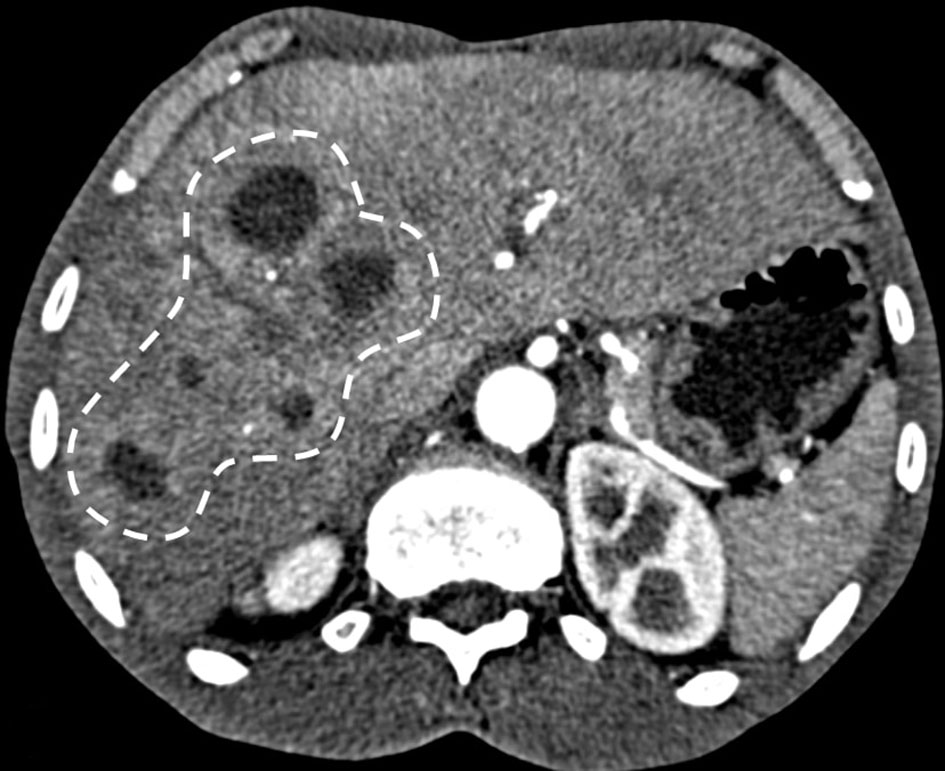
Figure 1. CT with contrast showing multiple hypoattenuating lesions in the liver (dashed line).
| Gastroenterology Research, ISSN 1918-2805 print, 1918-2813 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, Gastroenterol Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.gastrores.org |
Case Report
Volume 11, Number 3, June 2018, pages 241-246
Denture-Associated Oral Microbiome and Periodontal Disease Causing an Anaerobic Pyogenic Liver Abscess in an Immunocompetent Patient: A Case report and Review of the Literature
Figures

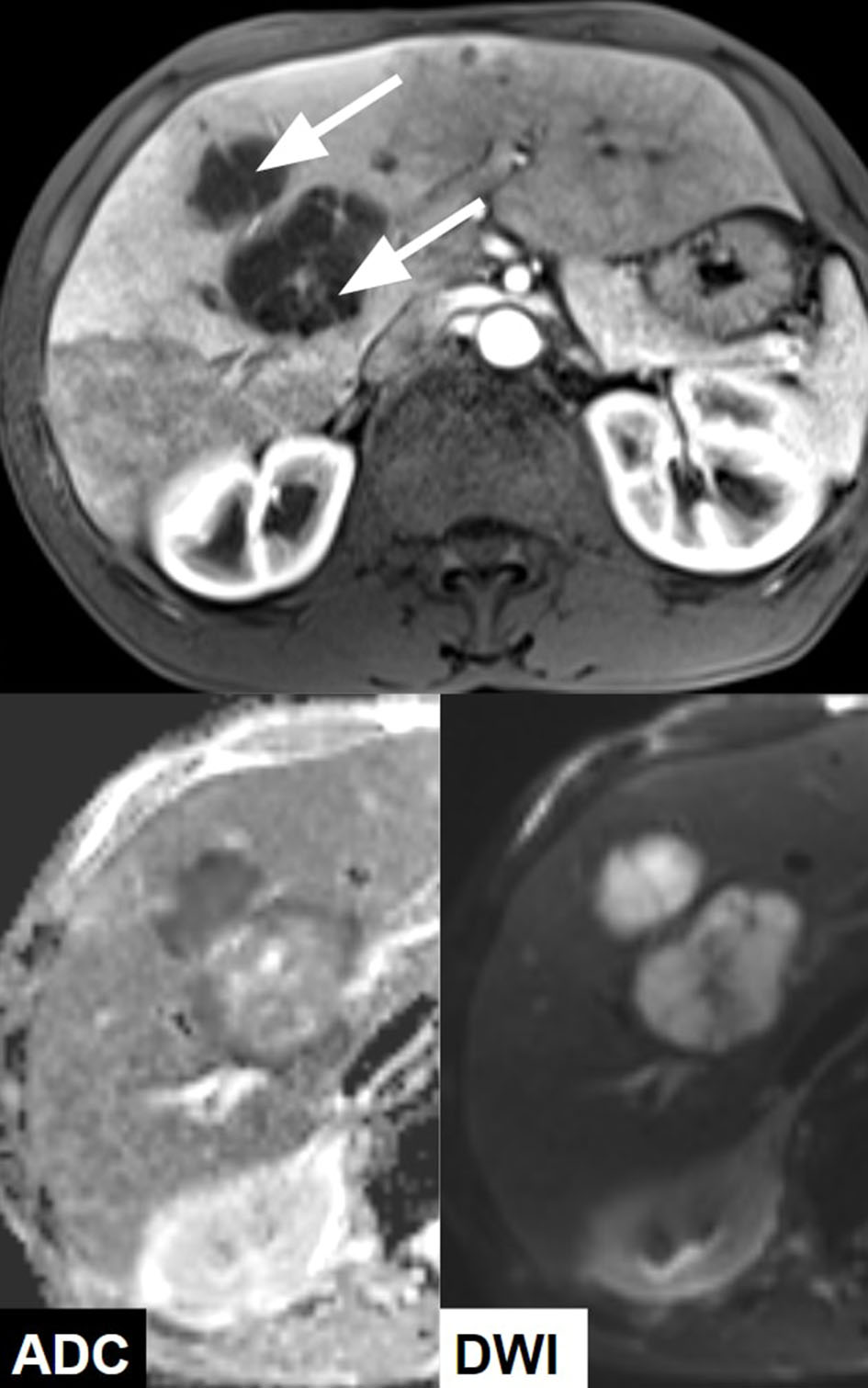
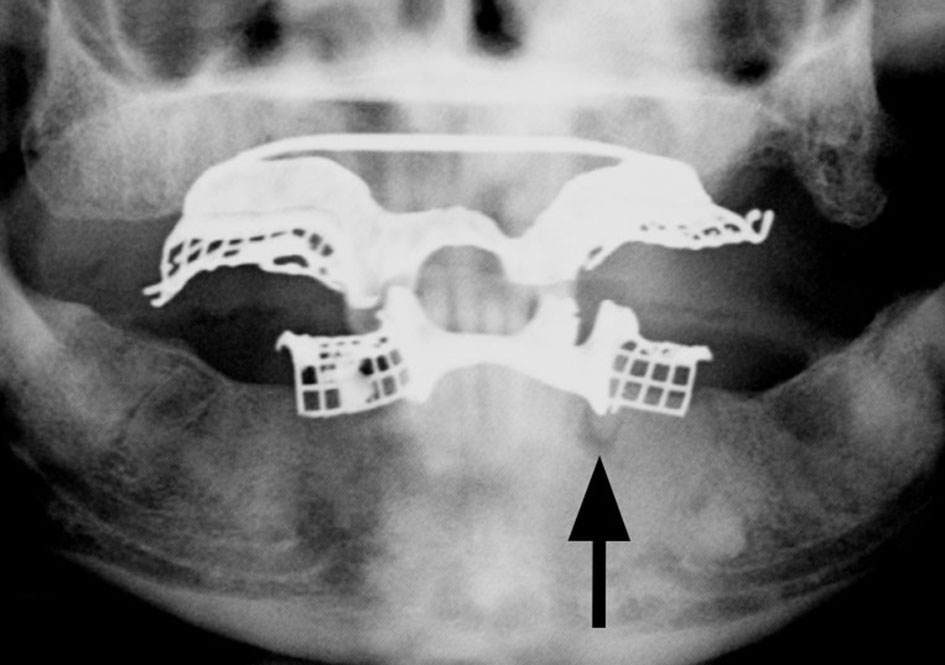
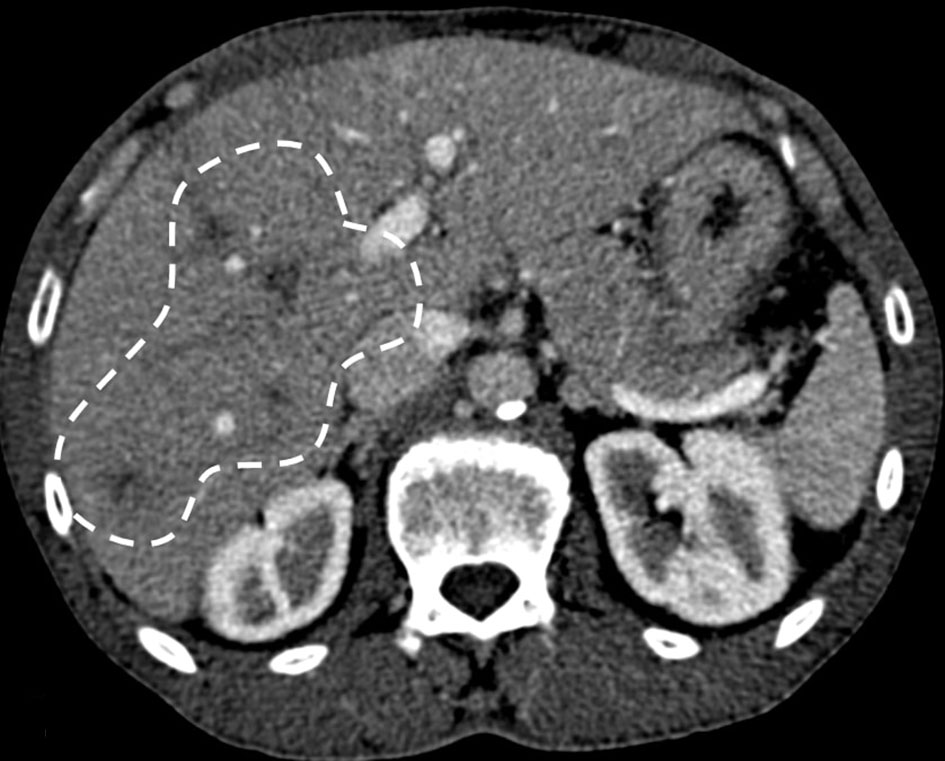
Tables
| Test (normal range) | Day 1 | Day 28 | Day 64 |
|---|---|---|---|
| WBC, white blood cell; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALP, alkaline phosphatase. | |||
| WBC (3.5 × 103 - 10.5 × 103/µL) | 28.5 | 7.6 | 5.4 |
| Albumin (3.4 - 5 g/dL) | 2.7 | 2.9 | 3.2 |
| ALT (0 - 55 units/L) | 117 | 29 | 17 |
| AST (5 - 34 units/L) | 88 | 28 | 20 |
| ALP (40 - 150 units/L) | 179 | 182 | 87 |
| Total bilirubin (0.2 - 1.2 mg/dL) | 1.6 | 0.4 | 0.4 |
