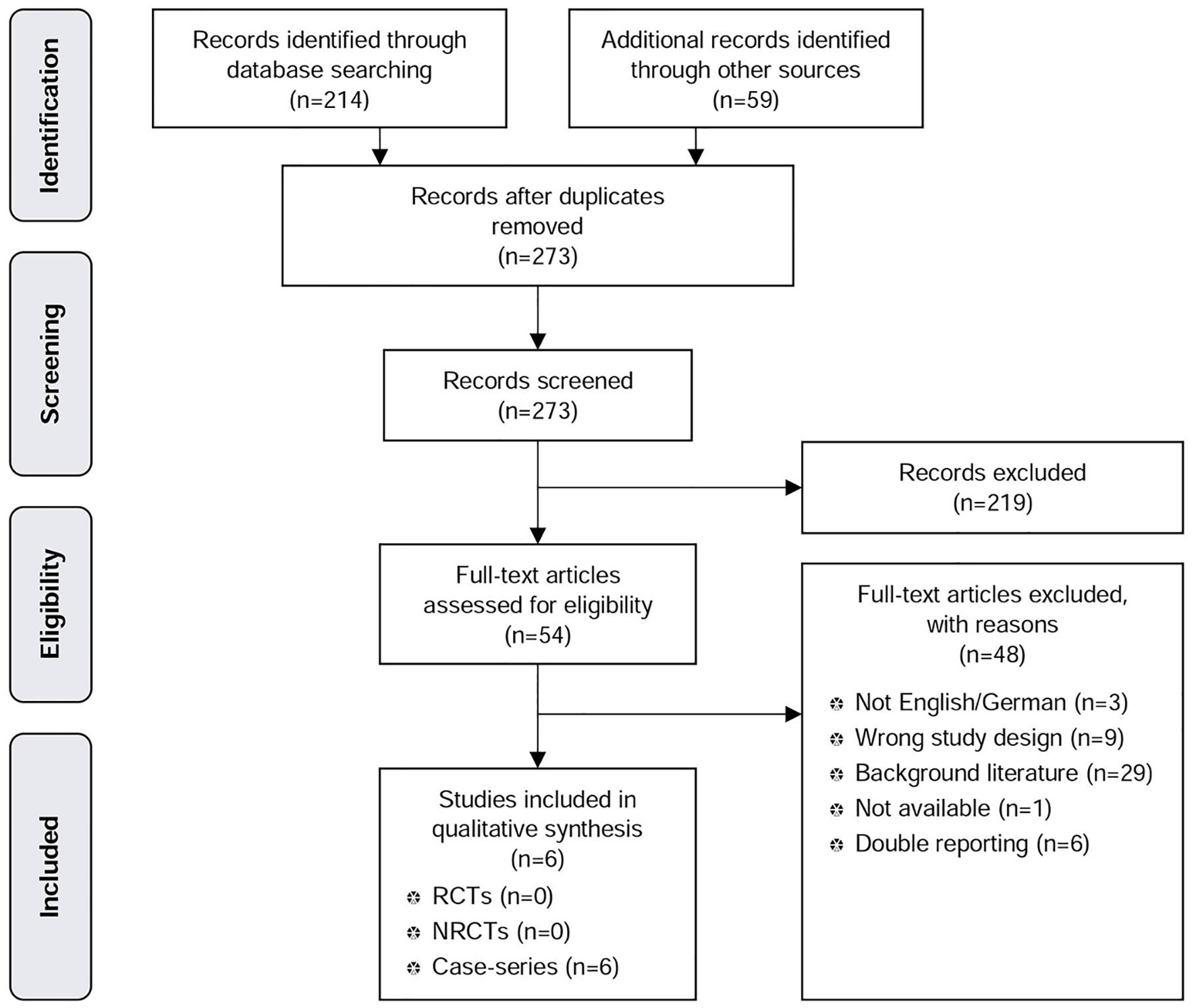
Figure 1. PRISMA tree MSAD.
