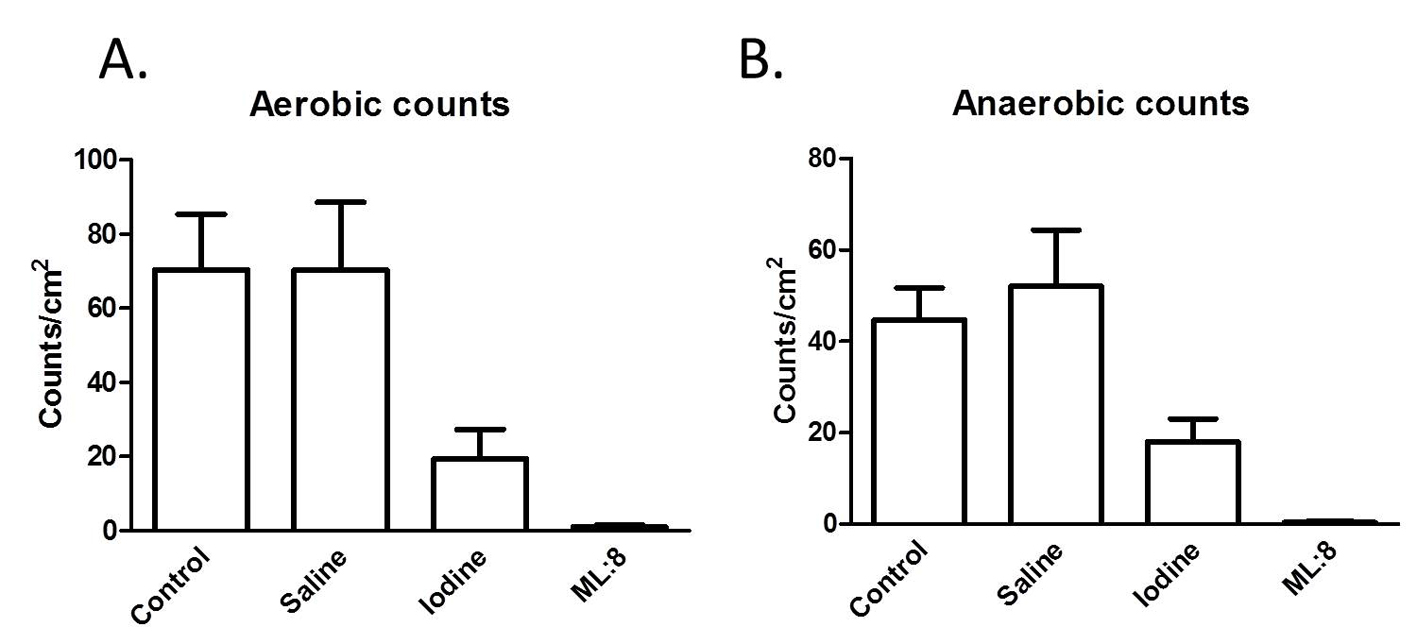
Figure 1. Swabs taken from the mucosal surfaces of tissues exposed to the different treatments were used to inoculate culture plates. After 48 h, numbers of colony forming units were counted as described in the “Methods” section. Results, which are similar for aerobic (A) and anaerobic (B) culture conditions indicate that ML:8 has greater efficacy than iodine at preventing bacterial growth.
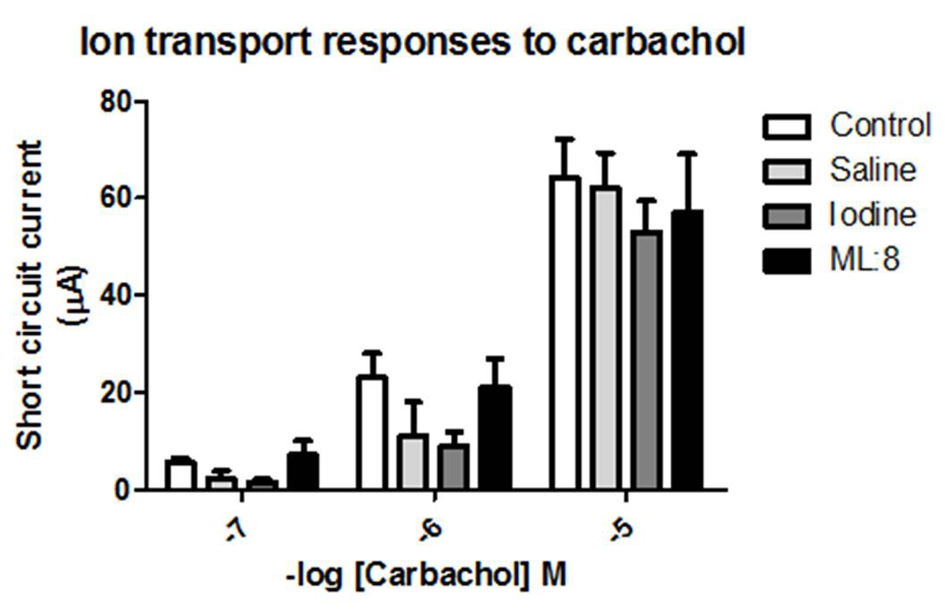
Figure 2. Carbachol applied to the basolateral domain of voltage-clamped human colonic mucosa evoked a rapid-onset inward short circuit current. These responses were unaffected in tissues which had been pre-exposed transiently to saline or to ML:8. Ion transport responses to carbachol in colonic sheets which had been pre-exposed to iodine were attenuated when compared to control responses by analysis of variance (P < 0.05; n = 4 - 5).

