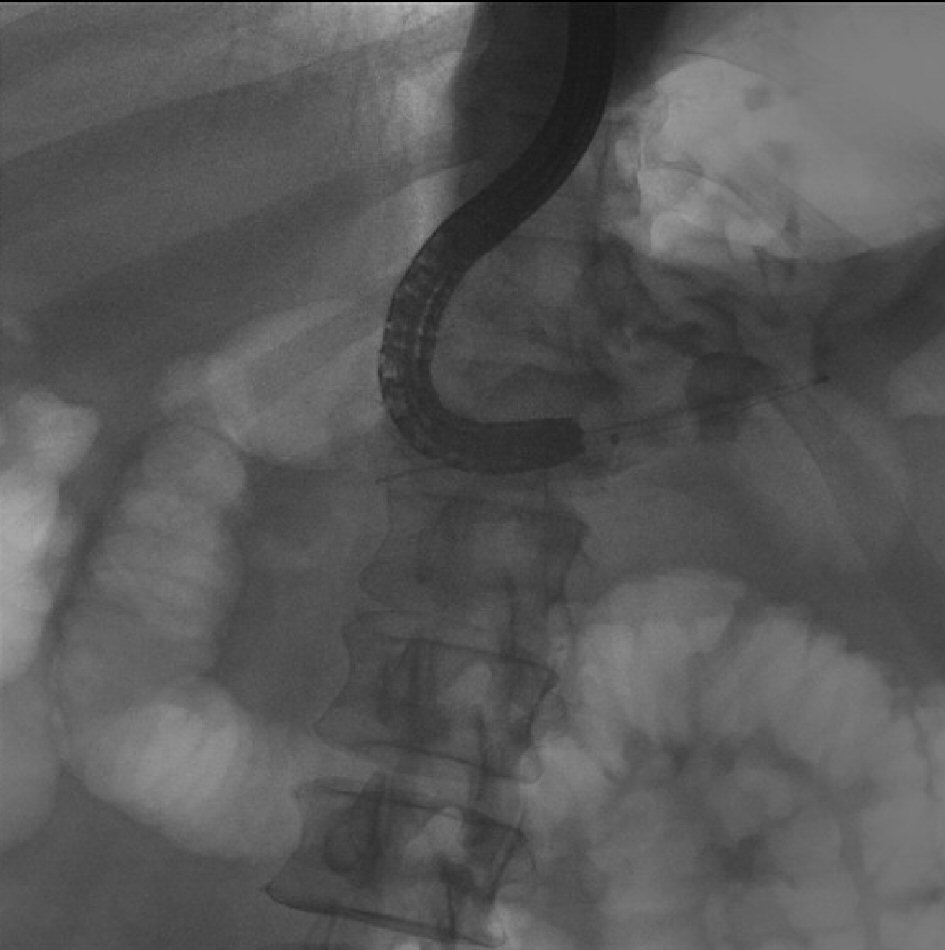
Table
| Management | 2006 Sendai Consensus Guidelines | 2012 Revision of Guidelines | 2017 Multi-institutional study |
|---|---|---|---|
| aPancreatitis, cyst size > 3 cm, thickened or enhancing cyst wall, non-enhancing mural nodule, duct caliber change, pancreas atrophy, and main duct size between 5 - 9 mm is considered a “worrisome feature”. bMPD diameter of ≥ 10 mm is one of the “high-risk stigmata”. | |||
| Main duct | Resect the main duct and mixed variant IPMNs as long as the patient is a good surgical candidate with a reasonable life expectancy. | Rest all surgically fit patients with main duct IPMN. | The presence of obstructive jaundice, lymphadenopathy, or pancreatitis had the greatest strength in predicting the presence of high grade dysplasia and invasive cancer. |
| Branch duct | Asymptomatic: observation | “Worrisome features”a, “low-risk features” as well as “high-risk stigmata”b are introduced. | Having multiple worrisome features was additive in predicting high grade dysplasia and invasive cancer, with each additional feature increasing the OR by 1.39. |
| Symptomatic: resection not only to alleviate the symptoms, but also because of a higher likelihood of malignancy. | More conservative approach: branch duct IPMN of > 3 cm without “high-risk stigmata” can be observed without immediate resection. | ||
| Individualize decision to treat based on patient preferences and willingness to undergo follow-up studies, and the availability of safe pancreatic resection. | |||