| Gastroenterology Research, ISSN 1918-2805 print, 1918-2813 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, Gastroenterol Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.gastrores.org |
Review
Volume 11, Number 3, June 2018, pages 161-173
Novel Surgical Treatments for Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: Systematic Review of Magnetic Sphincter Augmentation and Electric Stimulation Therapy
Figures

Tables
| MSAD prospective case series | MSAD prospective registry with control group | EST prospective case series | EST prospective registry | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bonavina et al, 2013 [17] | Schwameis et al, 2014 [15] | Smith et al, 2014 [16] | Reynolds et al, 2014 [14] | Ganz et al, 2015 [13] | Riegler et al, 2015 [12] | Kappelle et al, 2015 [18] | Rodriguez et al, 2015 [19] | Rodriguez et al, 2016 [20] | |
| aWhile the study refers to eight countries and 10 sites, www.clinicaltrials.gov lists seven countries and nine sites. bPatients 1 through 30 (30%) underwent the implantation procedure between March 2007 and May 2008 as part of a multi-center (US, IT) pilot study of 41 patients [21]. Patients 31 through 100 (70%) underwent the implantation procedure between December 2009 and February 2012 as part of a registry. Patients 1 - 30 from the multi-center study were recorded under NCT01057992 in Italy. cBaseline characteristics on 42 patients. d25 received intervention. eBaseline characteristics on 15 patients. fOut of the 41 patients of the pilot study [21], 11 patients were lost to follow-up. Out of the cohort of 100 patients (30 patients from the pilot study and 70 registry patients), five were lost to follow-up. gOne loss to follow-up, one Toupet fundoplication due to hiatal hernia > 3 cm, and one trocar perforation of the intestine during implant procedure. hOne loss to follow-up, one implant not attempted due to hiatal hernia > 3 cm, and three voluntary withdrawals. iOne loss to follow-up, one implant not attempted due to hiatal hernia > 3 cm, and three voluntary withdrawals. ASA: American Society of Anesthesiologics; BMI: body mass index; EST: electric stimulation therapy; GERD: gastroesophageal reflux disease; LES: lower esophageal sphincter; LF: laparoscopic fundoplication; MSAD: magnetic sphincter augmentation device; NA: not available; PPIs: proton pump inhibitors. | |||||||||
| Country | Italy | Austria | US | US | US, The Netherlands | Austria, Germany, Italy, UK | Chile, Colombia, India, Netherlands, Mexico, New Zealand, UKa | Chile | Chile |
| Sponsor | Torax Medical Inc. | Torax Medical Inc. | Torax Medical Inc. | Torax Medical Inc. | Torax Medical Inc. | Torax Medical Inc. | EndoStim Inc. | EndoStim Inc. | EndoStim Inc. |
| Study design | Single-center prospective case series | Single-center prospective case series | Single-center prospective case series | Two-center prospective case series | Multi-center prospective case series | Multi-center prospective registry with control group (NCT01624506) | Multi-center, prospective, international, open-label case series (NCT01574339) | Single-center, prospective, open-label case series (NCT01578642) | Single-center, prospective registry (NCT02441400) |
| Intervention | MSAD | MSAD | MSAD | MSAD | MSAD | MSAD | EST | EST | EST |
| Comparator | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | LF | NA | NA | NA |
| Number of patients | 100b | 23 | 66 | 67 | 100 | 249 (202 vs. 47) | 44c | 26d | 18e |
