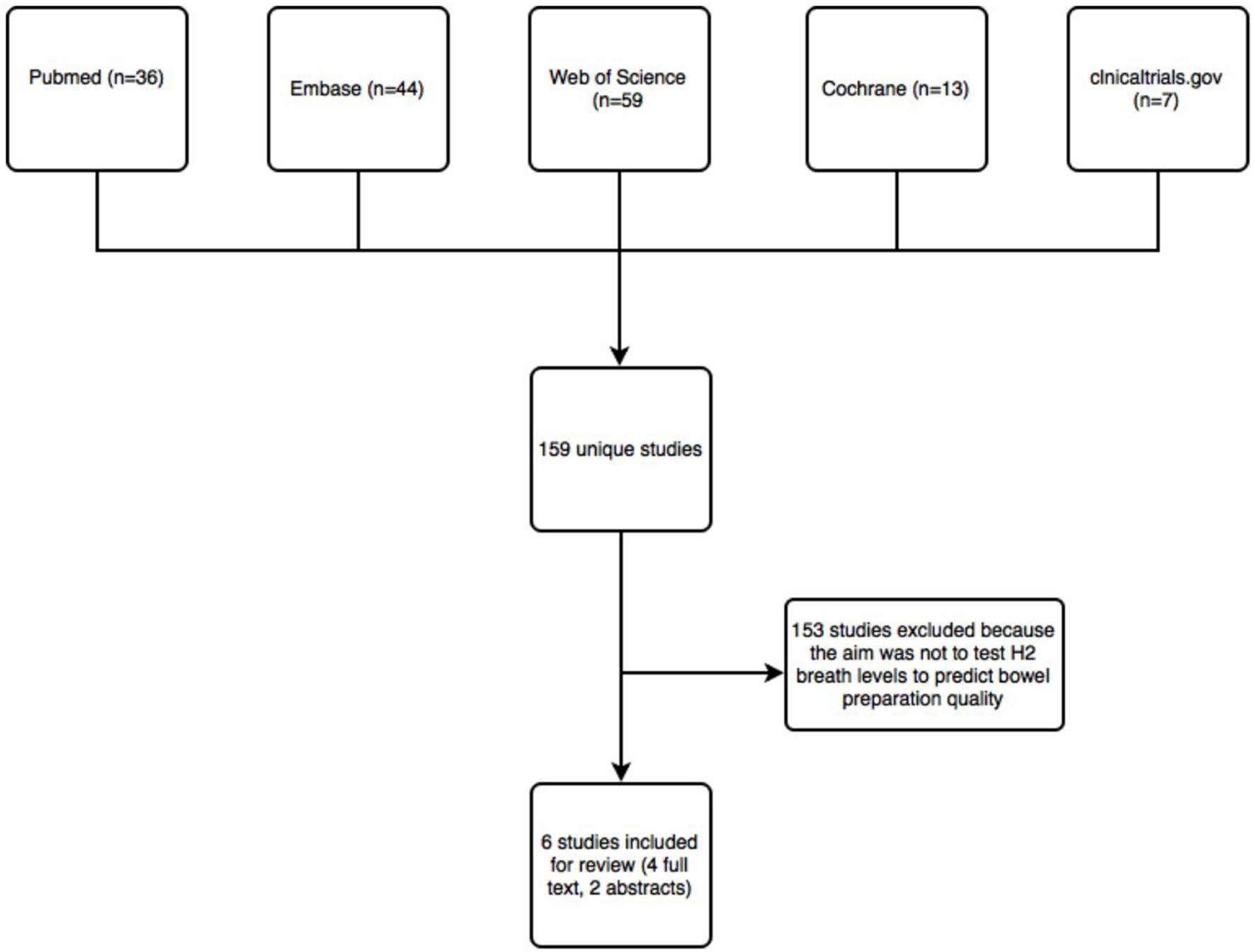
Figure 1. Flow chart of studies identified by literature search.