| Age (years old) Sex | Presentation | Imaging | Associated infection | Organisms | Treatment | Prognosis | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RUQ: right upper quadrant; US: ultrasound; CT: computed tomography; IV: intravenous; PLA: pyogenic liver abscess; VATS: video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery. | |||||||
| Crippin et al 1992 [3] | 69 M | 3-week history of fever and malaise | CT | Dental disease, molar abscess | Fusobacterium nucleatum | Percutaneous drainage and IV antibiotics for unknown duration. Dental surgery following hospitalization | No recurrence in 72 months of follow-up |
| Memain et al 2001 [21] | 24 F | 3 months of diarrhea and fevers | US & CT | Tonsil infection, sepsis | Fusobacterium nucleatum | Metronidazole and fluoroquinolone for 4 weeks. Tonsillectomy was performed without any histological abnormality | Rapid improvement with antibiotics treatment and intensive care. Follow-up course unknown |
| Kajiya et al 2008 [22] | 59 M | Fever, chills, malaise | US & CT | Dental caries, poor dental hygiene | Fusobacterium nucleatum | Imipenem/cilastatin, due to sensitivities changed to clindamycin (unknown durations). Patient refused percutaneous drainage | Full resolution of abscess on CT and US after 1 month |
| Fatakhov et al 2013 [23] | 30 M | Several days of fevers, chills, malaise, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea | US & CT | None | Fusobacterium necrophorum | Percutaneous drainage. Metronidazole and piperacillin/tazobactam for 8 days, narrowed to levofloxacin and metronidazole until abscess resolved on imaging (2 weeks post-drainage) | Abscess was resolved on CT at 2 weeks after drain insertion |
| Nagpal et al 2015 [24] | 69 F | 2-month history of vague RUQ pain, fevers and chills | US & CT | Severe chronic periodontitis Diverticulitis | Fusobacterium nucleatum | Percutaneous drainage. Vancomycin (stopped after 3 days) and meropenem, later changed to ertapenem for total of 2 weeks. Discharged on oral penicillin for 4 weeks | Full resolution on repeat CT at 4 months post-discharge |
| Ahmed et al 2015 [2] | 21 M | 2 weeks of RUQ pain, fevers, chills, weight loss, fatigue, diarrhea | CT | Recent routine dental cleaning. Complicated by sepsis, empyema, abdominal and pelvic abscesses | Fusobacterium nucleatum | Empiric vancomycin and piperacillin/tazobactam for unknown duration, treated with IV ertapenem for 8 weeks. Percutaneous drainage of PLA. Required VATS procedure for trapped lung. Drainage of abdominal and pelvic abscesses | Resolution of abscesses on CT after 9 weeks of treatment |