| Inclusion criteria | Patients > 18 years, GERD ≥ 6 months, PPI resistant GERD, reflux confirmed by ambulatory esophageal pH monitoring | At least partial response to PPIs, PPI resistant GERD | GERD, acceptable esophageal motility, clinical improvement on antisecretory medication with incomplete symptom control, medication intolerance, or side effects | Patients > 18 years, GERD > 6 months | Patients > 18 years < 75 years, GERD ≥ 6 months, at least partial response to PPIs, reflux confirmed by ambulatory esophageal pH monitoring | Advanced GERD with hiatal hernia > 3 cm, Barrett’s esophagus, motility disorder, or esophagitis grade C or D Moderate GERD with abnormal esophageal pH, reflux symptoms despite PPI use | Patients 21 - 80 years, reflux symptoms, GERD-HRQL score ≥ 20 off PPIs and, an increase of ≥ 5 on PPIs, prior PPI use for 12 months, diagnosis based on 24-h pH monitoring result, LES end-expiratory 5 - 15 mm Hg, peristaltic contractions in ≥ 50% of swallows with contraction amplitude of ≥ 30 mm Hg esophageal manometry, excessive lower esophageal acid exposure as pH < 4.0 for ≥ 5% of the total time. | Patients 21 - 65 years, reflux symptoms ≥ 6 months, prior PPI use, GERD-HRQL score ≥ 20 off PPIs and, an increase of ≥ 10 on PPIs, ASA Physical Status Classification ≤ II, distal esophageal acid ex-posure during 24-h pH measurement pH of ≤ 4 for > 5% of total or > 3% of supine, time off, anti-secretory therapy, LES end-expiratory ≥ 5 mm Hg, esophageal body contraction amplitude of ≥ 30 mm Hg for ≥ 70% of swallows and ≥ 50% peristaltic contractions on manometry, esophagitis grade ≤ C. | NA |
| Exclusion criteria | Hiatal hernia > 3 cm, esophagitis grade B+, BMI > 35, Barrett’s esophagus, motility disorder, gross esophageal anatomic abnormalities, allergy to the device’s material (titanium, stainless steel, nickel, or ferrous materials) | Hiatal hernia > 3 cm, Barrett’s esophagus, motility disorder, dysphagia, esophagitis grade C or D, allergy to the device’s material | Hiatal hernia > 3 cm, advanced GERD, Barrett’s esophagus, esophagitis grade B+ | Hiatal hernia > 3 cm, motility disorder, esophagitis grade C or D, Barrett’s esophagus, gross esophageal anatomic abnormalities, allergy to the device’s material | Hiatal hernia ≥ 3 cm, esophagitis grade C or D, BMI > 35, Barrett’s esophagus, motility disorder | Known conditions that make it unlikely to complete a 3-year follow-up | History of esophageal or gastric surgery, gastroparesis, multisystem disease, autoimmune or connective tissue disorder in past 2 years, Barrett’s epithelium, any grade dysplasia, hiatal hernia > 3 cm, esophagitis grade D on upper endoscopy within 6 months, BMI > 35, T1DM or uncontrolled T2DM defined as HbA1c ≥ 9.5 in the previous 6 ms, or T2DM for ≥ 10 years, suspected or confirmed esophageal or gastric cancer, any malignancy in last 2 years, esophageal or gastric varices or dysphagia or esophageal peptic stricture, significant cardiac arrhythmia or cardiovascular disease, implanted electrical stimulator or chronic anticoagulant therapy, pregnant patients. | Non-GERD esophageal motility disorders or gastroparesis, multi-system diseases, Barrett’s (> M2; > C1) esophagus, any grade of dysplasia, hiatal hernia ≥ 3 cm, BMI > 35, uncontrolled type 2 or history of type 2 or 1 diabetes mellitus for > 10 years, esophageal or gastric malignancy or varices, cardiac arrhythmia, ectopy, significant cardiovascular disease, implanted electro-medical device, pregnancy, esophageal or gastric surgery, anti-reflux surgery. | NA |
| Follow-up time | 3 years (range 378 days - 6 years) | 1 month | 5.8 months (range 1 - 18.6 months) | 5 months (range 3 - 14 months) | 5 years | 1 | 0.5 year | 2 years | 3 years |
| Loss to follow-up, n | 5f | 0 | 1 | 15 | 15 | 0 | 6.8g | 19.2h | 16.6i |
| MSAD prospective case series | MSAD prospective registry with control group | EST prospective case series | EST prospective registry | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bonavina et al, 2013 [17] | Schwameis et al, 2014 [15] | Smith et al, 2014 [16] | Reynolds et al, 2014 [14] | Ganz et al, 2015 [13] | Riegler et al, 2015 [12] | Kappelle et al, 2015 [18] | Rodriguez et al, 2015 [19] | Rodriguez et al, 2016 [20] | |