| Gastroenterology Research, ISSN 1918-2805 print, 1918-2813 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, Gastroenterol Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.gastrores.org |
Original Article
Volume 11, Number 5, October 2018, pages 361-368
Hydrogen Breath Testing Predicts Bowel Preparation Quality Prior to Colonoscopy: A Systematic Review
Figure

Tables
| Altomare group A (PEG only) [5] | Altomare group B (PEG + inulin) [5] | Mann et al (2003) [6] | Urita et al (2003) [7] | Meyer et al (2001) [9] | Meyer et al (2002) [8] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study setting and design | ||||||
| Country | Italy | USA | Japan | USA | USA | |
| Study design | Prospective | |||||
| Colonoscopy indication | Screening, surveillance and diagnostic | Unstated | Diagnostic | Unstated | Unstated | |
| Patient selection | Non-consecutive | Unstated | Consecutive | Unstated | ||
| Patient blinded? | Unstated | |||||
| Endoscopist blinded? | Yes | Unstated | ||||
| Breath tester blinded? | Yes | Unstated | ||||
| Exclusion of H2 non-producers? | Yes | No | Included, analyzed as subgroup | No | No | |
| Inclusion criteria | Signs/symptoms of distal small intestinal diseases, screening or surveillance for colorectal cancer, follow up evaluation of IBD under medical therapy | Unstated | Diagnostic, non-emergent endoscopy | Unstated | Unstated | |
| Exclusion criteria | History of liver, lung, heart, metabolic or neurological disease; lack of compliance, emergency colonoscopy, antibiotic or motility agent 1 month before endoscopy or recent smoking | Unstated | Renal insufficiency, ascites, heart failure, history of abdominal surgery, treatment prokinetics or antibiotics in 6 weeks before endoscopy | Unstated | Unstated | |
| Breath testing protocol | ||||||
| Baseline (pre-preparation) HBT? If yes, timing | Yes, 5 min before preparation | No | Yes, before starting preparation after fasting | No | Yes, timing unstated | |
| Timing of HBT relative to colonoscopy | 5 min before colonoscopy | Unstated | Every 15 min for 4 h before colonoscopy | Unstated | Unstated | |
| Non-hydrogen gases assessed? | No | |||||
| Substrate used | None | Inulin | None | Lactulose | None | ½ pt received 1,250 mg Fibercon the day before colonoscopy |
| Equipment used | LactoFAN | Bedfont Scientific EC 60 gastrolyzer | TGA-2000, Teramecs | MD-80 breath analyzer | Unstated | |
| Colonoscopy protocol | ||||||
| Timing of colonoscopy | 9 a.m. | Unstated | 1 p.m. | Unstated | ||
| Bowel preparation scale | Excellent/fair/poor | Excellent/fair/poor | Excellent/fair/poor | 1 - 5 (best to worst) | 1 - 5 (best to worst) | |
| Definition of “adequate preparation” | Unstated | Unstated | Excellent/fair considered “adequate” | Adequate=1 - 2, inadequate=3 - 5 | ||
| Pre-colonoscopy dietary changes | 12 h fast before colonoscopy | Clear-liquid diet the day before colonoscopy followed by overnight fast | “Usual diet” the day before procedure, then overnight fast before morning time preparation | Unstated | ||
| Group A: 11 patients fasted 1 day before colonoscopy, 31 had carbohydrates without starches 1 day before, 54 pts had no restrictions Group B: No specific dietary changes | ||||||
| Purgative used | PEG | PEG | PEG | Unstated | Fleet’s phosphosoda, visicol or golytely | |
| Single versus split dose preparation | Unstated | Single | Single | Unstated | ||
| Altomare group A (PEG only) [5] | Altomare group B (PEG + inulin) [5] | Mann et al. (2003) [6] | Urita et al. (2003) [7] | Meyer et al. (2001) [9] | Meyer et al. (2002) [8] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HBT outcomes | Patients did HBT once (inpatient and outpatient). H2 level in excellent/fair versus poor was 1.4 ± 0.1 ppm versus 3.5 ± 0.2 ppm (P < 0.001). Patients did HBT twice (inpt only): H2 level in excellent/fair versus poor was 1.2 ± 0.3 ppm versus 3.3 ± 0.1 ppm (P = 0.005) | Pre-prep to post-prep H2 levels: 23.8 ± 2.9 ppm versus 2.3 ± 0.3 ppm (P < 0.001). | H2 levels were lower in the fair-to-excellent prep group (2.2 ± 0.2 ppm) relative to the poor prep group (14.5 ± 1.5 ppm, P < 0.005) | No difference in baseline H2 levels between the adequate and inadequate group At 90 min into preparation, the H2 level in the adequate group (18 ppm) was lower than the inadequate group (32 ppm) but without a reported P value At 240 min into preparation, the H2 level in the adequate group (1.6 ppm) was significantly lower than in the inadequate group (43.4 ppm, P < 0.01) | H2 levels were lower in the adequately prepared group (1.56 ppm) relative to the inadequately prepared group (2.11 ppm, P < 0.05) | No difference between baseline H2 levels and post-prep H2 levels in the adequately prepared group relative to the inadequately prepared group |
