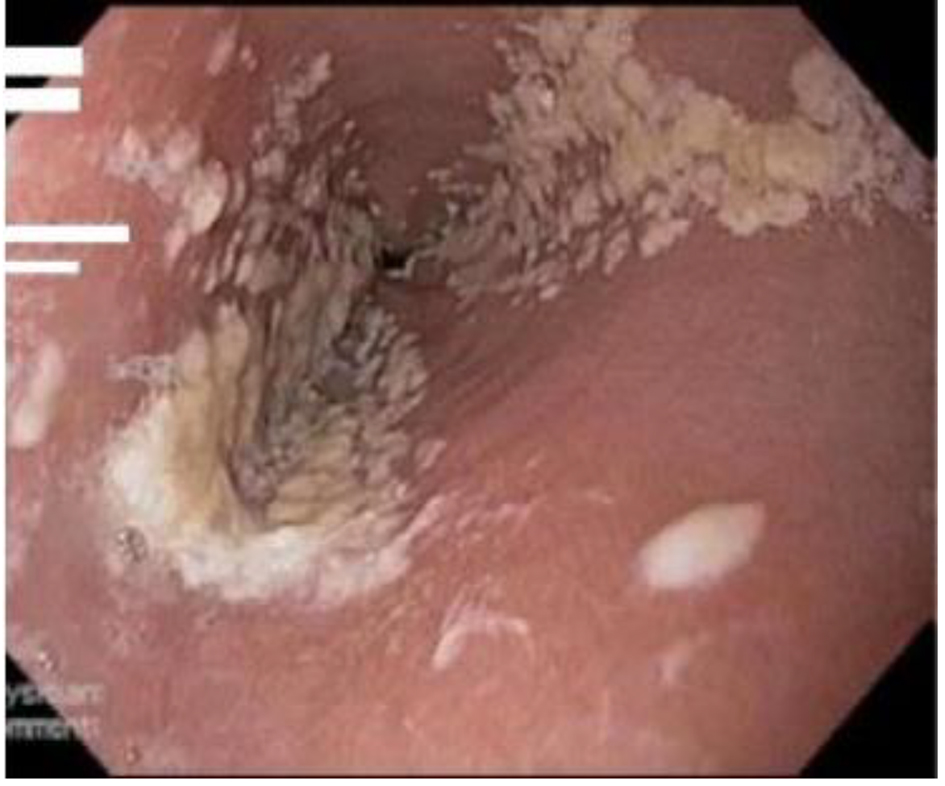
Figure 1. Candida esophagitis in one of the study patients.
| Gastroenterology Research, ISSN 1918-2805 print, 1918-2813 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, Gastroenterol Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.gastrores.org |
Original Article
Volume 11, Number 3, June 2018, pages 195-199
Possible Risk Factors for Candida Esophagitis in Immunocompetent Individuals
Figures

Tables
| n (%) | |
|---|---|
| Comorbidities* | |
| Asthma | 13 (16.3%) |
| Hypertension | 11 (13.8%) |
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | 11 (13.8%) |
| Hyperlipidemia | 7 (8.8%) |
| Gallbladder stones | 6 (7.5%) |
| Coronary artery disease | 4 (5.0%) |
| Thyroid disorder (hypo- or hyperthyroidism) | 4 (5.0%) |
| Atrial fibrillation | 3 (3.8%) |
| Irritable bowel syndrome | 3 (3.8%) |
| Liver cirrhosis | 2 (2.5%) |
| Indication for endoscopy | |
| Abdominal pain | 40 (50.0%) |
| Evaluation of esophageal reflux | 13 (16.0%) |
| Dysphagia | 9 (11.3%) |
| Odynophagia | 5 (6.3%) |
| Hematemesis | 4 (5.0%) |
| Anemia | 4 (5.0%) |
| Barrett’s disease (follow-up) | 2 (2.5%) |
| Melena | 2 (2.5%) |
| Screening for esophageal varices | 1 (1.3%) |
| Endoscopic findings | |
| White plaques and/or patches | 54 (67.5%) |
| Esophagitis or esophageal friability, esophageal erythema | 20 (25.5%) |
| Normal esophagus | 4 (5.0%) |
| Esophageal ulcer | 1 (1.3%) |
| Irregular z-line | 1 (1.3%) |
| n (%) | |
|---|---|
| Proton pump inhibitor | 59 (73.8%) |
| Corticosteroids (inhaled) | 15 (18.9%) |
| No risk factors identified | 16 (20.0%) |
| Gastroesophageal reflux | 50 (62.8%) |
| Patients with previous endoscopies prior to CE diagnosis with findings of reflux esophagitis | 15 (18.8%) |
| Patients who were started on a proton pump inhibitor therapy at the time of diagnosis of reflux esophagitis (15 patients with previous endoscopy) | 15 (100%) |