| a100% no hernia or < 2 cm hernia. The mean hiatal hernia size was 1.34 cm (range 0 - 2 cm). bAll hernias < 3 cm. cDifferent distinction: none/1 - 3 cm/> 3 cm. BMI: body mass index; EST: electric stimulation therapy; GERD: gastroesophageal reflux disease; MSAD: magnetic sphincter augmentation device; n: number; NA: not available; SD: standard deviation. | |||||||||
| Age, years | Median 44.5 (range 23 - 77) | Median 43 (range 20 - 68) | Median 53.7 (range 18 - 86) | Median 53 (range 19 - 81) | Median 53 (range 18 - 75) | Mean 46.6 vs. 52.8 (P = 0.007) | Mean 49.6 (SD 12.4) | Mean 52 (SD 12) | Mean 56.1 (SD 9.7) |
| Sex, female vs. male | (26 vs. 74) | 12 vs. 11 | 38 vs. 28 | 20 vs. 47 | 48 vs. 52 | (77 vs. 125) vs. (19 vs. 28) (p=0.866) | 18 vs. 24 | 11 vs. 14 | 7 vs. 8 |
| Moderate GERD, % | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 94 vs. 38.3 | NA | NA | NA |
| BMI | Median 24 (range 17.3 - 33.0) | Median 26 (range 20 - 32) | Mean 26 (range 17.6 - 34.1) | NA | Median 28 (range 20 - 35) | Mean 25.7 vs. 26.1 (P = 0.611) | Mean 27.2 (2.4) | Mean 27.7 (SD 3.2) | Mean 27.4 (SD 3.2) |
| Hiatal hernia, none/< 2/≥ 2 cm, % | 21/ 27/52 | 100/0a | 67b | NA | NA | 14.1/84.4/1.6 vs. 10.9/43.5/45.7c | 39/22/39 | 88/8/4 | 93.3/0/6.7 |
| Yrs of PPI use | Median 4 | Median 1 (range 0 - 20) | NA | NA | Median 5 | Mean 6.3 vs. 5.1 (P = 0.098) | NA | Mean 5.6 (SD 3.4) | Mean 5.9 (SD 3.3) |
| Yrs with GERD | Median 5.5 | Median 4 (range 1 - 20) | NA | NA | Median 10 (range 1 - 40) | 8.7 vs. 7.3 (P = 0.086) | NA | Mean 11.0 (SD 7.9) | Mean 12.2 (SD 9.1) |
| Barrett’s esophagus, n | 2 | NA | 3 | NA | NA | 8.7 vs. 7.3 (P = 0.086) | NA | NA | NA |
| Esophagitis, % | |||||||||
| Grade A and B | 16 | 21.7 | NA | NA | NA | 41.4 vs. 44.7 (P = 0.212) | 54 | NA | 93.3 |
| Grade C and D | 1 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 vs. 8.5 (P = 0.212) | 5 | NA | 6.7 |
| MSAD prospective case series | MSAD prospective registry with control group (I vs. C) | EST prospective case series | EST prospective registry | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bonavina et al, 2013 [17] | Schwameis et al, 2014 [15] | Smith et al, 2014 [16] | Reynolds et al, 2014 [14] | Ganz et al, 2015 [13] | Riegler et al, 2015 [12] | Kappelle et al, 2015 [18] | Rodriguez et al, 2015 [19] | Rodriguez et al, 2016 [20] | |
| a42 patients at baseline, 41 at last follow-up. b24 patients at baseline, 21 at last follow-up. c18 patients’ analysis. d55.8 described it as mild. A total of 44.2 described their dysphagia as severe. eTwo patients (9.5%) were already off medication at baseline due to severe side-effects from PPIs. Two further patients were able to halve their daily PPI dosage. fAt 5 years, 75.3% of patients reported complete cessation of PPIs, and 9.4% reported PPI use only as needed. g42 patients at baseline, 40 at last follow-up. h24 patients at baseline, 18 at last follow-up. iPatients who were satisfied or neutral about the intervention. jDefined through patient dissatisfaction where at baseline, 95% were dissatisfied and at 5 years, 7.1% were dissatisfied. k42 patients at baseline, 39 at last follow-up. lOut of 39 patients. mData on 12 patients: six patients showed improvement by 1 grade, three patients have stable and three patients worsening esophagitis. nIncludes both, post-operative bloating and belching. oA total of 8.58% of patients underwent 11.22% of contrast swallows, 4.62% of dilatations, 7.91% of esophagogastroduodenoscopy, 3.3% of pH testing and 0.66% of motility test mainly for diagnosis. Dilatations were done in 2.64% of patients for dysphagia. pAn injury to the pleura