| Altomare group A (PEG only) [5] | Altomare group B (PEG + inulin) [5] | Mann et al (2003) [6] | Urita et al (2003) [7] | Meyer et al (2001) [9] | Meyer et al (2002) [8] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2 cutoff value suggested (ppm) | 3 | 3 | 5 | 10 at 90 and 240 min into prep ingestion | Unstated | N/a since no difference was found |
| Sensitivity (%) | 72 | 83 | 96.7 | 100 | ||
| Specificity (%) | 93 | 87 | 87.5 | 100 | ||
| NPV (%) | 93 | 93 | 77.8 | 100 | ||
| PPV (%) | 72 | 69 | 98.3 | 100 | ||
| AUROC/c-statistic | Not available | 0.93 | Not available | Not available |
| Altomare et al (both studies) [5] | Mann et al (2003) [6] | Urita et al (2003) [7] | Meyer et al (2001) [9] | Meyer et al (2002) [8] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall QUADAS-2 rating | Low risk of bias | Medium risk of bias | Low risk of bias | Medium risk of bias | Medium risk of bias |
| Domain 1 (patient selection) | Unclear if selection introduced bias; overall low concern that included patients did not match the review question | Unclear if selection introduced bias; overall low concern that included patients did not match the review question | Low risk of selection introducing bias; overall low concern that included patients did not match the review question | Unclear if selection introduced bias; overall low concern that included patients did not match the review question | Unclear if selection introduced bias; overall low concern that included patients did not match the review question |
| Domain 2 (index test) | Low risk that conduction or interpretation of the index test could have introduced bias; low concern that the index test, its conduct or interpretation differed from the review question | Low risk that conduction or interpretation of the index test could have introduced bias; low concern that the index test, its conduct or interpretation differed from the review question | Low risk that conduction or interpretation of the index test could have introduced bias; low concern that the index test, its conduct or interpretation differed from the review question | Low risk that conduction or interpretation of the index test could have introduced bias; low concern that the index test, its conduct or interpretation differed from the review question | Low risk that conduction or interpretation of the index test could have introduced bias; unclear concern that the index test, its conduct or interpretation differed from the review question |
| Domain 3 (reference standard) | Low risk that the reference standard, its conduct or interpretation could have introduced bias; low concern regarding the target condition matching the review question | Unclear risk that the reference standard, its conduct or interpretation could have introduced bias; low concern regarding the target condition matching the review question | Unclear risk that the reference standard, its conduct or interpretation could have introduced bias; low concern regarding the target condition matching the review question | Unclear risk that the reference standard, its conduct or interpretation could have introduced bias; low concern regarding the target condition matching the review question | Unclear risk that the reference standard, its conduct or interpretation could have introduced bias; low concern regarding the target condition matching the review question |
| Domain 4 (flow and timing) | Low risk that patient flow introduced bias | Unclear risk that patient flow introduced bias | Low risk that patient flow introduced bias | Unclear risk that patient flow introduced bias | Unclear risk that patient flow introduced bias |