in both groups, minor bleeding in two patients in the MSDA group. rReoperations in the MSAD group were performed for device removal due to dysphagia, pain or persistent GERD, while in the LF group were for persistent GERD and herniation of the fundic wrap. ADE: adverse device effect; EST: electric stimulation therapy; GERD: gastroesophageal reflux disease; SADE: serious adverse device effect; HRQL: health-related quality of life; IQR: interquartile range; LF: laparoscopic fundoplication; MSAD: magnetic sphincter augmentation device; n: number; NA: not available; CI: confidence interval; PPIs: proton pump inhibitors; pre-op: pre-operation; SD: standard deviation. | |||||||||
| Efficacy | |||||||||
| Median GERD HRQL score (pre-op./last follow-up) | Off PPIs 24/2 | 29/4 (P < 0.001) | 26/6 | NA/4 (0 - 26) | 27/4 (P < 0.001) | 20/3 vs. 23/3.5 (P = 0.177) | On PPIs 16.5/5.0 Off PPIs 31.0/5.0a | On PPIs 9/0b/1 Off PPIs 23.5/0/1 | |
| Heartburn | % (pre-op./last follow-up) | % of days (pre-op./last follow-up)(IQR) | |||||||
| NA | 95.7/22 (P < 0.001) | NA | NA | 89/11.9 (P < 0.001) | 30.8/3.5 vs. 40/8.5 (P = 0.229) | 86 (64 -100)/17 (0 - 93)a | 92/7c/NA | ||
| Regurgitation | Daily regurgitation, % (pre-op./last follow-up) | Median regurgitation % of days (pre-op./last follow-up) (IQR) | |||||||
| 72/2 | 65/57 (P > 0.1) | NA | NA/44.2 | 57/1.2 (P < 0.001) | 58.2/3.1 vs. 60/13 (P = 0.014) | 79 (54 - 100)/0 (0 - 21)a | 66/0c/NA | ||
| Dysphagia, % (pre-op./last follow-up) | 8/0 | 48/70 (P > 0.1) | NA | 0.02/82.7d | 5/6 (P = 0.739) | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Excessive bloating, % (pre-op./last follow-up) | 48/2 | 70/30 (P = 0.006) | NA | NA | 52/8.3 (P < 0.001) | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Extra-esophageal symptoms (asthma, chronic cough, laryngitis), % (pre-op./last follow-up) | 52/16 | 57/17 (P = 0.039) | NA | NA | NA | 63.9/22.3 vs. 53.3/17.4 (P = 0.552) | NA | NA | NA |
| Discontinuation of medication (PPIs), % | 85 | 71.4e | 83 | 76.9 | 84.7f (CI 95%, 81 - 95) | 81.8 vs. 63 (P = 0.009) | NA | 76 | 73 |
| DeMeester pH score (pre-op./last follow-up) | Median 30.1/11.2 | NA | Mean 32.3 (range 1.4 - 67)/NA | NA | Median 36.6 (16.3 - 83.8)/NA | NA | Median 35.1 (IQR 27.1 - 51.9)/17.5 (IQR 10.9 - 23.4)g | Median 36.6 (IQR 29.6 - 50.2)/16.1 (IQR 12.2 - 29.1)h/12.8 (IQR 7.2 - 18.8) | |
| Hospital discharge, % | 96 (within 48 h) | 52 (within 24 h), 82.6 (within 48 h) | 25 (within 24 h) | 51 (within 12 h), 100 (within 36 h) | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Patient satisfaction, % (pre-op./last follow-up) | 5/87 | 0/74 | NA/92i | NA | 5/92.9j (P < 0.001) | 91.8 vs. 86.7 | 7/54k | 29/100/NA | |
| Esophagitis, % (pre-op./last follow-up) | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | ||
| None | 41/51l | 0/NAm | |||||||
| Grade A | 323/181/31 | 60/NA | |||||||
| Grade B | 5/0 | 33.3/NA | |||||||
| Grade C | 6.7/NA | ||||||||
| Safety | |||||||||
| Inability to belch, % | 1 | 0 | NA | NA | NA | 1.6 vs. 10.1 (P = 0.007) | 7.1n | 0 | 0 |
| Inability to vomit, % | 1 | 0 | NA | NA | NA | 8.7 vs. 56.6 (P < 0.001) | 4.8 | NA | NA |
| Other non-serious ADEs, % | Mild odynophagia: 4, increased belching: 3 | NA | NAo | Dehydration: 0.67, urinary retentions: 2 | NA | Excessive bloating: 10 vs. 31.9 (P < 0.001) | Constipation, epigastric pain, fever, mesh repair hernia cicatricialis: 2.4 hiccups, impedance out of range: 4.8, weight loss/anorexia: 11.9 | Skin infection at pocket site, psychotic disturbance/nervous breakdown: 4, shoulder pain and a hypersensitive episode: 8 | NA |
| Dysphagia, % | 2 | 0.23 | 2.64 | 5.36 | NA | 7 vs. 10.6 (P = 0.373) | 9.5 | 0 | 0 |
| Pain/discomfort, % | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 45.2 | 20 | 0 |
| Nausea/vomiting, % | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7.1 | 12 | 0 |
| Intraoperative complications, % | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | NA | 1.49 vs. 2.13p (P = 1.00) | Trocar perforation of the small bowel during laparoscopy: 2.4 | NA | NA |
| Reoperation rate, % | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 vs. 6.4r | NA | NA | NA |
| Hospital readmission, % | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5.4 vs. 4.3 | NA | NA | NA |
| Device erosion, % | 0 | NA | 0 | NA | 0 | NA | 2.4 | NA | NA |
| Device migration, % | 0 | NA | NA | NA | 0 | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Device malfunction, % | NA | NA | NA | NA | 0 | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Device removal, % | 3 | 0 | 0 | NA | 7 | 4 | NA | NA | NA |
| No. of studies/patients | Study design | Estimate of effect | Study limitations | Inconsistency | Indirectness | Other modifying factors | Strength of evidence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| aUnclear risk of bias due to unclear allocation concealment, no blinding, no control group. bHeterogeneous results, no P-value reported. cSmall sample size. C: control; EST: electric stimulation therapy; GERD: gastroesophageal reflux disease; I: intervention; LF: laparoscopic fundoplication; MSAD: magnetic sphincter augmentation device; NA: not available; SEA: serious adverse event. | |||||||
| Efficacy of MSAD | |||||||
| Median GERD-HRQL score (pre-op./last follow-up) I vs. C | |||||||
| 1/249 [12] | Prospective registry with control group | 20/3 vs. 23/3.5 (P = 0.177) | 0 | NA | 0 | 0 | Moderate |
| Efficacy of EST | |||||||
| Due to the lack of a controlled group, no data on efficacy can be reported. | |||||||
| Safety of MSAD | |||||||
| Overall complication rate, % I vs. C | |||||||
| 1/249 [12] | Prospective registry with control group | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Intraoperative complications, % I vs. C | |||||||
| 1/249 [12] | Prospective registry with control group | 1.49 vs. 2.13 (P = 1.00) | 0 | NA | 0 | 0 | Moderate |
| Dysphagia, % I vs. C | |||||||
| 1/249 [12] | Prospective registry with control group | 7 vs. 10.6 (P = 0.373) | 0 | NA | 0 | 0 | Moderate |
| Device removal, % | |||||||
| 5/336 [13-17] | Prospective case series + prospective registry with control group | 0 - 7 | -1 | -1 | 0 | -1 | Very low |
| Safety of EST | |||||||
| Adverse events (AEs) | |||||||
| Post-operative bloating/belching | |||||||
| 3/67 [18-20] | Prospective case series + prospective registry | Not reported | -1a | -1b | 0 | -1c | Very low |
| Post-operative dysphagia | |||||||
| 3/67 [18-20] | Prospective case series + prospective registry | Not reported | -1 | -1 | 0 | -1 | Very low |
| Nausea/vomiting | |||||||
| 3/67 [18-20] | Prospective case series + prospective registry | Not reported | -1 | -1 | 0 | -1 | Very low |
| Pain/discomfort | |||||||
| 3/67 [18-20] | Prospective case series + prospective registry | Not reported | -1 | -1 | 0 | -1 | Very low |
| Serious adverse events (SAEs) | |||||||
| Trocar perforation of the small bowel | |||||||
| 1/42 [18] | Prospective case series | Not reported | -1 | NA | 0 | -1 | Very low |
| Device erosion lead through esophagus | |||||||
| 1/42 [18] | Prospective case series | Not reported | -1 | NA | 0 | -1 | Very low |
| Study reference/ID | Bonavina et al, 2013 [17] | Schwameis et al, 2014 [15] | Smith et al, 2014 [16] | Reynolds et al, 2014 [14] | Ganz et al, 2015 [13] | Riegler et al, 2015 [12] | Kappelle et al, 2015 [18] | Rodriguez et al, 2015 [19] | Rodriguez et al, 2016 [20] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| aExclusion criteria are too vague (patients were excluded if they had known conditions that would make it unlikely for them to complete a 3-year follow-up). bPatients 1 through 30 (30%) underwent the implantation procedure as part of a multicenter pilot study of 41 patients (Magnetic Augmentation of the Lower Esophageal Sphincter: Results of a Feasibility Clinical Trial, Bonavina et al. 2008). Patients 31 through 100 (70%) underwent the implantation procedure as part of a registry. c150 patients were evaluated for device implant, 68 were implanted. The selection process is not detailed. dFrom the 257 patients that signed the consent 100 underwent device implant. The 157 who discontinued: 96 eligibility criteria not met, 36 consent withdrawn, 24 discontinuation when implant limit met and one discontinuation by investigator (Ganz 2013). e“Unclear”: 110 patients screened and 66 specified screen failures. f“Unclear”: 75 patients screened and 49 unspecified screen failures. g“Unclear”: 21 patients at 24 months follow-up, 18 recruited for 5 years registry (3/21 elected not to join the 5 years observational registry). h“Unclear”: only mean duration of PPI use and mean duration of GERD symptoms is reported. | |||||||||
| 1. Is the hypothesis/aim/objective of the study stated clearly in the abstract, introduction, or methods section? | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 2. Are the characteristics of the participants included in the study described? | Yes | Yes | Yes | Partially reported | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 3. Were the cases collected in more than one centre? | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| 4. Are the eligibility criteria (inclusion and exclusion criteria) for entry into the study explicit and appropriate? | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Partially reporteda | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 5. Were participants recruited consecutively? | Nob | Yes | Unclearc | Yes | Uncleard | Yes | Uncleare | Unclearf | Unclearg |
| 6. Did participants enter the study at similar point in the disease? | No | No | Unclear | Unclear | No | Unclear | Unclear | Unclearh | Unclear |
| 7. Was the intervention clearly described in the study? | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 8. Were additional interventions (co-interventions) clearly reported in the study? | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 9. Are the outcome measures clearly defined in the introduction or methods section? | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 10. Were relevant outcomes appropriately measured with objective and/or subjective methods? | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 11. Were outcomes measured before and after intervention? | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 12. Were the statistical tests used to assess the relevant outcomes appropriate? | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 13. Was the length of follow-up reported? | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 14. Was the loss to follow-up reported? | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 15. Does the study provide estimates of the random variability in the data analysis of relevant outcomes? | No | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Patrially reported | Yes |
| 16. Are adverse events reported? | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 17. Are the conclusions of the study supported by results? | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | Partially reported | Partially reported | Partially reported |
| 18. Are both competing interest and source of support for the study reported? | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Overall risk of bias | High | High | High | High | High | Low | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate |